above. Deathstars - Trinity Fields
Blog Archive
- Apr 12 (12)
- Apr 13 (2)
- Apr 14 (7)
- Apr 15 (11)
- Apr 16 (5)
- Apr 17 (14)
- Apr 18 (16)
- Apr 19 (17)
- Apr 20 (28)
- Apr 21 (29)
- Apr 22 (15)
- Apr 23 (19)
- Apr 24 (8)
- Apr 25 (58)
- Apr 26 (44)
- Apr 28 (6)
- Apr 29 (6)
- Apr 30 (7)
- May 01 (8)
- May 02 (9)
- May 03 (4)
- May 04 (6)
- May 05 (14)
- May 06 (20)
- May 07 (11)
- May 08 (18)
- May 09 (6)
- May 10 (17)
- May 11 (8)
- May 12 (25)
- May 13 (8)
- May 14 (2)
- May 15 (2)
- May 17 (16)
- May 18 (1)
- May 19 (5)
- May 20 (22)
- May 21 (6)
- May 22 (3)
- May 23 (2)
- May 24 (7)
- May 25 (1)
- May 26 (6)
- May 27 (3)
- May 28 (3)
- May 29 (10)
- May 30 (8)
- May 31 (12)
- Jun 01 (1)
- Jun 02 (1)
- Jun 03 (9)
- Jun 04 (1)
- Jun 05 (2)
- Jun 07 (4)
- Jun 08 (8)
- Jun 09 (1)
- Jun 10 (1)
- Jun 19 (1)
- Jun 27 (1)
- Jun 29 (1)
- Jun 30 (7)
- Jul 01 (3)
- Jul 02 (1)
- Jul 03 (1)
- Jul 04 (2)
- Jul 05 (1)
- Jul 06 (3)
- Jul 08 (9)
- Jul 09 (1)
- Jul 10 (1)
- Jul 11 (2)
- Jul 12 (2)
- Jul 13 (4)
- Jul 14 (4)
- Jul 15 (2)
- Jul 17 (8)
- Jul 18 (17)
- Jul 19 (1)
- Jul 20 (8)
- Jul 21 (6)
- Jul 22 (12)
- Jul 23 (10)
- Jul 25 (6)
- Jul 26 (23)
- Jul 28 (50)
- Jul 30 (12)
- Jul 31 (5)
- Aug 01 (16)
- Aug 02 (5)
- Aug 03 (5)
- Aug 04 (11)
- Aug 05 (13)
- Aug 06 (7)
- Aug 07 (10)
- Aug 08 (2)
- Aug 09 (27)
- Aug 10 (15)
- Aug 11 (67)
- Aug 12 (44)
- Aug 13 (29)
- Aug 14 (120)
- Aug 15 (61)
- Aug 16 (36)
- Aug 17 (21)
- Aug 18 (5)
- Aug 21 (5)
- Aug 22 (54)
- Aug 23 (101)
- Aug 24 (100)
- Aug 25 (99)
- Aug 26 (100)
- Aug 27 (84)
- Aug 28 (73)
- Aug 29 (76)
- Aug 30 (67)
- Aug 31 (95)
- Sep 01 (126)
- Sep 02 (68)
- Sep 03 (11)
- Sep 04 (14)
- Sep 05 (47)
- Sep 06 (101)
- Sep 07 (61)
- Sep 08 (57)
- Sep 09 (46)
- Sep 10 (14)
- Sep 11 (93)
- Sep 12 (101)
- Sep 13 (101)
- Sep 14 (100)
- Sep 15 (77)
- Sep 16 (2)
- Sep 17 (101)
- Sep 18 (91)
- Sep 19 (102)
- Sep 20 (102)
- Sep 21 (94)
- Sep 22 (84)
- Sep 23 (110)
- Sep 24 (101)
- Sep 25 (76)
- Sep 26 (43)
- Sep 27 (87)
- Sep 28 (104)
- Sep 29 (92)
- Sep 30 (33)
- Oct 01 (58)
- Oct 02 (1)
- Oct 05 (8)
- Oct 06 (6)
- Oct 07 (4)
- Oct 08 (4)
- Oct 09 (1)
- Oct 10 (18)
- Oct 11 (8)
- Oct 12 (26)
- Oct 13 (6)
- Oct 14 (2)
- Oct 15 (4)
- Oct 16 (3)
- Oct 17 (4)
- Oct 18 (3)
- Oct 19 (11)
- Oct 20 (5)
- Oct 21 (7)
- Oct 22 (5)
- Oct 23 (8)
- Oct 24 (9)
- Oct 25 (14)
- Oct 26 (8)
- Oct 27 (13)
- Oct 28 (7)
- Oct 29 (7)
- Oct 30 (22)
- Oct 31 (13)
- Nov 01 (13)
- Nov 02 (6)
- Nov 03 (10)
- Nov 04 (17)
- Nov 05 (8)
- Nov 06 (9)
- Nov 07 (11)
- Nov 08 (3)
- Nov 09 (7)
- Nov 10 (5)
- Nov 11 (5)
- Nov 12 (5)
- Nov 13 (10)
- Nov 14 (7)
- Nov 15 (15)
- Nov 16 (8)
