09-02-2021-2056 - 2371/2-3,4
Blog Archive
- Apr 12 (12)
- Apr 13 (2)
- Apr 14 (7)
- Apr 15 (11)
- Apr 16 (5)
- Apr 17 (14)
- Apr 18 (16)
- Apr 19 (17)
- Apr 20 (28)
- Apr 21 (29)
- Apr 22 (15)
- Apr 23 (19)
- Apr 24 (8)
- Apr 25 (58)
- Apr 26 (44)
- Apr 28 (6)
- Apr 29 (6)
- Apr 30 (7)
- May 01 (8)
- May 02 (9)
- May 03 (4)
- May 04 (6)
- May 05 (14)
- May 06 (20)
- May 07 (11)
- May 08 (18)
- May 09 (6)
- May 10 (17)
- May 11 (8)
- May 12 (25)
- May 13 (8)
- May 14 (2)
- May 15 (2)
- May 17 (16)
- May 18 (1)
- May 19 (5)
- May 20 (22)
- May 21 (6)
- May 22 (3)
- May 23 (2)
- May 24 (7)
- May 25 (1)
- May 26 (6)
- May 27 (3)
- May 28 (3)
- May 29 (10)
- May 30 (8)
- May 31 (12)
- Jun 01 (1)
- Jun 02 (1)
- Jun 03 (9)
- Jun 04 (1)
- Jun 05 (2)
- Jun 07 (4)
- Jun 08 (8)
- Jun 09 (1)
- Jun 10 (1)
- Jun 19 (1)
- Jun 27 (1)
- Jun 29 (1)
- Jun 30 (7)
- Jul 01 (3)
- Jul 02 (1)
- Jul 03 (1)
- Jul 04 (2)
- Jul 05 (1)
- Jul 06 (3)
- Jul 08 (9)
- Jul 09 (1)
- Jul 10 (1)
- Jul 11 (2)
- Jul 12 (2)
- Jul 13 (4)
- Jul 14 (4)
- Jul 15 (2)
- Jul 17 (8)
- Jul 18 (17)
- Jul 19 (1)
- Jul 20 (8)
- Jul 21 (6)
- Jul 22 (12)
- Jul 23 (10)
- Jul 25 (6)
- Jul 26 (23)
- Jul 28 (50)
- Jul 30 (12)
- Jul 31 (5)
- Aug 01 (16)
- Aug 02 (5)
- Aug 03 (5)
- Aug 04 (11)
- Aug 05 (13)
- Aug 06 (7)
- Aug 07 (10)
- Aug 08 (2)
- Aug 09 (27)
- Aug 10 (15)
- Aug 11 (67)
- Aug 12 (44)
- Aug 13 (29)
- Aug 14 (120)
- Aug 15 (61)
- Aug 16 (36)
- Aug 17 (21)
- Aug 18 (5)
- Aug 21 (5)
- Aug 22 (54)
- Aug 23 (101)
- Aug 24 (100)
- Aug 25 (99)
- Aug 26 (100)
- Aug 27 (84)
- Aug 28 (73)
- Aug 29 (76)
- Aug 30 (67)
- Aug 31 (95)
- Sep 01 (126)
- Sep 02 (68)
- Sep 03 (11)
- Sep 04 (14)
- Sep 05 (47)
- Sep 06 (101)
- Sep 07 (61)
- Sep 08 (57)
- Sep 09 (46)
- Sep 10 (14)
- Sep 11 (93)
- Sep 12 (101)
- Sep 13 (101)
- Sep 14 (100)
- Sep 15 (77)
- Sep 16 (2)
- Sep 17 (101)
- Sep 18 (91)
- Sep 19 (102)
- Sep 20 (102)
- Sep 21 (94)
- Sep 22 (84)
- Sep 23 (110)
- Sep 24 (101)
- Sep 25 (76)
- Sep 26 (43)
- Sep 27 (87)
- Sep 28 (104)
- Sep 29 (92)
- Sep 30 (33)
- Oct 01 (58)
- Oct 02 (1)
- Oct 05 (8)
- Oct 06 (6)
- Oct 07 (4)
- Oct 08 (4)
- Oct 09 (1)
- Oct 10 (18)
- Oct 11 (8)
- Oct 12 (26)
- Oct 13 (6)
- Oct 14 (2)
- Oct 15 (4)
- Oct 16 (3)
- Oct 17 (4)
- Oct 18 (3)
- Oct 19 (11)
- Oct 20 (5)
- Oct 21 (7)
- Oct 22 (5)
- Oct 23 (8)
- Oct 24 (9)
- Oct 25 (14)
- Oct 26 (8)
- Oct 27 (13)
- Oct 28 (7)
- Oct 29 (7)
- Oct 30 (22)
- Oct 31 (13)
- Nov 01 (13)
- Nov 02 (6)
- Nov 03 (10)
- Nov 04 (17)
- Nov 05 (8)
- Nov 06 (9)
- Nov 07 (11)
- Nov 08 (3)
- Nov 09 (7)
- Nov 10 (5)
- Nov 11 (5)
- Nov 12 (5)
- Nov 13 (10)
- Nov 14 (7)
- Nov 15 (15)
- Nov 16 (8)
- Nov 17 (6)
- Nov 18 (5)
- Nov 19 (7)
- Nov 20 (8)
- Nov 21 (12)
- Nov 22 (5)
- Nov 23 (7)
- Nov 24 (7)
- Nov 25 (8)
- Nov 26 (2)
- Nov 27 (12)
- Nov 28 (2)
- Nov 29 (2)
- Dec 01 (1)
- Dec 02 (3)
- Dec 03 (2)
- Dec 04 (1)
- Dec 05 (9)
- Dec 06 (22)
- Dec 07 (2)
- Dec 08 (3)
- Dec 09 (1)
- Dec 13 (2)
- Dec 14 (12)
- Dec 15 (1)
- Dec 17 (1)
- Dec 23 (4)
- Dec 24 (2)
- Dec 25 (1)
- Dec 27 (2)
- Dec 28 (1)
- Dec 29 (6)
- Dec 30 (2)
- Dec 31 (6)
- Jan 03 (3)
- Jan 04 (12)
- Jan 05 (5)
- Jan 06 (7)
- Jan 07 (1)
- Jan 08 (3)
