
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium 3-[(4-anilinophenyl)diazenyl]benzenesulfonate
| |
| Other names
Acid Yellow 36; Acid Metanil Yellow; Monoazo
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.736 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| C18H15N3NaO3S | |
| Molar mass | 376.39 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | > 250 °C[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Metanil Yellow (Acid Yellow 36) is a dye of the azo class. In analytical chemistry, it is used as a pH indicator and it has a color change from red to yellow between pH 1.2 and 3.2.[1]
Although it is an unpermitted food dye, because of its bright yellow color, Metanil Yellow has been used as an adulterant in turmeric powder and arhar dal, particularly in India.[2][3][4][5]
Animal studies have suggested that Metanil Yellow is neurotoxic[3] and hepatotoxic.[6]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metanil_Yellow
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
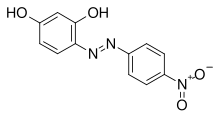
| IUPAC name
4-[(E)-(4-Nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzene-1,3-diol
| |
| Other names
(E)-4-[(4-Nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzene-1,3-diol
4-(4-Nitrophenyl)azobenzene-1,3-diol Magneson I p-Nitrophenylazoresorcinol 4-Nitrophenylazoresorcinol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.735 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H9N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 259.318 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark red to brown crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.45 g/cm3 |
| 1 g/L H2O; 4 g/L Ethanol | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 261.7 °C (503.1 °F; 534.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Azo violet (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 11.0 |
|
above pH 13.0 |
| 11.0 | ⇌ | 13.0 |
Azo violet (Magneson I;[1] p-nitrobenzeneazoresorcinol) is an azo compound with the chemical formula C12H9N3O4. It is used commercially as a violet dye and experimentally as a pH indicator, appearing yellow below pH 11, and violet above pH 13.[2] It also turns deep blue in the presence of magnesium salt in a slightly alkaline, or basic, environment.[3][4] Azo violet may also be used to test for the presence of ammonium ions[citation needed]. The color of ammonium chloride or ammonium hydroxide solution will vary depending upon the concentration of azo violet used. Magneson I is used to test Be also; it produces an orange-red lake with Be(II) in alkaline medium.[5]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Azo_violet
No comments:
Post a Comment