Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Perissodactyla (/pəˌrɪsoʊˈdæktɪlə/, from Ancient Greek περισσός, perissós 'odd', and δάκτυλος, dáktylos 'finger, toe'[3]), are animals—ungulates—who have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three (rhinoceroses and tapirs, with tapirs still using four toes on the front legs) or one (equines, third toe) of the five original toes. The non-weight-bearing toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, the even-toed ungulates bear most of their weight equally on four or two (an even number) of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that odd-toed ungulates digest plant cellulose in their intestines rather than in one or more stomach chambers as even-toed ungulates, with the exception of Suina, do.
The order includes about 17 species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs).
Despite their very different appearances, they were recognized as related families in the 19th century by the zoologist Richard Owen, who also coined the order name.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Odd-toed_ungulate
| Eohippus Temporal range: Ypresian,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Reconstructed skeleton, National Museum of Natural History, Washington, DC, United States | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Perissodactyla |
| Family: | Equidae |
| Genus: | †Eohippus Marsh, 1876 |
| Species: | †E. angustidens
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Eohippus angustidens (Cope, 1875)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eohippus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mesohippus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protohippus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acritohippus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archaeohippus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dinohippus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circulatory_system_of_the_horse
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monocular_vision
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chestnut_(horse_anatomy)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hinny
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genomic_imprinting
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uniparental_disomy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trisomic_rescue
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isodisomy
Uniparental disomy (UPD) occurs when a person receives two copies of a chromosome, or of part of a chromosome, from one parent and no copy from the other parent.[1] UPD can be the result of heterodisomy, in which a pair of non-identical chromosomes are inherited from one parent (an earlier stage meiosis I error) or isodisomy, in which a single chromosome from one parent is duplicated (a later stage meiosis II error).[2] Uniparental disomy may have clinical relevance for several reasons. For example, either isodisomy or heterodisomy can disrupt parent-specific genomic imprinting, resulting in imprinting disorders. Additionally, isodisomy leads to large blocks of homozygosity, which may lead to the uncovering of recessive genes, a similar phenomenon seen in inbred children of consanguineous partners.[3]
UPD has been found to occur in about 1 in 2,000 births.[4]
Pathophysiology
UPD can occur as a random event during the formation of egg cells or sperm cells or may happen in early fetal development. It can also occur during trisomic rescue.
- When the child receives two (different) homologous chromosomes (inherited from both grandparents) from one parent, this is called heterodisomic UPD. Heterodisomy (heterozygous) indicates a meiosis I error if the gene loci in question didn't cross over.[5]
- When the child receives two (identical) replica copies of a single homologue of a chromosome, this is called an isodisomic UPD. Isodisomy (homozygous) indicates either a meiosis II (if the gene loci in question didn't cross over[5]) or postzygotic chromosomal duplication.
- A meiosis I error can result in isodisomic UPD if the gene loci in question crossed over, for example, a distal isodisomy would be due to duplicated gene loci from the maternal grandmother that crossed over and due to an error during meiosis I, ended up in the same gamete.[5]
- A meiosis II error can result in heterodisomy UPD if the gene loci crossed over in a similar fashion.[5]
Phenotype
Most occurrences of UPD result in no phenotypical anomalies. However, if the UPD-causing event happened during meiosis II, the genotype may include identical copies of the uniparental chromosome (isodisomy), leading to the manifestation of rare recessive disorders. UPD should be suspected in an individual manifesting a recessive disorder where only one parent is a carrier.
Uniparental inheritance of imprinted genes can also result in phenotypical anomalies. Although few imprinted genes have been identified, uniparental inheritance of an imprinted gene can result in the loss of gene function, which can lead to delayed development, intellectual disability, or other medical problems.[citation needed]
- The most well-known conditions include Prader–Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome. Both of these disorders can be caused by UPD or other errors in imprinting involving genes on the long arm of chromosome 15.[6]
- Other conditions, such as Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome, are associated with abnormalities of imprinted genes on the short arm of chromosome 11.
- Chromosome 14 is also known to cause particular symptoms such as skeletal abnormalities, intellectual disability, and joint contractures, among others.[7][8]
UPD has rarely been studied prospectively, with most reports focusing on either known conditions or incidental findings. It has been proposed that the incidence may not be as low as believed, rather it may be under-reported.[9]
All chromosomes
Genome wide UPD, also called uniparental diploidy, is when all chromosomes are inherited from one parent. Only in mosaic form can this phenomenon be compatible with life. As of 2017, there have only been 18 reported cases of genome wide UPD.[10]
History
The first clinical case of UPD was reported in 1988 and involved a girl with cystic fibrosis and short stature who carried two copies of maternal chromosome 7.[11] Since 1991, out of the 47 possible disomies, 29 have been identified among individuals ascertained for medical reasons. This includes chromosomes 2, 5–11, 13–16, 21 and 22.