- Jan 09 (1)
- Jan 11 (1)
- Jan 12 (5)
- Jan 14 (1)
- Jan 16 (1)
- Jan 17 (1)
- Jan 18 (2)
- Jan 23 (1)
- Jan 26 (3)
- Jan 28 (2)
- Jan 29 (3)
- Jan 30 (1)
- Jan 31 (1)
- Feb 04 (2)
- Feb 05 (2)
- Feb 08 (2)
- Feb 09 (1)
- Feb 13 (3)
- Feb 15 (2)
- Feb 16 (1)
- Feb 17 (1)
- Feb 25 (2)
- Feb 28 (2)
- Mar 03 (1)
- Mar 08 (3)
- Mar 16 (2)
- Mar 17 (1)
- Mar 18 (11)
- Mar 20 (9)
- Mar 22 (1)
- Mar 23 (3)
- Mar 31 (1)
- Apr 01 (2)
- Apr 02 (1)
- Apr 03 (2)
- Apr 04 (1)
- Apr 05 (2)
- Apr 06 (6)
- Apr 07 (1)
- Apr 08 (7)
- Apr 09 (4)
- Apr 10 (7)
- Apr 19 (18)
- Apr 20 (12)
- Apr 21 (1)
- Apr 24 (2)
- May 11 (1)
- May 16 (4)
- May 20 (2)
- May 24 (2)
- May 27 (3)
- Jun 02 (2)
- Jun 06 (1)
- Jun 07 (9)
- Jun 10 (1)
- Jun 11 (2)
- Jun 12 (3)
- Jun 15 (1)
- Jun 17 (1)
- Jun 20 (5)
- Jun 21 (12)
- Jun 22 (21)
- Jun 23 (10)
- Jun 24 (4)
- Jun 25 (10)
- Jun 26 (5)
- Jun 28 (4)
- Jun 29 (2)
- Jun 30 (2)
- Jul 01 (1)
- Jul 04 (1)
- Jul 05 (2)
- Jul 06 (1)
- Jul 07 (2)
- Jul 08 (1)
- Jul 09 (3)
- Jul 10 (6)
- Jul 11 (7)
- Jul 12 (2)
- Jul 13 (3)
- Jul 14 (7)
- Jul 15 (4)
- Jul 16 (9)
- Jul 17 (2)
- Jul 18 (6)
- Jul 19 (6)
- Jul 20 (14)
- Jul 21 (2)
- Jul 22 (6)
- Jul 23 (14)
- Jul 24 (6)
- Jul 25 (5)
- Jul 26 (5)
- Jul 27 (2)
- Jul 28 (6)
- Jul 29 (1)
- Jul 30 (3)
- Jul 31 (1)
- Aug 01 (6)
- Aug 03 (6)
- Aug 04 (4)
- Aug 05 (2)
- Aug 06 (2)
- Aug 07 (1)
- Aug 08 (1)
- Aug 09 (1)
- Aug 10 (1)
- Aug 11 (3)
- Aug 12 (1)
- Aug 13 (1)
- Aug 14 (1)
- Aug 15 (1)
- Aug 17 (9)
- Aug 19 (1)
- Aug 24 (1)
- Aug 28 (1)
- Oct 14 (1)
- Oct 22 (1)
- Nov 13 (10)
- Nov 14 (1)
- Nov 15 (3)
- Nov 23 (2)
- Nov 24 (1)
- Nov 25 (1)
- Nov 26 (1)
- Dec 01 (3)
- Dec 07 (3)
- Dec 08 (1)
- Dec 10 (2)
- Dec 12 (22)
- Dec 13 (30)
- Dec 15 (7)
- Dec 20 (5)
- Dec 28 (1)
- Dec 29 (3)
- Dec 31 (1)
- Jan 02 (2)
- Jan 10 (1)
- Jan 14 (1)
- Jan 17 (4)
- Jan 29 (2)
- Feb 03 (1)
- Feb 04 (6)
- Feb 05 (5)
- Feb 06 (10)
- Feb 08 (16)
- Feb 10 (63)
- Feb 11 (39)
- Feb 12 (33)
- Feb 13 (27)
- Feb 14 (4)
- Feb 15 (66)
- Feb 16 (7)
- Feb 17 (22)
- Feb 18 (14)
- Feb 19 (44)
- Feb 20 (3)
- Feb 21 (12)
- Feb 22 (68)
- Feb 23 (78)
- Feb 25 (3)
- Feb 26 (10)
- Feb 27 (28)
- Feb 28 (26)
- Mar 01 (17)
- Mar 02 (7)
- Mar 03 (6)
- Mar 04 (3)
- Mar 05 (7)
- Mar 06 (8)
- Mar 07 (13)
- Mar 08 (6)
- Mar 09 (3)
- Mar 10 (2)
- Mar 11 (15)
- Mar 12 (6)
- Mar 13 (2)
- Mar 14 (15)
- Mar 15 (10)
- Mar 16 (6)
- Mar 17 (5)
- Mar 18 (3)
- Mar 19 (3)
- Mar 20 (9)
- Mar 21 (2)
- Mar 22 (1)
- Mar 23 (15)
- Mar 24 (1)
- Mar 25 (1)
- Mar 26 (7)
- Mar 27 (5)
- Mar 28 (2)
- Mar 29 (8)
- Mar 30 (21)
- Mar 31 (10)
- Apr 01 (3)
- Apr 02 (3)
- Apr 03 (9)
- Apr 04 (1)
- Apr 05 (4)
- Apr 06 (4)
- Apr 07 (4)
- Apr 08 (4)
- Apr 09 (1)
- Apr 10 (1)
- Apr 11 (6)
- Apr 12 (7)
- Apr 13 (3)
- Apr 14 (2)
- Apr 15 (11)
- Apr 16 (16)
- Apr 17 (12)
- Apr 18 (29)
- Apr 19 (21)
- Apr 20 (3)
- Apr 21 (8)
- Apr 22 (3)
- Apr 23 (5)
- Apr 24 (1)
- Apr 25 (4)
- Apr 26 (6)
- Apr 27 (8)
- Apr 28 (10)
- Apr 30 (2)
- May 01 (7)
- May 02 (3)
- May 03 (16)
- May 04 (3)
- May 05 (11)
- May 06 (41)
- May 07 (2)
- May 08 (18)
- May 09 (117)
- May 10 (15)
- May 11 (85)
- May 12 (12)
- May 13 (54)
- May 14 (73)
- May 15 (85)