- Nov 17 (6)
- Nov 18 (5)
- Nov 19 (7)
- Nov 20 (8)
- Nov 21 (12)
- Nov 22 (5)
- Nov 23 (7)
- Nov 24 (7)
- Nov 25 (8)
- Nov 26 (2)
- Nov 27 (12)
- Nov 28 (2)
- Nov 29 (2)
- Dec 01 (1)
- Dec 02 (3)
- Dec 03 (2)
- Dec 04 (1)
- Dec 05 (9)
- Dec 06 (22)
- Dec 07 (2)
- Dec 08 (3)
- Dec 09 (1)
- Dec 13 (2)
- Dec 14 (12)
- Dec 15 (1)
- Dec 17 (1)
- Dec 23 (4)
- Dec 24 (2)
- Dec 25 (1)
- Dec 27 (2)
- Dec 28 (1)
- Dec 29 (6)
- Dec 30 (2)
- Dec 31 (6)
- Jan 03 (3)
- Jan 04 (12)
- Jan 05 (5)
- Jan 06 (7)
- Jan 07 (1)
- Jan 08 (3)
- Jan 09 (1)
- Jan 11 (1)
- Jan 12 (5)
- Jan 14 (1)
- Jan 16 (1)
- Jan 17 (1)
- Jan 18 (2)
- Jan 23 (1)
- Jan 26 (3)
- Jan 28 (2)
- Jan 29 (3)
- Jan 30 (1)
- Jan 31 (1)
- Feb 04 (2)
- Feb 05 (2)
- Feb 08 (2)
- Feb 09 (1)
- Feb 13 (3)
- Feb 15 (2)
- Feb 16 (1)
- Feb 17 (1)
- Feb 25 (2)
- Feb 28 (2)
- Mar 03 (1)
- Mar 08 (3)
- Mar 16 (2)
- Mar 17 (1)
- Mar 18 (11)
- Mar 20 (9)
- Mar 22 (1)
- Mar 23 (3)
- Mar 31 (1)
- Apr 01 (2)
- Apr 02 (1)
- Apr 03 (2)
- Apr 04 (1)
- Apr 05 (2)
- Apr 06 (6)
- Apr 07 (1)
- Apr 08 (7)
- Apr 09 (4)
- Apr 10 (7)
- Apr 19 (18)
- Apr 20 (12)
- Apr 21 (1)
- Apr 24 (2)
- May 11 (1)
- May 16 (4)
- May 20 (2)
- May 24 (2)
- May 27 (3)
- Jun 02 (2)
- Jun 06 (1)
- Jun 07 (9)
- Jun 10 (1)
- Jun 11 (2)
- Jun 12 (3)
- Jun 15 (1)
- Jun 17 (1)
- Jun 20 (5)
- Jun 21 (12)
- Jun 22 (21)
- Jun 23 (10)
- Jun 24 (4)
- Jun 25 (10)
- Jun 26 (5)
- Jun 28 (4)
- Jun 29 (2)
- Jun 30 (2)
- Jul 01 (1)
- Jul 04 (1)
- Jul 05 (2)
- Jul 06 (1)
- Jul 07 (2)
- Jul 08 (1)
- Jul 09 (3)
- Jul 10 (6)
- Jul 11 (7)
- Jul 12 (2)
- Jul 13 (3)
- Jul 14 (7)
- Jul 15 (4)
- Jul 16 (9)
- Jul 17 (2)
- Jul 18 (6)
- Jul 19 (6)
- Jul 20 (14)
- Jul 21 (2)
- Jul 22 (6)
- Jul 23 (14)
- Jul 24 (6)
- Jul 25 (5)
- Jul 26 (5)
- Jul 27 (2)
- Jul 28 (6)
- Jul 29 (1)
- Jul 30 (3)
- Jul 31 (1)
- Aug 01 (6)
- Aug 03 (6)
- Aug 04 (4)
- Aug 05 (2)
- Aug 06 (2)
- Aug 07 (1)
- Aug 08 (1)
- Aug 09 (1)
- Aug 10 (1)
- Aug 11 (3)
- Aug 12 (1)
- Aug 13 (1)
- Aug 14 (1)
- Aug 15 (1)
- Aug 17 (9)
- Aug 19 (1)
- Aug 24 (1)
- Aug 28 (1)
- Oct 14 (1)
- Oct 22 (1)
- Nov 13 (10)
- Nov 14 (1)
- Nov 15 (3)
- Nov 23 (2)
- Nov 24 (1)
- Nov 25 (1)
- Nov 26 (1)
- Dec 01 (3)
- Dec 07 (3)
- Dec 08 (1)
- Dec 10 (2)
- Dec 12 (22)
- Dec 13 (30)
- Dec 15 (7)
- Dec 20 (5)
- Dec 28 (1)
- Dec 29 (3)
- Dec 31 (1)
- Jan 02 (2)
- Jan 10 (1)
- Jan 14 (1)
- Jan 17 (4)
- Jan 29 (2)
- Feb 03 (1)
- Feb 04 (6)
- Feb 05 (5)
- Feb 06 (10)
- Feb 08 (16)
- Feb 10 (63)
- Feb 11 (39)
- Feb 12 (33)
- Feb 13 (27)
- Feb 14 (4)
- Feb 15 (66)
- Feb 16 (7)
- Feb 17 (22)
- Feb 18 (14)
- Feb 19 (44)
- Feb 20 (3)
- Feb 21 (12)
- Feb 22 (68)
- Feb 23 (78)
- Feb 25 (3)
- Feb 26 (10)