See also
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uniparental_disomy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome_14
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ACIN1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FSCB
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monosomy_14
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nonsyndromic_deafness
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome
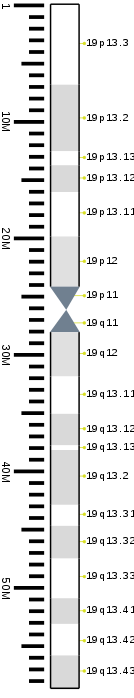
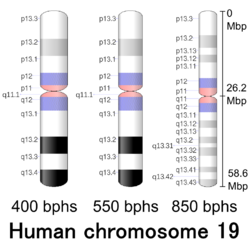
| Chromosome 19 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 19 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 19 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 61,707,364 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 1,357 (CCDS)[1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Metacentric[2] (26.2 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 19 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 19 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 19 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 19 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000019 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000681 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 61.7 million base pairs, the building material of DNA. It is considered the most gene-rich chromosome containing roughly 1,500 genes, despite accounting for only 2 percent of the human genome.[4][5]
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 19. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation, their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[6]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 1,357 | — | — | [1] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 1,372 | 299 | 413 | [7] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 1,469 | 894 | 514 | [8] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 1,435 | — | — | [9] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 1,430 | 604 | 528 | [10][11][12] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 19. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
- A1BG: encoding protein Alpha-1-B glycoprotein
- AAVS1, viral integration site
- ACSBG2: encoding enzyme Long-chain-fatty-acid—CoA ligase
- ANKRD24: encoding protein Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 24
- ARMC6: encoding protein Armadillo repeat-containing protein 6
- ATG4D: encoding protein Autophagy related 4D, cysteine peptidase
- ATP5SL: encoding protein ATP synthase subunit s-like protein
- ATPase ASNA1: encoding enzyme ATPase ASNA1 also known as arsenical pump-driving ATPase and arsenite-stimulated ATPase
- BTBD14B: encoding protein Nucleus accumbens-associated protein 1
- C19orf18: encoding protein Chromosome 19 open reading frame 18
- C19orf44: encoding protein Chromosome 19 open reading frame 44
- C19orf70: encoding protein Chromosome 19 open reading frame 70
- CACTIN: encoding protein Cactin
- CCDC130: encoding protein Coiled-coil domain containing 130
- CCDC151: encoding protein Coiled-coil domain containing 151
- CCDC8: encoding protein Coiled-coil domain containing 8
- CCDC94: encoding protein Coiled-coil domain containing 94 (CCDC94),
- CXB3S: encoding protein Coxsackie virus B3 sensitivity
- DHX34: encoding protein Dexh-box helicase 34
- DNASE2: encoding protein Deoxyribonuclease II, lysosomal
- DPF1: encoding protein D4, zinc and double PHD fingers family 1
- EID2:
- ETV2: encoding protein Ets variant 2
- FIZ1: encoding protein FLT3 interacting zinc finger 1
- HCST: encoding protein Hematopoietic cell signal transducer
- HRC: encoding protein Sarcoplasmic reticulum histidine-rich calcium-binding protein
- IFI30: encoding enzyme Gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase
- IGFL3: encoding protein IGF like family member 3
- KRTDAP: encoding protein Keratinocyte differentiation-associated protein
- LENG9: encoding protein Leukocyte Receptor Cluster Member 9 (LENG 9)
- LIM2: encoding protein Lens fiber membrane intrinsic protein
- LRG1: encoding protein Leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1
- LRRC25: encoding protein Leucine rich repeat containing 25
- LSM4: encoding protein U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm4
- LSR: encoding protein Lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor
- LYPD5: encoding protein LY6/PLAUR domain containing 5
- MBOAT7: encoding enzyme Lysophospholipid acyltransferase 7
- MOBKL2A: encoding enzyme Mps one binder kinase activator-like 2A
- MZF1-AS1: encoding protein MZF1 antisense RNA 1
- NCLN: encoding protein Nicalin
- NFKBID: encoding protein Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor
- NOSIP: encoding enzyme Nitric oxide synthase-interacting protein
- NWD1: NACHT and WD repeat domain containing 1.