- May 16 (148)
- May 17 (101)
- May 18 (100)
- May 19 (99)
- May 20 (101)
- May 21 (101)
- May 22 (101)
- May 23 (101)
- May 24 (101)
- May 25 (7)
- May 27 (1)
- May 28 (1)
- May 29 (29)
- Jun 02 (1)
- Jun 03 (21)
- Jun 04 (7)
- Jun 05 (8)
- Jun 06 (1)
- Jun 22 (5)
- Jun 23 (10)
- Jun 24 (10)
- Jun 25 (4)
- Jun 26 (7)
- Jun 27 (22)
- Jun 28 (12)
- Jun 29 (11)
- Jun 30 (23)
- Jul 01 (10)
- Jul 02 (13)
- Jul 03 (17)
- Jul 04 (41)
- Jul 05 (17)
- Jul 06 (8)
- Jul 07 (10)
- Jul 08 (6)
- Jul 09 (3)
- Jul 10 (2)
- Jul 11 (2)
- Jul 12 (12)
- Jul 13 (6)
- Jul 14 (14)
- Jul 15 (5)
- Jul 17 (1)
- Jul 18 (1)
- Jul 19 (1)
- Jul 20 (1)
- Jul 22 (2)
- Jul 23 (30)
- Jul 24 (5)
- Jul 25 (55)
- Jul 27 (8)
- Jul 28 (26)
- Jul 29 (15)
- Jul 30 (35)
- Jul 31 (5)
- Aug 01 (13)
- Aug 02 (3)
- Aug 04 (1)
- Aug 05 (2)
- Aug 11 (11)
- Aug 13 (3)
- Aug 14 (7)
- Aug 15 (3)
- Aug 16 (5)
- Aug 17 (4)
- Aug 18 (4)
- Aug 19 (2)
- Aug 20 (19)
- Aug 21 (38)
- Aug 23 (14)
- Aug 24 (6)
- Aug 25 (30)
- Aug 26 (57)
- Aug 27 (19)
- Aug 28 (25)
- Aug 29 (120)
- Aug 30 (82)
- Aug 31 (46)
- Sep 01 (96)
- Sep 02 (101)
- Sep 03 (62)
- Sep 04 (32)
- Sep 05 (44)
- Sep 06 (91)
- Sep 07 (22)
- Sep 08 (100)
- Sep 09 (71)
- Sep 10 (15)
- Sep 11 (90)
- Sep 13 (2)
Friday, September 3, 2021
09-02-2021-2055 - Arsenic As 33
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.
The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds.[8]
A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, hamsters, goats, chickens, and presumably other species. A role in human metabolism is not known.[9][10][11] However, arsenic poisoning occurs in multicellular life if quantities are larger than needed. Arsenic contamination of groundwater is a problem that affects millions of people across the world.
The United States' Environmental Protection Agency states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health.[12] The United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites.[13] Arsenic is classified as a Group-A carcinogen.[12]
 | |
| Arsenic |
|---|
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsenic
09-02-2021-2053 - African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, Trypanosoma brucei. Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense Trypanosoma brucei gambiense insect borne parasitic infection insect transmission vector flys malaria blood cell parasite tsetse fly trypano soma animal trypanosomiasis. tropics tropical disease
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.[3] It is caused by the species Trypanosoma brucei.[3] Humans are infected by two types, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (TbG) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (TbR).[3] TbG causes over 98% of reported cases.[1] Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.[3]
Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite.[1][2] Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping.[2] Diagnosis is by finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node.[2] A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease.[2]