- Feb 27 (28)
- Feb 28 (26)
- Mar 01 (17)
- Mar 02 (7)
- Mar 03 (6)
- Mar 04 (3)
- Mar 05 (7)
- Mar 06 (8)
- Mar 07 (13)
- Mar 08 (6)
- Mar 09 (3)
- Mar 10 (2)
- Mar 11 (15)
- Mar 12 (6)
- Mar 13 (2)
- Mar 14 (15)
- Mar 15 (10)
- Mar 16 (6)
- Mar 17 (5)
- Mar 18 (3)
- Mar 19 (3)
- Mar 20 (9)
- Mar 21 (2)
- Mar 22 (1)
- Mar 23 (15)
- Mar 24 (1)
- Mar 25 (1)
- Mar 26 (7)
- Mar 27 (5)
- Mar 28 (2)
- Mar 29 (8)
- Mar 30 (21)
- Mar 31 (10)
- Apr 01 (3)
- Apr 02 (3)
- Apr 03 (9)
- Apr 04 (1)
- Apr 05 (4)
- Apr 06 (4)
- Apr 07 (4)
- Apr 08 (4)
- Apr 09 (1)
- Apr 10 (1)
- Apr 11 (6)
- Apr 12 (7)
- Apr 13 (3)
- Apr 14 (2)
- Apr 15 (11)
- Apr 16 (16)
- Apr 17 (12)
- Apr 18 (29)
- Apr 19 (21)
- Apr 20 (3)
- Apr 21 (8)
- Apr 22 (3)
- Apr 23 (5)
- Apr 24 (1)
- Apr 25 (4)
- Apr 26 (6)
- Apr 27 (8)
- Apr 28 (10)
- Apr 30 (2)
- May 01 (7)
- May 02 (3)
- May 03 (16)
- May 04 (3)
- May 05 (11)
- May 06 (41)
- May 07 (2)
- May 08 (18)
- May 09 (117)
- May 10 (15)
- May 11 (85)
- May 12 (12)
- May 13 (54)
- May 14 (73)
- May 15 (85)
- May 16 (148)
- May 17 (101)
- May 18 (100)
- May 19 (99)
- May 20 (101)
- May 21 (101)
- May 22 (101)
- May 23 (101)
- May 24 (101)
- May 25 (7)
- May 27 (1)
- May 28 (1)
- May 29 (29)
- Jun 02 (1)
- Jun 03 (21)
- Jun 04 (7)
- Jun 05 (8)
- Jun 06 (1)
- Jun 22 (5)
- Jun 23 (10)
- Jun 24 (10)
- Jun 25 (4)
- Jun 26 (7)
- Jun 27 (22)
- Jun 28 (12)
- Jun 29 (11)
- Jun 30 (23)
- Jul 01 (10)
- Jul 02 (13)
- Jul 03 (17)
- Jul 04 (41)
- Jul 05 (17)
- Jul 06 (8)
- Jul 07 (10)
- Jul 08 (6)
- Jul 09 (3)
- Jul 10 (2)
- Jul 11 (2)
- Jul 12 (12)
- Jul 13 (6)
- Jul 14 (14)
- Jul 15 (5)
- Jul 17 (1)
- Jul 18 (1)
- Jul 19 (1)
- Jul 20 (1)
- Jul 22 (2)
- Jul 23 (30)
- Jul 24 (5)
- Jul 25 (55)
- Jul 27 (8)
- Jul 28 (26)
- Jul 29 (15)
- Jul 30 (35)
- Jul 31 (5)
- Aug 01 (13)
- Aug 02 (3)
- Aug 04 (1)
- Aug 05 (2)
- Aug 11 (11)
- Aug 13 (3)
- Aug 14 (7)
- Aug 15 (3)
- Aug 16 (5)
- Aug 17 (4)
- Aug 18 (4)
- Aug 19 (2)
- Aug 20 (19)
- Aug 21 (38)
- Aug 23 (14)
- Aug 24 (6)
- Aug 25 (30)
- Aug 26 (57)
- Aug 27 (19)
- Aug 28 (25)
- Aug 29 (120)
- Aug 30 (82)
- Aug 31 (46)
- Sep 01 (96)
- Sep 02 (101)
- Sep 03 (62)
- Sep 04 (32)
- Sep 05 (44)
- Sep 06 (91)
- Sep 07 (22)
- Sep 08 (100)
- Sep 09 (71)
- Sep 10 (15)
- Sep 11 (90)
- Sep 13 (2)
Wednesday, September 8, 2021
09-08-2021-1518 - Oxyphilic Adenocarcinoma Follicule oncocytic hurthle cell Thyroid endocrine endocrinology adeno SEER & PUBMED Process "...abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm (oncocytes)."
Oxyphilic Adenocarcinoma
- MedGen UID:
- 61427
- •Concept ID:
- C0205642
- •
- Neoplastic Process