- OLFM2: encoding protein Olfactomedin 2
- OSCAR: encoding protein Osteoclast-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor
- PALM: encoding protein Paralemmin
- PDCD5: encoding protein Programmed cell death protein 5
- PEX11G: peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11 gamma
- PGK1P2: encoding Phosphoglycerate kinase 1, pseudogene 2 protein
- PLIN4: encoding protein Perilipin 4
- PLVAP: encoding protein Plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein
- PRR12: encoding protein Proline-rich 12
- PRR36 (Proline Rich Region 36) encoding protein PRP36 (Proline Rich Protein 36)
- KLK3: The Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
- PRX: Periaxin
- PTOV1: encoding protein Prostate tumor overexpressed gene 1 protein
- RFPL4A: encoding protein Ret finger protein like 4a
- SBNO2: encoding protein Strawberry notch homolog 2 (Drosophila)
- SEPW1: encoding protein Selenoprotein W
- SFRS14: encoding protein Putative splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 14
- SFRS16: encoding protein Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 16
- SLC5A5: Solute carrier family 5 (sodium iodide symporter), member 5
- STK11: Serine/threonine kinase 11 (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome)
- TBCB: encoding protein Tubulin-folding cofactor B
- TECR: encoding enzyme Trans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase
- THOP1: encoding enzyme Thimet oligopeptidase
- TIMM50: encoding enzyme Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM50
- TIP39: encoding protein Tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues
- TMED1: encoding protein Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 1
- TMEM160: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 160
- TMEM205: encoding protein Transmembrane Protein 205
- UBXN6: encoding protein UBX domain protein 6
- UCA1: a long non-coding RNA Urothelial cancer associated 1
- UPK1A: encoding protein Uroplakin-1a
- USE1: encoding protein Uncharacterized hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells protein MDS032
- ZFP82: encoding protein ZFP82 zinc finger protein
- ZSCAN4: Zinc finger and scan domain containing 4
- ZSCAN18: encoding protein Zinc finger and SCAN domain containing 18
- ZNF112: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 112
- ZNF134: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 134
- ZNF160: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 160
- ZNF180: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 180
- ZNF208: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 208
- ZNF224: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 224
- ZNF225: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 225
- ZNF226: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 226
- ZNF229: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 229
- ZNF257: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 257
- ZNF264: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 264
- ZNF266: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 266
- ZNF274: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 274
- ZNF320: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 320
- ZNF331: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 331
- ZNF347: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 347
- ZNF426: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 426
- ZNF444: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 444
- ZNF665 encoding protein Zinc finger protein 665
- ZNF473: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 473
- ZNF506: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 506
- ZNF507: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 507
- ZNF536: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 536
- ZNF541: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 541
- ZNF557: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 557
- ZNF571: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 571
- ZNF576: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 576
- Zinc finger protein 613: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 613
- ZNF649: Transcriptional suppressor
- ZNF71: encoding protein Endothelial zinc finger protein induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha
- ZNF737: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 737
- ZNF749: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 749
- ZNF676: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 676
- ZNF772: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 772
- ZNF784: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 784
- ZNF8: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 8
- ZNF83: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 83
- ZNF878: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 878
- ZNF880: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 880
Short arm
- CACNA1A: Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit (Familial hemiplegic migraine Type I). Gene map locus 19p13
- COMP: Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. Gene map locus 19p13.1
- NOTCH3: Notch homolog 3 (Drosophila): Gene map locus 19p13.1-p13.2
- GCDH: Glutaryl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase. Gene map locus 19p13.2
- ZNF121: Zinc finger protein 121. Gene map locus 19p13.2
- BSG: Basigin (Ok blood group)/Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147. Gene map locus 19p13.3
- ICAM4: Landsteiner and Weiner glycoprotein. Gene map locus 19p13.3
- NRTN: Neurturin, associated with Hirschsprung's disease: Gene locus map 19p13.3
- GTPBP3: GTP binding protein 3 19p13.11
- KLF2: Krüppel-like factor 2, also known as Lung Krüppel-like factor. Gene map locus 19p13.11 OMIM: 602016
- FAM32A: family with sequence similarity 32 member A 19q13.11
- DDX39: DExD-box helicase 39. Gene map locus 19p13.12
Long arm
- GAPDHS: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, spermatogenic 19q13.12
