Transverse myelitis (TM) is a rare neurological condition in which the spinal cord is inflamed. Transverse implies that the inflammation extends horizontally across the spinal cord.[1] Partial transverse myelitis and partial myelitis are terms sometimes used to specify inflammation that only affects part of the width of the spinal cord.[1] TM is characterized by weakness and numbness of the limbs, deficits in sensation and motor skills, dysfunctional urethral and anal sphincter activities, and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system that can lead to episodes of high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms vary according to the affected level of the spinal cord. The underlying cause of TM is unknown. The spinal cord inflammation seen in TM has been associated with various infections, immune system disorders, or damage to nerve fibres, by loss of myelin.[1] As opposed to leukomyelitis which affects only the white matter, it affects the entire cross-section of the spinal cord.[3] Decreased electrical conductivity in the nervous system can result.[citation needed]
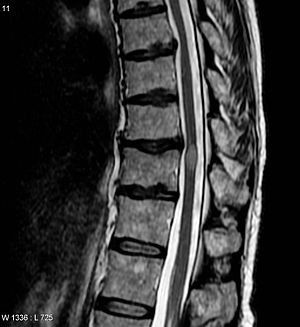 | |
| An MRI showing a transverse myelitis lesion, which is lighter, oval shape at center-right. The patient recovered 3 months later. |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transverse_myelitis
No comments:
Post a Comment