| Synonyms: | Adenocarcinoma, Oxyphilic; Adenocarcinomas, Oxyphilic; Oxyphilic Adenocarcinomas |
| SNOMED CT: | Follicular carcinoma, oxyphilic cell (57596004); Oxyphilic adenocarcinoma (443261008); Oxyphilic adenocarcinoma (57596004); Oncocytic carcinoma (57596004); Oncocytic adenocarcinoma (57596004); Hurthle cell carcinoma (57596004); Hurthle cell adenocarcinoma (57596004) |
09-08-2021-1517 - Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative neoplasm, unclassifiable IMMUNOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASES reticular reticulum reticulus endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria cell SEER
NEOPLASMS OF HISTIOCYTES AND ACCESSORY LYMPHOID CELLS IMMUNOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASES
PRECURSOR LYMPHOID NEOPLASMS
LYMPHOID LEUKEMIA, NOS PROLYMPH/PRECURS LEUKEMIA
CHRONIC MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DIS. MYELOPLASTIC/MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASMS
975 9759/3 976 9766/3 981 9811/3
Fibroblastic reticular cell tumor Lymphomatoid granulomatosis, grade 3
B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, NOS
982 9823/3
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma
9812/3 Leukemia/lymphoma with t(9;22)(q34;q11.2);BCR-ABL1
9813/3 Leukemia/lymphoma with t(v;11q23);MLL rearranged
9814/3 Leukemia/lymphoma with t(12;21)(p13;q22);TEL-AML1(ETV6-RUNX1) 9815/3 B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma with hyperdiploidy
9816/3 Leukemia/lymphoma with hypodiploidy (hypodiploid ALL)
9817/3 B lymphblastic leukemia/lymphoma with t(5;14)(q31;q32);IL3-IGH 9818/3 Leukemia/lymphoma with t(1;19)(q23;p13.3); E2A PBX1 (TCF3 PBX1) 9819/3 B-lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma, BCR-ABL1-like
T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
983 9831/3
9837/3 T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
996 9965/3
9967/3 Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasm with FGFR1 abnormalities
Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms with PDGFRB rearrangement
997 9971/3
9975/3 Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative neoplasm, unclassifiable
https://seer.cancer.gov/icd-o-3/sitetype.icdo3.20210607.pdf#search=plasma%20cell
Above. Lil Jon & The East Side Boyz - Get Low
09-08-2021-1515 - SEER Validation List https://seer.cancer.gov/icd-o-3/sitetype.icdo3.20210607.pdf#search=plasma%20cell Muller FBI & Friends
https://seer.cancer.gov/icd-o-3/sitetype.icdo3.20210607.pdf#search=plasma%20cell
(Repost, Original Post Present)
08-24-2021-1053 - Anemia - Autoimmune hemolytic anemia - The term "macrocytic" refers to the enlarged size of the red blood cells.