Prevention of severe disease involves screening the population at risk with blood tests for TbG.[3]Treatment is easier when the disease is detected early and before neurological symptoms occur.[3]Treatment of the first stage has been with the medications pentamidine or suramin.[3] Treatment of the second stage has involved eflornithine or a combination of nifurtimox and eflornithine for TbG.[2][3]Fexinidazole is a more recent treatment that can be taken by mouth, for either stages of TbG.[3] While melarsoprol works for both types, it is typically only used for TbR, due to serious side effects.[3] Without treatment sleeping sickness typically results in death.[3]
The disease occurs regularly in some regions of sub-Saharan Africa with the population at risk being about 70 million in 36 countries.[5] An estimated 11,000 people are currently infected with 2,800 new infections in 2015.[6][1] In 2018 there were 977 new cases.[3] In 2015 it caused around 3,500 deaths, down from 34,000 in 1990.[4][7] More than 80% of these cases are in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.[1] Three major outbreaks have occurred in recent history: one from 1896 to 1906 primarily in Uganda and the Congo Basin and two in 1920 and 1970 in several African countries.[1] It is classified as a neglected tropical disease.[8] Other animals, such as cows, may carry the disease and become infected in which case it is known as Nagana or animal trypanosomiasis.[1]
| African trypanosomiasis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Sleeping sickness, African sleeping sickness |
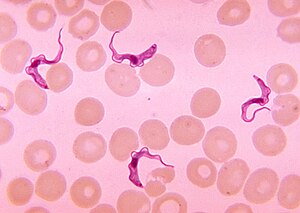 | |
| Trypanosoma forms in a blood smear | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Stage 1: Fevers, headaches, itchiness, joint pains[1] Stage 2: Trouble sleeping, confusion, poor coordination[2][1] |
| Usual onset | 1–3 weeks post exposure[2] |
| Types | Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (TbG), Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (TbR)[3] |
| Causes | Trypanosoma brucei spread by tsetse flies[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Blood smear, lumbar puncture[2] |
| Medication | Fexinidazole, pentamidine, suramin, eflornithine, nifurtimox[3] |
| Prognosis | Fatal without treatment[3] |
| Frequency | 977 (2018)[3] |
| Deaths | 3,500 (2015)[4] |
The causative agent and vector were identified in 1903 by David Bruce, and the subspecies of the protozoa were differentiated in 1910. Bruce had earlier shown that T. brucei was the cause of a similar disease in horses and cattle that was transmitted by the tse-tse fly (Glossina morsitans).[42]
The first effective treatment, atoxyl, an arsenic-based drug developed by Paul Ehrlich and Kiyoshi Shiga, was introduced in 1910, but blindness was a serious side effect.
Pentamidine, a highly effective drug for the first stage of the disease, has been used since 1937.[48] During the 1950s, it was widely used as a prophylacticagent in western Africa, leading to a sharp decline in infection rates. At the time, eradication of the disease was thought to be at hand.[citation needed][49]
Est. 1800 st.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/African_trypanosomiasis
