Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year.[4]
Phthalic anhydride
|
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Benzofuran-1,3-dione[1] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 118515 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.461 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 27200 | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2214 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C8H4O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 148.1 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white flakes | ||
| Odor | characteristic, acrid[2] | ||
| Density | 1.53 g/cm3, solid; 1.20 g/mL, molten[2] | ||
| Melting point | 131.6 °C (268.9 °F; 404.8 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 295 °C (563 °F; 568 K) sublimates | ||
| 0.62 g/100g (20—25 °C); 19.0 g/100g (100 °C); reacts slowly | |||
| Vapor pressure | 0.0015 mmHg (20 °C)[2] | ||
| −67.31×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H302, H315, H317, H318, H334, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P280, P285, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P304+P341, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P342+P311, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 152 °C (306 °F; 425 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 1.7%–10.5% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
4020 mg/kg (oral, rat) 1520 mg/kg (oral, mouse) 800 mg/kg (oral, cat) 800–1600 mg/kg (oral, rat) 2210 mg/kg (oral, mouse)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 12 mg/m3 (2 ppm)[2] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 6 mg/m3 (1 ppm)[2] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
60 mg/m3[2] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Phthalic acid Phthalimide Phthalide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phthalic_anhydride
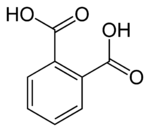
Phthalic acid is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. Although phthalic acid is of modest commercial importance, the closely related derivative phthalic anhydride is a commodity chemical produced on a large scale.[4] Phthalic acid is one of three isomers of benzenedicarboxylic acid, the others being isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid.
Phthalic acid
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
1,2-Benzenedioic acid
Phthalic acid Benzene-1,2-dioic acid ortho-Phthalic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.703 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 166.132 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.593 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K)[3] |
| 0.6 g / 100 mL [1] | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.89, 5.51[2] |
| -83.61·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related carboxylic acids
|
Isophthalic acid Terephthalic acid |
Related compounds
|
Phthalic anhydride Phthalimide Phthalhydrazide Phthaloyl chloride Benzene-1,2- dicarboxaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Reactions and uses
It is a dibasic acid, with pKas of 2.89 and 5.51. The monopotassium salt, potassium hydrogen phthalate is a standard acid in analytical chemistry. Typically phthalate esters are prepared from the widely available phthalic anhydride. Reduction of phthalic acid with sodium amalgam in the presence of water gives the 1,3-cyclohexadiene derivative.[11]
Safety
The toxicity of phthalic acid is moderate with LD50 (mouse) of 550 mg/kg.
Biodegradation
The bacteria Pseudomonas sp. P1 degrades phthalic acid.[12]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phthalic_acid




No comments:
Post a Comment