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Anemia (NOS) is a decrease in the number of red blood cells. Many cancer patients develop anemia due to the cancer and/or cancer therapy. This condition may be referred to as Anemia in neoplastic disease or anemia of chronic disorders. The anemia by itself is not reportable. The neoplasm causing the anemia would be reportable.
Aplastic anemia occurs when the bone marrow does not make enough new red cells. A neoplasm may cause the aplastic anemia; however, the aplastic anemia by itself is not reportable. (See also pancytopenia)
Hemolytic (autoimmune) anemia is a group of acute or chronic anemias, inherited or acquired, characterized by shortened survival of mature erythrocytes and inability of bone marrow to compensate for the decreased life span.
Idiopathic refractory anemia is when the cause of the anemia is not known. This is not the same thing as Refractory Anemia(9980/3).
Iron -refractory iron deficiency anemia (IRIDA) or refractory iron deficiency anemia is an autosomal recessive disorder.
Macrocytic anemia is usually caused by vitamin deficiencies, alcohol use, medications or thyroid. The term "macrocytic" refers to the enlarged size of the red blood cells.
Anemia
https://seer.cancer.gov/seertools/hemelymph/532b32a0e4b0626b1926e990/
The term "macrocytic" refers to the enlarged size of the red blood cells.
https://seer.cancer.gov/icd-o-3/sitetype.icdo3.20210607.pdf#search=plasma%20cell
ML, SMALL B-CELL LYMPHOCYTIC
PRECURS. CELL LYMPHOBLASTIC LYMPH.
PLASMA CELL TUMORS
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA, NOS
GIANT & SPINDLE CELL CARCINOMA
BRONCHIOLO-ALVEOLAR ADENOCA.
CLEAR CELL ADENOCARCINOMA, NOS
ACINAR CELL CARCINOMA
FIBROMATOUS NEOPLASMS
SARCOMA, NOS RHABDOMYOSARCOMA, NOS
EMBRYONAL RHABDOMYOSARCOMA MIXED TUMOR, MALIGNANT, NOS
ML, LARGE B-CELL, DIFFUSE
FOLLIC. & MARGINAL LYMPH, NOS
IMMUNOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASES
LYMPHOID LEUKEMIA, NOS PROLYMPH/PRECURS LEUKEMIA
CHRONIC MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DIS.
OXYPHILIC ADENOCARCINOMA
DUCT CARCINOMA
ACINAR CELL CARCINOMA ADENOSQUAMOUS CARCINOMA
ADENOCA. WITH METAPLASIA
SARCOMA, NOS
FIBROMATOUS NEOPLASMS
SARCOMA, NOS MYXOSARCOMA LIPOSARCOMA NEOPLASMS
MYOMATOUS NEOPLASMS
RHABDOMYOSARCOMA, NOS
MIXED TUMOR, MALIGNANT, NOS CARCINOSARCOMA, NOS
MESENCHYMOMA, MALIGNANT
ML, SMALL B-CELL LYMPHOCYTIC
ML, LARGE B-CELL, DIFFUSE
granuloma sarcoma lymphoma
immunoblastic
FOLLIC. & MARGINAL LYMPH, NOS
NEOPLASMS OF HISTIOCYTES AND ACCESSORY LYMPHOID CELLS
IMMUNOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASES
PRECURSOR LYMPHOID NEOPLASMS
MAL. MEL. IN JUNCT. NEVUS
MAL. MELAN. IN GIANT PIGMT. NEVUS
CLEAR CELL ADENOCARCINOMA, NOS MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA MUCINOUS ADENOCARCINOMA
PAPILLARY ADENOCARCINOMA, NOS
Lymphomatoid granulomatosis, grade 3
Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, NOS
8693/3 Extra-adrenal paraganglioma, malignant
MEDIASTINUM C381-C383,C388
THYMUS C379
PLEURA C384
RESPIRATORY,NOS C390,C398-C399
9690/3 Follicular lymphoma, NOS
9691/3 Follicular lymphoma, grade 2