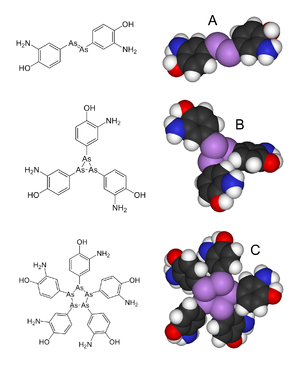
09-02-2021-2051 - Arsphenamine 606 66 syphilis and African trypanosomiasis 1910 organoarsenic arsenic phorphor dimer azobenzene VIV
Arsphenamine, also known as Salvarsan or compound 606, is a drug that was introduced at the beginning of the 1910s as the first effective treatment for syphilis and African trypanosomiasis.[2] This organoarsenic compound was the first modern antimicrobial agent.[3]
Arsphenamine was first synthesized in 1907 in Paul Ehrlich's lab by Alfred Bertheim.[3] The antisyphilitic activity of this compound was discovered by Sahachiro Hata in 1909, during a survey of hundreds of newly synthesized organic arsenical compounds. Ehrlich had theorized that by screening many compounds, a drug could be discovered that would have anti-microbial activity but not kill the human patient. Ehrlich's team began their search for such a "magic bullet" among chemical derivatives of the dangerously toxic drug atoxyl. This project was the first organized team effort to optimize the biological activity of a lead compound through systematic chemical modifications, the basis for nearly all modern pharmaceutical research.[citation needed]
Arsphenamine was used to treat the disease syphilis because it is toxic to the bacterium Treponema pallidum, a spirochete that causes syphilis.[citation needed]
Arsphenamine was originally called "606" because it was the sixth in the sixth group of compounds synthesized for testing; it was marketed by Hoechst AG under the trade name "Salvarsan" in 1910.[5][6] Salvarsan was the first organic antisyphilitic, and a great improvement over the inorganic mercury compounds that had been used previously. It was distributed as a yellow, crystalline, hygroscopic powder that was highly unstable in air.[7] This significantly complicated administration, as the drug had to be dissolved in several hundred milliliters of distilled, sterile water with minimal exposure to air to produce a solution suitable for injection. Some of the side effects attributed to Salvarsan, including rashes, liver damage, and risks of life and limb, were thought to be caused by improper handling and administration.[8] This caused Ehrlich, who worked assiduously to standardize practices, to observe, "the step from the laboratory to the patient's bedside ... is extraordinarily arduous and fraught with danger."[5]
Ehrlich's laboratory developed a more soluble (but slightly less effective) arsenical compound, Neosalvarsan(neoarsphenamine), which was easier to prepare, and it became available in 1912. Less severe side-effects such as nausea and vomiting were still common. An additional problem was that both Salvarsan and Neosalvarsan had to be stored in sealed vials under a nitrogen atmosphere to prevent oxidation. These arsenical compounds were supplanted as treatments for syphilis in the 1940s by penicillin.[9]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsphenamine
09-02-2021-2011 - Immersion foot syndromes Trench foot Tropical ulcer Jungle Rot mycobacteria mycosis sepsis bone