- HAMP: Hepcidin antimicrobial peptide. Gene map locus 19q13.12
- BCKDHA: Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, alpha polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease). Gene map location 19q13.1-q13.2
- APOE: Apolipoprotein E, gene associated with Alzheimer's disease. Gene map locus 19q13.2
- CIC: Capicua transcriptional repressor. Gene map locus 19q13.2
- FCGBP: Fc fragment of IgG binding protein
- SARS2: seryl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial. Gene map locus 19q13.2
- ATP1A3: ATPase. Gene map locus 19q13.31
- DMWD: DM1 locus, WD repeat containing. Gene map locus 19q13.32
- PNMA8A: paraneoplastic Ma antigen family member 8A 19q13.32
- DMPK: Dystrophia myotonica-protein kinase. Gene map locus 19q13.32
- GLTSCR2: Glioma tumor suppressor candidate region gene 2 protein 19q13.33
- A1BG: Plasma glycoprotein, unknown function. Gene map locus 19q13.43
- LRC: The Leukocyte Receptor Complex is a family of immunoreceptors expressed predominantly on monocytes and B cells and at lower levels on dendritic cells and natural killer (NK) cells. The LRC also includes the KIR locus. Gene map locus 19q13.4 OMIM: 604812
- KPTN: Kaptin (actin binding protein) at the tips of stereocilia. Gene map locus 19q13.4[13]
- FUT1: The H locus is located on chromosome 19 at 19q13.3. It contains three exons that span more than 5 kb of genomic DNA, and it encodes a fucosyltransferase that produces the H antigen on RBCs.[14]
- FUT2: The Se locus is located on chromosome 19 at 19q13.3. It contains two exons that span about 25 kb of genomic DNA. The Se locus encodes a specific fucosyltransferase that is expressed in the epithelia of secretory tissues, such as salivary glands, the gastrointestinal tract, and the respiratory tract. The enzyme it encodes catalyzes the production of H antigen.[14]
- MORT (Mortal Obligate RNA Transcript, lincRNA): Gene map locus 19q13.43
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are some of those related to genes on chromosome 19:[15]
- Alternating hemiplegia of childhood
- Alzheimer's disease
- CADASIL
- Centronuclear myopathy autosomal dominant form
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
- Congenital hearing loss
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Donohue syndrome
- Familial hemiplegic migraine
- Glutaric acidemia type 1
- Hemochromatosis
- HUPRA syndrome[16]
- Leber congenital amaurosis[17]
- Maple syrup urine disease
- Marfan syndrome
- Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Myotubular myopathy autosomal dominant form
- Oligodendroglioma
- Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
- Prolidase deficiency
- Pseudoachondroplasia
- Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia or Bruton's disease
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[23] | Band[24] | ISCN start[25] |
ISCN stop[25] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[26] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | p | 13.3 | 0 | 578 | 1 | 6,900,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | p | 13.2 | 578 | 870 | 6,900,001 | 12,600,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 19 | p | 13.13 | 870 | 1034 | 12,600,001 | 13,800,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | p | 13.12 | 1034 | 1216 | 13,800,001 | 16,100,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 19 | p | 13.11 | 1216 | 1581 | 16,100,001 | 19,900,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | p | 12 | 1581 | 1809 | 19,900,001 | 24,200,000 | gvar |
|
| 19 | p | 11 | 1809 | 1992 | 24,200,001 | 26,200,000 | acen |
|
| 19 | q | 11 | 1992 | 2159 | 26,200,001 | 28,100,000 | acen |
|
| 19 | q | 12 | 2159 | 2372 | 28,100,001 | 31,900,000 | gvar |
|
| 19 | q | 13.11 | 2372 | 2569 | 31,900,001 | 35,100,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | q | 13.12 | 2569 | 2737 | 35,100,001 | 37,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 19 | q | 13.13 | 2737 | 2949 | 37,800,001 | 38,200,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | q | 13.2 | 2949 | 3101 | 38,200,001 | 42,900,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 19 | q | 13.31 | 3101 | 3193 | 42,900,001 | 44,700,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | q | 13.32 | 3193 | 3390 | 44,700,001 | 47,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 19 | q | 13.33 | 3390 | 3649 | 47,500,001 | 50,900,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | q | 13.41 | 3649 | 3770 | 50,900,001 | 53,100,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 19 | q | 13.42 | 3770 | 3938 | 53,100,001 | 55,800,000 | gneg |
|
| 19 | q | 13.43 | 3938 | 4120 | 55,800,001 | 58,617,616 | gpos | 25 |
References
- gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Grimwood J, Gordon LA, Olsen A, Terry A, Schmutz J, Lamerdin J, Hellsten U, Goodstein D, Couronne O, Tran-Gyamfi M, Aerts A, Altherr M, Ashworth L, Bajorek E, Black S, Branscomb E, Caenepeel S, Carrano A, Caoile C, Chan YM, Christensen M, Cleland CA, Copeland A, Dalin E, Dehal P, Denys M, Detter JC, Escobar J, Flowers D, Fotopulos D, Garcia C, Georgescu AM, Glavina T, Gomez M, Gonzales E, Groza M, Hammon N, Hawkins T, Haydu L, Ho I, Huang W, Israni S, Jett J, Kadner K, Kimball H, Kobayashi A, Larionov V, Leem SH, Lopez F, Lou Y, Lowry S, Malfatti S, Martinez D, McCready P, Medina C, Morgan J, Nelson K, Nolan M, Ovcharenko I, Pitluck S, Pollard M, Popkie AP, Predki P, Quan G, Ramirez L, Rash S, Retterer J, Rodriguez A, Rogers S, Salamov A, Salazar A, She X, Smith D, Slezak T, Solovyev V, Thayer N, Tice H, Tsai M, Ustaszewska A, Vo N, Wagner M, Wheeler J, Wu K, Xie G, Yang J, Dubchak I, Furey TS, DeJong P, Dickson M, Gordon D, Eichler EE, Pennacchio LA, Richardson P, Stubbs L, Rokhsar DS, Myers RM, Rubin EM, Lucas SM (2004). "The DNA sequence and biology of human chromosome 19". Nature. 428 (6982): 529–35. Bibcode:2004Natur.428..529G. doi:10.1038/nature02399. PMID 15057824.