9695/3 Follicular lymphoma, grade 1
9698/3 Follicular lymphoma, grade 3
9699/3 Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, NOS
BONES & JOINTS (EXCL SKULL AND FACE, MANDIBLE) C400-C403,C408-C409,C412-C414,C418-C419 Dr. Layng Getting Some Brown Right
BLOOD, BONE MARROW, & HEMATOPOIETICSYS C420, C421, C424
FOLLIC. & MARGINAL LYMPH, NOS 969
Acute myelomonocytic leukemia
RETICULO-ENDOTHELIAL C423
Langerhans cell histiocytosis, disseminated
SPLEEN C422
Skin
Peripheral Nerves
Retroperitoneum
(Metastatic proc BK Study USA match)
RETROPERITONEUM & PERITONEUM C480-C482,C488
CONNECTIVE & SOFT TISSUE C490-C496,C498-C499
VAGINA & LABIA C510-C512,C518, C529 (AI or NAI)
CERVIX UTERI C530-C531,C538-C539
CORPUS UTERI C540-C543,C548-C549
UTERUS, NOS C559
OVARY C569
PRECURS. CELL LYMPHOBLASTIC LYMPH.
PLASMA CELL TUMORS
MAST CELL TUMORS
FALLOPIANTUBE C570
OTHER FEMALE GENITAL (EXCL FALLOPIAN TUBE) C571-C574,C577-C579
PLACENTA C589
MULLERIAN MIXED TUMOR
KIDNEY C649
RENAL PELVIS, URETER C659, C669
URINARYBLADDER C670-C679
OTHER URINARYORGANS C680-C681,C688-C689
ORBIT & LACRIMALGLAND, (EXCL. RETINA, EYE, NOS) C690-C691, C693, C695-C698
RETINA C692 - winner nikiya @ nlab
EYEBALL C694
EYE, NOS C699
MENINGES (CEREBRAL,SPINAL) C700-C701,C709
BRAIN, & CRANIAL NERVES, & SPINAL CORD, (EXCL. VENTRICLE, CEREBELLUM) C710-C714, C717-C719, C720-C725
VENTRICLE C715
CEREBELLUM C716
OTHER NERVOUS SYSTEM C728-C729
THYROID GLAND C739
ADRENALGLANDS C740-C741,C749
PARATHYROIDGLAND C750
PITUITARYGLAND C751
CRANIOPHARYNGEALDUCT C752
PINEAL GLAND C753
ICD-0-3 SEER SITE/HISTOLOGY VALIDATION LIST OTHER ENDOCRINE GLANDS C754-C755,C758-C759
ILL-DEFINED C760-C768
LYMPH NODES C770-C775,C778-C779
UNKNOWN C809
N/A 900
https://seer.cancer.gov/icd-o-3/sitetype.icdo3.20210607.pdf#search=plasma%20cell
above. Right Thurr chingy
09-08-2021-1008 - 1. Gas phase (tissue cell expansion by gas collection; nitrogen, voc, protein, virus) 2. fibroti scar inflammation post granulocyte infiltration 3. seppage and holleing with voc agglomerate (dysplasia proliferative granulomatosis cancotics virus gas induction by voc exposure inflam wound heal fibrotics scar deformation gen mod chrom transl/disl/etc. dna cystu w/ gas nuc rad heavy met etc. biofilm plaque tartar calculus mineralization liquefication)
Wednesday, September 8, 2021
09-08-2021-0937 - Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer.[1] ' This is most often associated with a somatic mutation in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL gene markers. In PMF, the healthy marrow is replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis), '
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer.[1] It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is growth of abnormal cells in the bone marrow. This is most often associated with a somatic mutation in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL gene markers. In PMF, the healthy marrow is replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis), resulting in a lack of production of normal blood cells. Symptoms include anemia, increased infection and an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly).