Immersion foot syndromes are a class of foot injury caused by water absorption in the outer layer of skin.[1][2] There are different subclass names for this condition based on the temperature of the water to which the foot is exposed. These include trench foot, tropical immersion foot, and warm water immersion foot.[3]:26–7 In one 3-day military study, it was found that submersion in water allowing for a higher skin temperature resulted in worse skin maceration and pain.[4]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immersion_foot_syndromes
Trench foot is a type of foot damage due to moisture.[1] Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness.[1][2] The feet may become red or bluish in color.[1] As the condition worsens the feet can start to swell and smell of decay.[1] Complications may include skin breakdown or infection.[1]
Trench foot occurs due to prolonged exposure of the feet to cold, damp, and often unsanitary conditions.[1] Unlike frostbite, trench foot usually occurs at temperatures above freezing.[1] Onset can be as rapid as 10 hours.[1] Risk factors include overly tight boots and not moving.[3] The underlying mechanism is believed to involve constriction of blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood flow to the feet.[1] Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination.[1]
Prevention involves keeping the feet warm, dry, and clean.[1] After the condition has occurred, pain medications may be required during the gradual rewarming process.[1] Pain may persist for months following treatment.[3] Surgery to remove damaged tissue or amputation may be necessary.[1]
Those in the military are most commonly affected, though cases may also occur in the homeless.[1] The condition was first described during Napoleon Bonaparte's retreat from Russia in the winter of 1812.[1]The word trench in the name is a reference to trench warfare, mainly associated with World War I.[1]
| Trench foot | |
|---|---|
| Other names | immersion foot |
 | |
| Trench foot as seen on an unidentified soldier during World War I. | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine |
| Symptoms |
|
| Complications |
|
| Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trench_foot
Tropical ulcer, more commonly known as jungle rot, is a chronic ulcerative skin lesion thought to be caused by polymicrobial infection with a variety of microorganisms, including mycobacteria. It is common in tropical climates.[2]
Ulcers occur on exposed parts of the body, primarily on anterolateral aspect of the lower limbs and may erode muscles and tendons, and sometimes, the bones.[3] These lesions may frequently develop on preexisting abrasions or sores sometimes beginning from a mere scratch.[1]
| Tropical ulcer | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Aden ulcer, Jungle rot, Malabar ulcer, Tropical phagedena[1] |
 | |
| The left foot of a person with acute tropical ulcer upon his admission to Toborra Goroka Hospital, in Goroka, Papua New Guinea. | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tropical_ulcer
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammationduring bacterial or fungal infection.[1][2] An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule, pimple or spot.