- Human Proteome Project Launch website~ https://web.archive.org/web/20110726163128/http://www.hupo.org/research/hpp/HPP_legrain_sep_2010.pdf
External links
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 19". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on August 3, 2004. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 19". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome_19
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 10. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[4]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 706 | — | — | [1] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 708 | 244 | 614 | [5] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 728 | 881 | 568 | [6] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 750 | — | — | [7] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 754 | 842 | 654 | [8][9][10] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 10. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
- AFAP1L2: actin filament associated protein 1 like 2
- ALL1 encoding protein Leukemia, acute lymphocytic, susceptibility to, 1
- ALOX5: Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase (processes essential fatty acids to leukotrienes, which are important agents in the inflammatory response; also facilitates development and maintenance of cancer stem cells, slow-dividing cells thought to give rise to a variety of cancers, including leukemia)
- ANKRD22: encoding protein Ankyrin repeat domain 22
- ARHGAP21: rho GTPase activating protein 21
- ARID5B: encoding protein AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5B
- ARMH3: Armadillo Like Helical Domain Containing 3
- AS3MT: encoding enzyme Arsenite methyltransferase
- AVPI1: encoding protein Arginine vasopressin-induced protein 1
- C10orf67: chromosome 10 open reading frame 67
- C10orf99: encoding protein Chromosome 10 open reading frame 99
- CAMK1D: calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID
- CCAR1: Cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator 1
- CCDC3: Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 3
- CCDC186: encoding protein CCDC186
- CCNY: Cyclin-Y
- CDC123: Cell division cycle protein 123 homolog
- CDH23: cadherin-like 23
- CDNF: cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor
- CEFIP: encoding protein Cardiac-enriched FHL2-interacting protein
- COMMD3-BMI1: COMMD3-BMI1 readthrough
- CPXM2: encoding protein Carboxypeptidase x, m14 family member 2
- CUTC: Copper homeostasis protein cutC homolog
- CXCL12: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12, SDF-1, scyb12
- DDX50: DExD-box helicase 50
- DEPP: decidual protein induced by progesterone
- DHX32: DEAH-box helicase 32
- DIP2C: encoding protein Disco interacting protein 2 homolog c
- DKK1: Dickkopf-related protein 1
- DNAJC12: DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily c, member 12
- DNAJC9: DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily c, member 9
- DPYSL4: Dihydropyrimidinase-related protein 4
- EBLN1: encoding protein Endogenous Bornavirus-like nucleoprotein 1
- ECD: ecdysoneless cell cycle regulator
- EGR2: early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila)
- EIF5AP1: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-like 1
- EPC1: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1
- ERCC6: excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6
- FAM107B: family with sequence similarity 107, member B
- FAM13C: family with sequence similarity 13, member C
- FAM170B: encoding protein Family with sequence similarity 170 member B
- FAM188A: family with sequence similarity 188, member A
- FAM208b: encoding protein FAM208b
- FAM213A: family with sequence similarity 213, member A
- FAM25BP encoding protein Protein FAM25
- FAS-AS1, long non-coding RNA
- FBXL15: encoding protein F-box and leucine rich repeat protein 15
- FGFR2: fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (bacteria-expressed kinase, keratinocyte growth factor receptor, craniofacial dysostosis 1, Crouzon syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, Jackson–Weiss syndrome)
- FRA10AC1: Fragile site, folic acid type
- FRAT1: WNT signaling pathway regulator
- FRAT2: WNT signaling pathway regulator
- FRMPD2 encoding protein FERM and PDZ domain containing 2
- GATA3: encoding the GATA3 transcription factor. GATA3 is critical for the embryonic development of the parathyroid gland, neural component of hearing, and kidney. Haploinsufficiency of the gene underlies a rare disorder, the hypoparathyrodism, deafness, and renal dysplasia syndrome
- GHITM: growth hormone-inducible transmembrane protein
- GPRIN2: G protein-regulated inducer of neurite outgrowth 2
- GTPBP4: Nucleolar GTP-binding protein 4
- HELLS: Lymphoid-specific helicase
- HKDC1: hexokinase domain containing 1
- KIN: DNA/RNA-binding protein KIN17
- LHPP: encoding protein Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase
- MTG1: mitochondrial GTPase 1
- NPM3: nucleoplasmin-3
- NRBF2: nuclear receptor-binding factor 2
- NSMCE4A: non-SMC element 4 homolog A
- OTUD1: encoding protein OTU deubiquitinase 1
- PAPSS2: encoding enzyme bifunctional 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate synthase 2
- PCBD1: 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase/dimerization cofactor of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (TCF1)
- PCDH15: protocadherin 15
- PI4K2A: phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2-alpha
- PIP4K2A: phosphatidylinositol 5 phosphate 4-kinase type-2 alpha
- PITRM1: pitrilysin metallopeptidase 1
- PLEKHS1 encoding protein Pleckstrin homology domain containing S1
- PLXDC2: plexin domain-containing protein 2
- PRAP1: encoding protein Proline rich acidic protein 1
- PROSER2: proline and serine rich 2 or c10orf47
- PTEN gene: phosphatase and tensin homolog (mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1)
- RET: ret proto-oncogene (multiple endocrine neoplasia and medullary thyroid carcinoma 1, Hirschsprung disease)
- RPP30: ribonuclease P protein subunit p30
- RRP12: ribosomal RNA processing 12 homolog
- RSU1: ras suppressor protein 1
- RTKN2: encoding protein Rhotekin 2
- SCZD11: encoding protein Schizophrenia susceptibility locus, chromosome 10q-related
- SGPL1: sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1
- SHTN1: encoding protein Shootin 1
- SLC16A12: encoding protein Solute carrier family 16 member 12
- SMNDC1: survival motor neuron domain containing 1
- SPG9 encoding protein Spastic paraplegia 9 (autosomal dominant)
- SRGN: serglycin
- STAMBPL1: STAM binding protein like 1
- STOX1: encoding protein Storkhead box 1
- SUPV3L1: Suv3 like RNA helicase
- SYCE1: encoding protein Synaptonemal complex central element protein 1
- TACC2 encoding protein Transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 2
- TBC1D12: TBC1 domain family, member 12
- TCTN3: tectonic family member 3
- TMEM10: opalin
- TMEM254: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 254
- TMEM26: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 26
- TMEM72: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 72
- TYSND1: encoding protein Trypsin domain containing 1
- UCN3: urocortin-3
- UROS: uroporphyrinogen III synthase (congenital erythropoietic porphyria)
- USMG5: Up-regulated during skeletal muscle growth protein 5
- USP54: encoding protein Ubiquitin specific peptidase 54
- USP6NL: USP6 N-terminal like protein
- UTF1: undifferentiated embryonic cell transcription factor 1
- VIM-AS1: VIM antisense RNA 1
- WASHC2C: WASH complex subunit 2C
- WBP1L: WW domain binding protein 1-like
- ZNF37A: zinc finger protein 37A
- ZNF438: zinc finger protein 438
- ZRANB1: Zinc finger ranbp2-type containing 1
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are related to genes on chromosome 10:
- Apert syndrome
- Barakat syndrome
- Beare–Stevenson cutis gyrata syndrome
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
- Cockayne syndrome
- Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
- Cowden syndrome
- Crouzon syndrome
- Genitopatellar syndrome
- Glioblastoma multiforme
- Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome
- Hirschprung disease
- Jackson–Weiss syndrome
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Pfeiffer syndrome
- Porphyria
- Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Pakistani type
- Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency
- Thiel–Behnke corneal dystrophy
- Usher syndrome
- Wolman syndrome
- Young-Simpson syndrome
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[16] | Band[17] | ISCN start[18] |
ISCN stop[18] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[19] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | p | 15.3 | 0 | 229 | 1 | 3,000,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 15.2 | 229 | 329 | 3,000,001 | 3,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | p | 15.1 | 329 | 630 | 3,800,001 | 6,600,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 14 | 630 | 917 | 6,600,001 | 12,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | p | 13 | 917 | 1175 | 12,200,001 | 17,300,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 12.33 | 1175 | 1361 | 17,300,001 | 18,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | p | 12.32 | 1361 | 1432 | 18,300,001 | 18,400,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 12.31 | 1432 | 1604 | 18,400,001 | 22,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | p | 12.2 | 1604 | 1662 | 22,300,001 | 24,300,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 12.1 | 1662 | 1891 | 24,300,001 | 29,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | p | 11.23 | 1891 | 2063 | 29,300,001 | 31,100,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 11.22 | 2063 | 2235 | 31,100,001 | 34,200,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | p | 11.21 | 2235 | 2406 | 34,200,001 | 38,000,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | p | 11.1 | 2406 | 2621 | 38,000,001 | 39,800,000 | acen |