In 2016, prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis was formally classified as a distinct condition that progresses to overt PMF in many patients, the primary diagnostic difference being the grade of fibrosis.[2]
| Primary myelofibrosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | PMF, Overt PMF, Myelofibrosis |
| Specialty | Oncology and Hematology |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primary_myelofibrosis

| Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C), right ventricular dysplasia |
 | |
| Typical micro-histologic features of ARVC/D. Ongoing myocyte death (upper) with early fibrosis and adipocyte infiltration (lower). | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
09-08-2021-0953 - tumor or dysplasia agglomeration or proliferation small capillary tumor/deformity and blood vessel tumor/deformity - NLAB
tumor or dysplasia agglomeration or proliferation
small capillary tumor and blood vessel tumor/deformity
small cell tumor
biofilm tumor
myx xy yxo
Last gen dis, met dis conde, immunosuppr, leukemia/cancer (dysplasia proliferative granulation dysfunction degen etc. matricing widening
cell proliferation metastatic dysplasia adeno
STD CL1 Syphalli, not agranulolytic. granulation disseminative granulation/granulomatoseous (Granulomatosis ) inflammation dna cystulation cystular fibrotics fibromatotics fibrotics sarcotikxs, etc..
Anticipation to CVD,
Granuloma Annulare Lupus erythematosus systemic Lyme Disease Autoimmune Disease
Blood vessel tumor, disseminated vascular lining tumor, shear/frictionated interspace




| Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C), right ventricular dysplasia |
 | |
| Typical micro-histologic features of ARVC/D. Ongoing myocyte death (upper) with early fibrosis and adipocyte infiltration (lower). | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
09-08-2021-0949 - Segmental arterial mediolysis (SAM)
Segmental arterial mediolysis (SAM) is a rare disorder of the arteries characterized by the development of aneurysms, blood clots, narrowing of the arteries (stenoses), and blood collections (hematomas) in the affected distribution.[1][2]
SAM most commonly affects the arteries supplying the intestines and abdominal organs.[citation needed]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Segmental_arterial_mediolysis
Above.
Ricky Martin - Livin' La Vida Loca (Lyrics)
09-08-2021-0948 - Laparotomy for visceral ischemia and gangrene
. 2007 Oct;73(10):1006-8.
Laparotomy for visceral ischemia and gangrene
Karen Woo 1, Kevin Major, Som Kohanzadeh, Alexander D Allins
Affiliations expand
PMID: 17983069
09-08-2021-0947 - Lipofibromatosis-like neural tumor (LPF-NT) lipo fibro matosis fibromatosis fibrosis cancer tumor lipoma
Lipofibromatosis-like neural tumor (LPF-NT) is an extremely rare soft tissue tumor first described by Agaram et al in 2016.[1] As of mid-2021, at least 39 cases of LPF-NT have been reported in the literature.[2][3][4][5] LPF-NT tumors have several features that resemble lipofibromatosis (LPF) tumors,[6] malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors, spindle cell sarcomas,[3] low-grade neural tumors, peripheral nerve sheath tumors, and other less clearly defined tumors;[1] Prior to the Agaram at al report, LPF-NTs were likely diagnosed as variants or atypical forms of these tumors. The analyses of Agaram at al and subsequent studies[4] uncovered critical differences between LPF-NT and the other tumor forms which suggest that it is a distinct tumor entity differing not only from lipofibromatosis but also the other tumor forms.[7]
LPF-NTs are locally invasive, are commonly treated by surgical excision, and have a relatively high rate of local recurrence if their surgical excisions are incomplete.[8] They are generally considered to be benign, non-metastasizing(i.e. not spreading to other parts of the body) tumors.[6][8] However, one case of LFT-NT reported by Agaram et al was associated with metastasis, apparently as a result of the tumor's cells transformation into a malignant sarcoma. Further studies are needed to determine the frequency of such cases and the overall metastatic potential of LPF-NT.[1]
LPF-NTs were given the "neural tumor" terminology because in at least some cases: 1) their tumor cells express S100 and CD34 but not SOX10 proteins, a pattern that is often found in neural[7] and neuroectodermal tumor cells;[1] and 2) their histopathology consists of tumor cell infiltrations into adipose tissues in a pattern that is very similar to that found in some low grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.[1]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipofibromatosis-like_neural_tumor
Above. M.I.A. - Paper Planes
09-08-2021-0945 - Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory disease of the blood vessels that causes abnormal growth within the wall of an artery.[1] FMD has been found in nearly every arterial bed in the body although the most common arteries affected are the renal and carotid arteries.[1][2][3]
There are various types of FMD, with multi-focal fibroplasia being the most common. Further, less common, forms of the disease include focal (previously known as intimal) and adventitial fibroplasia.[1][2][3][4] FMD predominantly affects middle-aged women, but has been found in men and people of all ages.[1] Pediatric cases of FMD are vastly different from that of the adult population, and poorly studied. The prevalence of FMD is not known and, although the disease was initially thought to be rare, some studies have suggested that it may be underdiagnosed.[5]
| Fibromuscular dysplasia | |
|---|---|
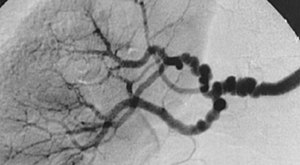 | |
| The "string-of-beads" feature in multi-focal fibromuscular dysplasia. The sign is caused by areas of relative stenoses alternating with small aneurysms. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibromuscular_dysplasia
above. Maneater Nelly Furtado
09-08-2021-0942 - Acute myeloid leukemia with mutated RUNX1
Acute myeloid leukemia with mutated RUNX1
Michael Jackson - Billie Jean (Official Video)
09-08-2021-0939 - Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH or sometimes EH) hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone (bone marrow).[2] It can be physiologic or pathologic.
