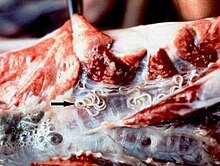
Parasitic bronchitis, also known as hoose, husk, or verminous bronchitis,[1] is a disease of sheep, cattle, goats,[2] and swine caused by the presence of various species of parasite, commonly known as lungworms,[3] in the bronchial tubes or in the lungs. It is marked by cough, dyspnea, anorexia and constipation. Lungworms which cause parasitic bronchitis include nematodes of the genera Dictyocaulus, Metastrongylus, and Protostrongylus.[4] Hoose is essentially an infantile disease, almost always afflicting animals under one year of age.[5]
It can be diagnosed through fecal examination[6] or taking a sputum sample[7] and treated by killing the nematode larvae and adults.[8] In severe cases, additional antibiotics may be needed.[7] The most effective prevention is via vaccination, especially important for cattle.[9]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parasitic_bronchitis
No comments:
Post a Comment