 A glockenspiel made by Malletech | |
| Percussion instrument | |
|---|---|
| Other names |
|
| Classification | Keyboard percussion |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 111.222 (Sets of percussion plaques) |
| Playing range | |
| Related instruments | |
The glockenspiel (/ˈɡlɒkənʃpiːl/ GLO-kən-shpeel; German pronunciation: [ˈɡlɔkənˌʃpiːl] or [ˈɡlɔkŋ̍ˌʃpiːl], Glocken: bells and Spiel: play) or bells is a percussion instrument consisting of pitched aluminum or steel bars arranged in a keyboard layout. This makes the glockenspiel a type of metallophone, similar to the vibraphone.
The glockenspiel is played by striking the bars with mallets, often made of a hard material such as metal or plastic. Its clear, high-pitched tone is often heard in orchestras, wind ensembles, marching bands, and in popular music.
Terminology
In German, a carillon is also called a Glockenspiel, and in French, the glockenspiel is sometimes called a carillon. It may also be called a jeu de timbres (lit. 'set of colors') in French, although this term may sometimes be specifically reserved for the keyboard glockenspiel.[1] In Italian, the term campanelli (lit. 'little bells') is used.[2]
The glockenspiel is sometimes erroneously referred to as a xylophone. (The xylophone has wooden bars, unlike the glockenspiel which has metal bars.)[3] The Pixiphone, a type of toy glockenspiel, was one such instrument sold as a xylophone.
Range
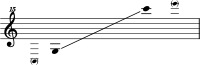
The glockenspiel is limited to the upper register and typically covers between 2+1⁄2 and 3 octaves, though certain professional models may reach up to 3+1⁄2 octaves.[4] The glockenspiel is often a transposing instrument and sounds two octaves above the written pitch, though this is sometimes remedied by using an octave clef.[5]
History
Early glockenspiels were percussion instruments that produced notes via small bronze bells that were tuned with a drumstick. The bells were replaced by metal sound plates in the 17th century. In the 18th century the instrument was played using a keyboard that struck the bottom of each plate with a hammer.[6] The use of mallets evolved during the 19th century, coinciding with Romanticism.[7]
Construction
When used in a marching or military band, the bars are sometimes mounted in a portable case and held vertically, sometimes in a lyre-shaped frame. However, the bars may be held horizontally, using a harness similar to that found on a marching snare. In orchestral use, the bars are mounted horizontally.
Larger sets of glockenspiel (i.e. sets three octaves or larger) are often equipped with a sustain pedal, not unlike that of a vibraphone.[8]
From 1918 to 1932, J.C. Deagan, Inc. manufactured bells equipped with a resonator under the name Parsifal bells.[9] Both Adams and Yamaha model their professional-grade glockenspiels on the Deagan design.[10]
Mallets
The glockenspiel is played with unwrapped mallets made of hard material, such as metal (usually brass or aluminum) or a type of polymer (usually Lexan, acrylic, phenolic, or nylon). Non-metal mallets are used for general playing, while metal mallets produce a more brilliant sound. Rubber mallets may be used for a warmer sound, although rubber that is too soft may struggle to excite the metal bars. Playing chords on a glockenspiel can be done with four mallets using a grip such as Stevens technique.
Bell-lyre
In the United Kingdom, the United States, and Canada, a form of glockenspiel is called a bell lyre, bell lyra, or lyra-glockenspiel.[11] The bell lyre is a form of glockenspiel commonly used in marching bands.[12]
One variation is played vertically and has an extendable spike that is held on a strap. The player marches with the strap over one's shoulder and plays the instrument upright with a mallet. Another variation of the bell lyre exists that is supported by a strap around the shoulders and back. This variation is played horizontally with two mallets. Since the middle of the 19th century this form has been used in military and civil bands in Germany, where it is called a Stahlspiel or Militär-Glockenspiel.
The all-percussion drum and lyre corps in the Philippines uses this as a main instrument. This form of glockenspiel is also popular in Colombian marching band music.[13]
Many marching bands stopped using bell lyres with the introduction of the front ensemble. One of the few college marching bands with a glockenspiel section is UC Berkeley's University of California Marching Band, where they are affectionately referred to as "glocks".[14]
See also
References
- Chen, Jeremy (27 January 2013). "Glocks, Oboes and Violins? Oh, My!". Halftime Magazine.
Bibliography
- Beck, John H. (2014). Encyclopedia of Percussion (2nd ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-0415971232. OCLC 939052116.
External links
 Media related to Glockenspiels at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Glockenspiels at Wikimedia Commons- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). 1911.
- "Glockenspiel Excerpts from The Sorcerer's Apprentice" performed by William James of the St. Louis Symphony Orchestra
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glockenspiel
| Glock | |
|---|---|
 Glock 17 "First-generation" full-size model adopted in 1985 by the Norwegian military under the P80 designation | |
| Type |
|
| Place of origin | Austria |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1982–present |
| Used by | See Users |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Gaston Glock |
| Designed | 1979–1982 |
| Manufacturer | Glock Ges.m.b.H. |
| Produced | 1982–present |
| No. built | 20,000,000 as of 2020[1] |
| Variants | See Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Cartridge | |
| Action | Short recoil, locked breech, tilting barrel (straight blowback for Glock 25, 28 and 44) |
| Rate of fire | Glock 18 (Full Auto): 1,100–1,200 RPM (rounds per minute) |
| Muzzle velocity | 375 m/s (1,230 ft/s) (Glock 17, 17C, 18, 18C)[2] |
| Effective firing range | 50 m (55 yd) (Glock 17, 17C, 18, 18C)[3][4] |
| Feed system | 6-, 10-, 13-, 15-, 17-, 19-, 24-, 31-, 33-, or 40-round[5] detachable box magazine, or 50- or 100-round[6] detachable drum magazine |
Glock (stylized as GLOCK) is a brand of polymer-framed, short recoil-operated, locked-breech semi-automatic pistols designed and produced by Austrian manufacturer Glock Ges.m.b.H.
The firearm entered Austrian military and police service by 1982 after becoming the top performer in reliability and safety tests.[7]
Glock pistols have become the company's most profitable line of products, and have been supplied to national armed forces, security agencies, and police forces in at least 48 countries.[8] Glocks are also popular firearms among civilians for recreational and competition shooting, home- and self-defense, both in concealed or open carry.[9] In 2020, the Glock 19 was the best selling pistol on GunBroker.com.[10]
History
The company's founder, head engineer Gaston Glock, had no experience with firearms design or manufacture at the time their first pistol, the Glock 17, was being prototyped. Glock had extensive experience in advanced synthetic polymers, which was instrumental in the company's design of the first commercially successful line of pistols with a polymer frame.[11] Glock introduced ferritic nitrocarburizing into the firearms industry as an anticorrosion surface treatment for metal gun parts.[12]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glock




No comments:
Post a Comment