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH or sometimes EH[1]) refers to hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone (bone marrow).[2] It can be physiologic or pathologic.
Physiologic EMH occurs during embryonic and fetal development; during this time the main site of fetal hematopoiesis are liver and the spleen.
Pathologic EMH can occur during adulthood when physiologic hematopoiesis can't work properly in the bone marrow and the hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) have to migrate to other tissues in order to continue with the formation of blood cellular components. Pathologic EMH can be caused by myelofibrosis,[3] thalassemias or disorders caused in the hematopoietic system.
Physiologic EMH[edit]
During fetal development, hematopoiesis occurs mainly in the fetal liver and in the spleen followed by localization to the bone marrow.[4] Hematopoiesis also takes place in many other tissues or organs such as the yolk sac, the aorta-gonad mesonephros (AGM) region, the spleen, and lymph nodes. During development, vertebrates go through a primitive and a definitive phase of hematopoiesis. The lungs also play a role in platelet production in adults.[5]
Primitive hematopoiesis[edit]
Primitive hematopoiesis occurs in the yolk sac during early embryonic development. It is characterized by the production of erythroid progenitors or nucleated erythrocytes, also known as erythroblasts or megaloblasts. The main objective of the production of these cells will be the facilitation of tissue oxygenation to support rapid embryonic growth. This primitive phase is transitory and the cells that are produced express embryonic globins, aren't pluripotent, and aren't capable of self-renewal.
Definitive hematopoiesis[edit]
Definitive hematopoiesis differs from the primitive phase through the production of hematopoietic stem cells. The formation of these cells occurs in the AGM later in development. Later, they migrate to the fetal liver where the majority of physiologic EMH takes place. Finally, once the bone marrow has developed, they migrate there. They can also migrate to the spleen and lymph nodes where hematopoiesis can occur, but to a lesser degree.
Pulmonary hematopoiesis[edit]
Pulmonary hematopoiesis also appears to play an important role in adults.[5] In comparison to the bone marrow, where trilineage hematopoiesis occurs, the lungs preferentially contribute to the production of platelets through a resident population of megakaryocytes. This is supported by studies showing that blood leaving the lungs has more platelets and fewer progenitor cells than blood entering the lungs. It has been seen that in cases of severe thrombocytopenia, pulmonary megakaryocytes migrate out of lungs into the bone marrow, where they help to replenish the depleted bone marrow population.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extramedullary_hematopoiesis
above.
Ginuwine - Pony
09-08-2021-0938 - Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs)
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of rare blood cancers in which excess red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets are produced in the bone marrow. Myelo refers to the bone marrow, proliferativedescribes the rapid growth of blood cells and neoplasm describes that growth as abnormal and uncontrolled.
The overproduction of blood cells is often associated with a somatic mutation, for example in the JAK2, CALR, TET2, and MPL gene markers.
In rare cases, some MPNs such as primary myelofibrosis may accelerate and turn into acute myeloid leukemia.[1]
| Myeloproliferative neoplasm | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Myeloproliferative diseases (MPDs) |
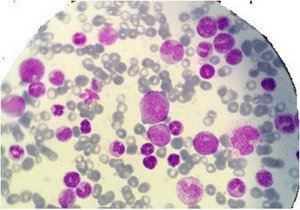 | |
| Myelogram of someone with a myeloproliferative disorder. | |
| Specialty | Hematology and oncology |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myeloproliferative_neoplasm
above.

