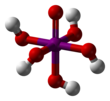
Orthoperiodic acid
| |||
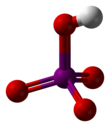
Metaperiodic acid
| |||
 HIO4·2H2O
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.839 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
| UN number | UN3085 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| HIO4 (metaperiodic) H5IO6 (orthoperiodic) | |
| Molar mass | 190.91 g/mol (HIO4) 227.941 g/mol (H5IO6) |
| Appearance | Colourless crystals |
| Melting point | 128.5 °C (263.3 °F; 401.6 K)[1] |
| Solubility | soluble in water, alcohols |
| Conjugate base | Periodate |
| Hazards[2] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H271, H314, H372, H400 | |
| P210, P260, P273, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
|
Other cations
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Periodic acid (/ˌpɜːraɪˈɒdɪk/ per-eye-OD-ik) is the highest oxoacid of iodine, in which the iodine exists in oxidation state +7. It can exist in two forms: orthoperiodic acid, with the chemical formula H5IO6, and metaperiodic acid, which has the formula HIO4.
Periodic acid was discovered by Heinrich Gustav Magnus and C. F. Ammermüller in 1833.[3]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periodic_acid



No comments:
Post a Comment