|
| 10 | q | 11.1 | 2621 | 2850 | 39,800,001 | 41,600,000 | acen |
|
| 10 | q | 11.21 | 2850 | 3051 | 41,600,001 | 45,500,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 11.22 | 3051 | 3252 | 45,500,001 | 48,600,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | q | 11.23 | 3252 | 3409 | 48,600,001 | 51,100,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 21.1 | 3409 | 3753 | 51,100,001 | 59,400,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 21.2 | 3753 | 3839 | 59,400,001 | 62,800,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 21.3 | 3839 | 4097 | 62,800,001 | 68,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 22.1 | 4097 | 4469 | 68,800,001 | 73,100,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 22.2 | 4469 | 4655 | 73,100,001 | 75,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 22.3 | 4655 | 4970 | 75,900,001 | 80,300,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 23.1 | 4970 | 5200 | 80,300,001 | 86,100,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 23.2 | 5200 | 5331 | 86,100,001 | 87,700,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 23.31 | 5331 | 5558 | 87,700,001 | 91,100,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | q | 23.32 | 5558 | 5672 | 91,100,001 | 92,300,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 23.33 | 5672 | 5887 | 92,300,001 | 95,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 24.1 | 5887 | 5973 | 95,300,001 | 97,500,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 24.2 | 5973 | 6131 | 97,500,001 | 100,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 24.31 | 6131 | 6202 | 100,100,001 | 101,200,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 24.32 | 6202 | 6317 | 101,200,001 | 103,100,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | q | 24.33 | 6317 | 6374 | 103,100,001 | 104,000,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 25.1 | 6374 | 6646 | 104,000,001 | 110,100,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 25.2 | 6646 | 6761 | 110,100,001 | 113,100,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 25.3 | 6761 | 6890 | 113,100,001 | 117,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | q | 26.11 | 6890 | 7090 | 117,300,001 | 119,900,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 26.12 | 7090 | 7219 | 119,900,001 | 121,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 26.13 | 7219 | 7506 | 121,400,001 | 125,700,000 | gneg |
|
| 10 | q | 26.2 | 7506 | 7721 | 125,700,001 | 128,800,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 26.3 | 7721 | 8050 | 128,800,001 | 133,797,422 | gneg |
|
References
- gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Deloukas P, Earthrowl ME, Grafham DV, Rubenfield M, French L, Steward CA, Sims SK, Jones MC, Searle S, Scott C, Howe K, Hunt SE, Andrews TD, Gilbert JG, Swarbreck D, Ashurst JL, Taylor A, Battles J, Bird CP, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Ashwell RI, Ambrose KD, Babbage AK, Bagguley CL, Bailey J, Banerjee R, Bates K, Beasley H, Bray-Allen S, Brown AJ, Brown JY, Burford DC, Burrill W, Burton J, Cahill P, Camire D, Carter NP, Chapman JC, Clark SY, Clarke G, Clee CM, Clegg S, Corby N, Coulson A, Dhami P, Dutta I, Dunn M, Faulkner L, Frankish A, Frankland JA, Garner P, Garnett J, Gribble S, Griffiths C, Grocock R, Gustafson E, Hammond S, Harley JL, Hart E, Heath PD, Ho TP, Hopkins B, Horne J, Howden PJ, Huckle E, Hynds C, Johnson C, Johnson D, Kana A, Kay M, Kimberley AM, Kershaw JK, Kokkinaki M, Laird GK, Lawlor S, Lee HM, Leongamornlert DA, Laird G, Lloyd C, Lloyd DM, Loveland J, Lovell J, McLaren S, McLay KE, McMurray A, Mashreghi-Mohammadi M, Matthews L, Milne S, Nickerson T, Nguyen M, Overton-Larty E, Palmer SA, Pearce AV, Peck AI, Pelan S, Phillimore B, Porter K, Rice CM, Rogosin A, Ross MT, Sarafidou T, Sehra HK, Shownkeen R, Skuce CD, Smith M, Standring L, Sycamore N, Tester J, Thorpe A, Torcasso W, Tracey A, Tromans A, Tsolas J, Wall M, Walsh J, Wang H, Weinstock K, West AP, Willey DL, Whitehead SL, Wilming L, Wray PW, Young L, Chen Y, Lovering RC, Moschonas NK, Siebert R, Fechtel K, Bentley D, Durbin R, Hubbard T, Doucette-Stamm L, Beck S, Smith DR, Rogers J (2004). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 10". Nature. 429 (6990): 375–81. Bibcode:2004Natur.429..375D. doi:10.1038/nature02462. PMID 15164054.
- Deloukas P, French L, Meitinger T, Moschonas NK (2000). "Report of the third international workshop on human chromosome 10 mapping and sequencing 1999". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 90 (1–2): 1–12. doi:10.1159/000015653. PMID 11060438. S2CID 28931509.
- Gilbert F (2001). "Chromosome 10". Genet Test. 5 (1): 69–82. doi:10.1089/109065701750168824. PMID 11336406.