| Pus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Eye with conjunctivitis exuding pus | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pus
Herou Purease, Tank You. Left Amcan; Right AziV. - SSF
Right Viet-Canco-Phili-Nor-Fin-Attempt (Slav/switz) w/ Left Hook GL deper-neandre. middle East (hair), latino high, brows. Liver failure, lipodystrophy, bone malacia, ricketts, small channular parasite viral loading fung arsenic responsive, thymal disease degen early, neural sloughig-plaquening-malacia (channular/interspaces). 1990, 1930SLV peripheral nervy decars. Oncogenic Virus. FLV. HFV. Avian Synctal Chick Virus Derivative Hum. Cancer Bone Cancer. Fibrotic Cystular Fibrotic. Genetic Deletion/Decay, DEcay signature of asian gene and chromosomal deletion occurance or syndrome USA. Yellow-Browning. Moles-Warts-Tumors dark brown. ARtheriocalssification calcs liques necrots. bubulants. HEP HER HIV PEST. Migrans As, Arthropod-Worm, extremophile. Schitz outcome trend-trad. bone cavitation. mole bone. F-Gan Bubules Dissem Gran Dissem Can. HFM, Hemorrhagia @ GRN, BRN, Purp, [Black] Bluds cryst excissions. ascitic-mito-met. rad-K/Rad-I. WHKAZIVLAYNG
- Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (also known as "Palmoplantar keratoderma cum degeneratione granulosa Vörner," "Vörner's epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma", and "Vörner keratoderma"[4]) is one of the most common patterns of palmoplantar keratoderma, an autosomal dominant condition that presents within the first few months of life, characterized by a well-demarcated, symmetric thickening of palms and soles, often with a "dirty" snakeskin appearance due to underlying epidermolysis.[1]:506
- Aquagenic keratoderma, also known as acquired aquagenic palmoplantar keratoderma,[4]:788 transient reactive papulotranslucent acrokeratoderma,[4]aquagenic syringeal acrokeratoderma,[4] and aquagenic wrinkling of the palms,[2] is a skin condition characterized by the development of white papuleson the palms after water exposure.[2]:215 The condition causes irritation of the palms when touching certain materials after being wet, e.g., paper, cloth. An association with cystic fibrosis has been suggested.[21] The association with cystic fibrosis suggests an increased salt content in the skin.[22]
Left Cancotic Papulation Neck Rubules. 1945. Mixed Wallace-Smith-Petersen-STDGerm. Infectious Cancer. Zoonit dis, Cancer Bone Cancer. Sarcotic Fibrotic. Lipodystrophy, Redding. Specklularation light brown or red. swelling inflammation clogulation. purulants. HER HIV POX. hole bone. overvaccination. eczema hypersensitivity immunsuppression immune dysfunction degeneratio cancer bone cancer disseminative metastatic type. wee walish weattey. pus blood, chol plam.
Necrobiosis lipoidica is a necrotising skin condition that usually occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus but can also be associated with rheumatoid arthritis.[1] In the former case it may be called necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (NLD).[2] NLD occurs in approximately 0.3% of the diabetic population, with the majority of sufferers being women (approximately 3:1 females to males affected).
The severity or control of diabetes in an individual does not affect who will or will not get NLD.[3] Better maintenance of diabetes after being diagnosed with NLD will not change how quickly the NLD will resolve.
| Necrobiosis lipoidica | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endogenous_retrovirus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NF-κB
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciphylaxis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dystrophic_calcification
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pasteurella
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palmoplantar_keratoderma
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vaccinia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generalized_vaccinia
https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Granulosis_Virus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methotrexate
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myxococcus
https://seer.cancer.gov/seertools/hemelymph/532b32a0e4b0626b1926e990/
https://seer.cancer.gov/seertools/hemelymph/51f6cf57e3e27c3994bd5363/?q=cytoid#
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Treponema_pallidum
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simian_immunodeficiency_virus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_T-lymphotropic_virus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacillus_thuringiensis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Visna-maedi_virus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jaagsiekte_sheep_retrovirus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caprine_arthritis_encephalitis_virus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhabdomyolysis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_necrosis_factor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_lysis_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuberculosis
Dr. F
| Palmoplantar keratoderma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Patient with severe plantar keratosis. | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by abnormal thickening of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles.