External links
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 10". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 2010-04-08. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 10". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome_10
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome_9
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marfan_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_epiphyseal_dysplasia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centronuclear_myopathy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spinocerebellar_ataxia_type_6
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uniparental_disomy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Platelet-derived_growth_factor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosomal_translocation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resection_margin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_resonance_imaging
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TAR_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uniparental_disomy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dermatofibrosarcoma_protuberans
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trisomy_X
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fragile_X_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acute_megakaryoblastic_leukemia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acute_promyelocytic_leukemia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myxoid_liposarcoma
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolar_rhabdomyosarcoma
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Neurogenetic_disorders
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Syndromes_with_craniofacial_abnormalities
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Rare_syndromes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Syndromes_affecting_the_eye
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Trinucleotide_repeat_disorders
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deaflympics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alien_hand_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisynthetase_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATR-16_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birt%E2%80%93Hogg%E2%80%93Dub%C3%A9_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blue_diaper_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraser_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Felty%27s_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gray_platelet_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greig_cephalopolysyndactyly_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greig_cephalopolysyndactyly_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hereditary_fibrosing_poikiloderma_with_tendon_contractures,_myopathy,_and_pulmonary_fibrosis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunodeficiency_26
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joubert_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperphosphatasia_with_mental_retardation_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jalili_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kaufman_oculocerebrofacial_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keratitis%E2%80%93ichthyosis%E2%80%93deafness_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KBG_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/13q_deletion_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_novo_mutation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syndactyly-nystagmus_syndrome_due_to_2q31.1_microduplication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beare%E2%80%93Stevenson_cutis_gyrata_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carpenter_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CLOVES_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/COACH_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marshall_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L1_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IVIC_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graham%E2%80%93Boyle%E2%80%93Troxell_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibular_aplasia-ectrodactyly_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microcephaly_albinism_digital_anomalies_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skin_fragility-woolly_hair-palmoplantar_keratoderma_syndrome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syndactyly-nystagmus_syndrome_due_to_2q31.1_microduplication
| Syndactyly-nystagmus syndrome due to 2q31.1 duplication | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2q31.1 microduplication syndrome |
 | |
| The microduplication associated with this condition is autosomal dominant | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Mainly syndactyly and congenital bilateral pendular nystagmus |
| Complications | none |
| Usual onset | birth |
| Duration | lifelong (unless surgically corrected) |
| Causes | genetic mutation (more specifically an autosomal dominant chromosomal microduplication containing HOX genes) |
| Prevention | none |
| Prognosis | good |
| Frequency | rare |
| Deaths | - |
Syndactyly-nystagmus syndrome due to 2q31.1 microduplication, also known as 2q31.1 microduplication syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder characterized by syndactyly affecting the third-fourth fingers and bilateral congenital nystagmus.[1]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syndactyly-nystagmus_syndrome_due_to_2q31.1_microduplication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triphalangeal_thumb
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome_2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_duplication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homeobox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Switzerland
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilateria
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antiparallel_(biochemistry)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homeobox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lambda_phage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiogenesis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_duplication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unequal_crossing-over
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_conversion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concerted_evolution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudoautosomal_region
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudogene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_conversion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_duplication
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Modification_of_genetic_information
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacterial_conjugation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fusion_gene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transfection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antigenic_shift
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Macrosatellite
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retroposon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LINE1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P_element
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_amplification
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_cluster
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pathogenicity_island
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low_copy_repeats
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Directional_selection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Negative_selection_(natural_selection)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stabilizing_selection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balancing_selection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synonymous_substitution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silent_mutation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nonsynonymous_substitution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stop_codon#Nonstop
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytotoxicity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stop_codon#Nonstop
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ribosomal_frameshift
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycoplasma_laboratorium#Watermarks
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_use_restriction_technology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome_segregation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synthesis-dependent_strand_annealing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_repair#Double-strand_breaks
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/V(D)J_recombination
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_end_resection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyrimidine_dimer#Mutagenesis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lesion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteolytic_lesion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoporosis_circumscripta
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghon_focus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionizing_radiation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_repair#Double-strand_breaks
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyrimidine_dimer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATM_serine/threonine_kinase
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transduction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transduction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Repressor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spirochaete
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deinococcus_radiodurans
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie_restriction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_dosage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trichothiodystrophy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ataxia%E2%80%93telangiectasia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progeroid_syndromes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_repair-deficiency_disorder
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Missense_mutation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:DNA_damage,_repair,_alteration_of_repair_in_cancer.png
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_repair#translesion_synthesis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacteriophage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Structural_motif
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Oxidation_Event
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fossil
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Germline
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_diversity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitotic_catastrophe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schizosaccharomyces_pombe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetically_modified_crops
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genome_instability
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spindle_checkpoint
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anaphase-promoting_complex
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinesin-like_protein_KIF11
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recombinant_DNA
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA_microarray
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cistron
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operon#Operator
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nematode
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Structural_gene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inducer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corepressor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TcoF-DB
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Negative_feedback
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NRIP1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acute_myeloid_leukemia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BCL-6_corepressor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rheumatoid_arthritis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulator_gene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derepression
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attenuator_(genetics)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_code
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_regulatory_network
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gal_operon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internal_control_region
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intrinsic_termination
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neoteny
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heterochrony
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neoteny_in_humans
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fecundity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Northwestern_salamander
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centriole
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microtubule
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flagellum
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gram-negative_bacteria
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotating_locomotion_in_living_systems
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_III_secretion_system
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemiosmosis#Proton-motive_force
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrochemical_gradient
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitochondria
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molecular_diffusion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photophosphorylation
Chemiosmotic phosphorylation is the third pathway that produces ATP from inorganic phosphate and an ADP molecule. This process is part of oxidative phosphorylation.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemiosmosis#Proton-motive_force
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemiosmosis#Proton-motive_force
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ion_channel
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ferredoxin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plastoquinone
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b6f_complex
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plastocyanin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transient_receptor_potential_channel
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inward-rectifier_potassium_channel
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloprotein
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron%E2%80%93sulfur_cluster
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_potential_iron%E2%80%93sulfur_protein
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paracoccus_denitrificans





No comments:
Post a Comment