Autosomal recessive, dominant, X-linked, and acquired forms have all been described.[1]:505[2]:211[3]
- Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (also known as "Palmoplantar keratoderma cum degeneratione granulosa Vörner," "Vörner's epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma", and "Vörner keratoderma"[4]) is one of the most common patterns of palmoplantar keratoderma, an autosomal dominant condition that presents within the first few months of life, characterized by a well-demarcated, symmetric thickening of palms and soles, often with a "dirty" snakeskin appearance due to underlying epidermolysis.[1]:506
- Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez (also known as "Huriez syndrome," "Palmoplantar keratoderma with scleroatrophy,"[4] "Palmoplantar keratoderma with sclerodactyly," "Scleroatrophic and keratotic dermatosis of the limbs," and "Sclerotylosis") is an autosomal dominant keratoderma with sclerodactylypresent at birth with a diffuse symmetric keratoderma of the palms and soles.[1]:513[2]:576 An association with 4q23 has been described.[14] It was characterized in 1968.[15]
- Vohwinkel syndrome (also known as "Keratoderma hereditaria mutilans,"[4] "Keratoma hereditaria mutilans,"[4] "Mutilating keratoderma of Vohwinkel",[2]:213 "Mutilating palmoplantar keratoderma"[4]) is a diffuse autosomal dominant keratoderma with onset in early infancy characterized by a honeycombed keratoderma involving the palmoplantar surfaces.[1]:512 Mild to moderate sensorineural hearing loss is often associated.[1] It has been associated with GJB2.[16] It was characterized in 1929.[17]
- Olmsted syndrome (also known as "Mutilating palmoplantar keratoderma with periorificial keratotic plaques," "Mutilating palmoplantar keratoderma with periorificial plaques"[4] and "Polykeratosis of Touraine") is a keratoderma of the palms and soles, with flexion deformity of the digits, that begins in infancy.[1]:510[2]:214[4][18] Treatment with retinoids has been described.[19] It has been associated with mutations in TRPV3.[20]
| Granuloma annulare | |
|---|---|
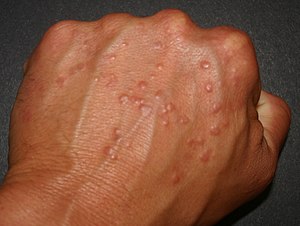 | |
| Perforating form of Granuloma annulare on hand | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Trench fever (also known as "five-day fever", "quintan fever" (Latin: febris quintana), and "urban trench fever"[1]) is a moderately serious disease transmitted by body lice. It infected armies in Flanders, France, Poland, Galicia, Italy, Salonika, Macedonia, Mesopotamia, Russia and Egypt in World War I.[2][3] Three noted sufferers during WWI were the authors J. R. R. Tolkien,[4] A. A. Milne,[5] and C. S. Lewis.[6] From 1915 to 1918 between one-fifth and one-third of all British troops reported ill had trench fever while about one-fifth of ill German and Austrian troops had the disease.[2] The disease persists among the homeless.[7] Outbreaks have been documented, for example, in Seattle[8] and Baltimore in the United States among injection drug users[9]and in Marseille, France,[8] and Burundi.[10]
Trench fever is also called Wolhynia fever, shin bone fever, Meuse fever, His disease and His–Werner disease or Werner-His disease (after Wilhelm His Jr. and Heinrich Werner).
The disease is caused by the bacterium Bartonella quintana (older names: Rochalimea quintana, Rickettsia quintana), found in the stomach walls of the body louse.[3] Bartonella quintana is closely related to Bartonella henselae, the agent of cat scratch fever and bacillary angiomatosis.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trench_fever
Serological testing is typically used to obtain a definitive diagnosis. Most serological tests would succeed only after a certain period of time past the symptom onset (usually a week). The differential diagnosis list includes typhus, ehrlichiosis, leptospirosis, Lyme disease, and virus-caused exanthema (measles or rubella).[citation needed]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trench_fever
Bacillary angiomatosis (BA) is a form of angiomatosis associated with bacteria of the genus Bartonella.[1]
| Bacillary angiomatosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Bartonella (bacterial species which causes this condition) | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacillary_angiomatosis
Bartonella henselae, formerly Rochalimæa, is a proteobacterium that is the causative agent of cat-scratch disease[1] (bartonellosis).
B. henselae is a member of the genus Bartonella, one of the most common types of bacteria in the world. It is a facultative intracellular microbe that targets red blood cells. One study showed it invaded the mature blood cells of humans.[2] It infects the host cell by sticking to it using trimeric autotransporter adhesins.[3] In the United States, about 22,000 people are diagnosed, most under the age of 20. Most often, it is transmitted from kittens.[4]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bartonella_henselae
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.[3] It is caused by the species Trypanosoma brucei.[3] Humans are infected by two types, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (TbG) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (TbR).[3] TbG causes over 98% of reported cases.[1] Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.[3]
Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite.[1][2] Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping.[2] Diagnosis is by finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node.[2] A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease.[2]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/African_trypanosomiasis
Arsphenamine, also known as Salvarsan or compound 606, is a drug that was introduced at the beginning of the 1910s as the first effective treatment for syphilis and African trypanosomiasis.[2] This organoarsenic compound was the first modern antimicrobial agent.[3]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsphenamine