Wire drawing is a metalworking process used to reduce the cross-section of a wire by pulling the wire through a single, or series of, drawing die(s). There are many applications for wire drawing, including electrical wiring, cables, tension-loaded structural components, springs, paper clips, spokes for wheels, and stringed musical instruments. Although similar in process, drawing is different from extrusion, because in drawing the wire is pulled, rather than pushed, through the die. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process, but it may be performed at elevated temperatures for large wires to reduce forces.[1]
Of the elemental metals, copper, silver, gold, and platinum are the most ductile and immune from many of the problems associated with cold working.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire_drawing
In metallurgy, cold forming or cold working is any metalworking process in which metal is shaped below its recrystallization temperature, usually at the ambient temperature. Such processes are contrasted with hot working techniques like hot rolling, forging, welding, etc.[1]: p.375 The same or similar terms are used in glassmaking for the equivalents; for example cut glass is made by "cold work", cutting or grinding a formed object.
Cold forming techniques are usually classified into four major groups: squeezing, bending, drawing, and shearing. They generally have the advantage of being simpler to carry out than hot working techniques.
Unlike hot working, cold working causes the crystal grains and inclusions to distort following the flow of the metal; which may cause work hardening and anisotropic material properties. Work hardening makes the metal harder, stiffer, and stronger, but less plastic, and may cause cracks of the piece.[1]: p.378
The possible uses of cold forming are extremely varied, including large flat sheets, complex folded shapes, metal tubes, screw heads and threads, riveted joints, and much more.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cold_working
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire_gauge
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire
Pearlite is a two-phased, lamellar (or layered) structure composed of alternating layers of ferrite (87.5 wt%) and cementite (12.5 wt%) that occurs in some steels and cast irons. During slow cooling of an iron-carbon alloy, pearlite forms by a eutectoid reaction as austenite cools below 723 °C (1,333 °F) (the eutectoid temperature). Pearlite is a microstructure occurring in many common grades of steels.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearlite
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silver
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Niobium%E2%80%93tin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire_wrap
Drawing is a metalworking process that uses tensile forces to elongate metal, glass, or plastic. As the material is drawn (pulled), it stretches and becomes thinner, achieving a desired shape and thickness. Drawing is classified into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. Sheet metal drawing is defined as a plastic deformation over a curved axis. For wire, bar, and tube drawing, the starting stock is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process; however, drawing may also be performed at higher temperatures to hot work large wires, rods, or hollow tubes in order to reduce forces.[1][2]
Drawing differs from rolling in that pressure is not applied by the turning action of a mill but instead depends on force applied locally near the area of compression. This means the maximal drawing force is limited by the tensile strength of the material, a fact particularly evident when drawing thin wires.[3]
The starting point of cold drawing is hot-rolled stock of a suitable size.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drawing_(manufacturing)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gold
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overhead_line
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Garrote
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire_bonding
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammeter
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_wiring
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire-frame_model
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PC_strand
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Draw_plate#Drawing_wire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wheel#Wire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Horsecar
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Twist-on_wire_connector
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_and_neutral
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three-phase_electric_power
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_wire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chicken_wire_(chemistry)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chennai_Suburban_Railway
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copper_conductor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communication_protocol#Wire_image
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_(electricity)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circuit_diagram
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ferrite_bead
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyboard_technology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hot-wire_barretter
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tantalum
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Die_(manufacturing)#Wire_pulling
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_symbol
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spoke
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_field#Force_on_current-carrying_wire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Victor_Harbor_Horse_Drawn_Tram
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crown_Jewels_of_the_United_Kingdom
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artillery
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Victorian_fashion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bank
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_States_Marine_Corps#Capabilities
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anti-aircraft_warfare
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normandy_landings
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wiretapping
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beryllium_copper
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lemon_battery
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forrest_Gump
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tube_drawing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potentiometer_(measuring_instrument)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reaper-binder
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Popeye
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russo-Ukrainian_War#A_stable_line_of_conflict_%282015%E2%80%932021%29
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistivity_and_conductivity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MacOS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Godzilla
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Machine_Stops
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elastigirl
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stranger_Things
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adobe_Photoshop
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shape-memory_alloy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brokeback_Mountain
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Lord_of_the_Rings_(film_series)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer-generated_imagery
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1060_aluminium_alloy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_Deposit_Insurance_Corporation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inductive_coupling
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A_Call_to_Spy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plastic_extrusion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Golden_Temple
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dachau_concentration_camp
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Good_Wife
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/On_the_Internet,_nobody_knows_you%27re_a_dog
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planar_graph
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DreamWorks_Animation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faraday_cage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_World_Order_(conspiracy_theory)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lapis_lazuli
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black_Panther_(film)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amiga
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organized_crime
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watch
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spike_(missile)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hand_Drawn_Pressing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mockup
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEC_60309#Preferred_current_ratings_and_wire_gauges
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Changes_in_Star_Wars_re-releases
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_Khe_Sanh
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_chloride
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steven_Universe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prehistoric_beads_in_the_Philippines#Drawn_Beads
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Neon_Genesis_Evangelion_characters
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bob%27s_Burgers
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_field
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yosemite_National_Park
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joker_(character)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_American_Civil_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Bone_Collector_(novel)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_in_a_vat
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inter-Services_Intelligence
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lincoln_Cathedral
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uncanny_valley
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extrusion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_theory
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carmel-by-the-Sea,_California
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comanche
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ranks_and_insignia_of_the_German_Army_(1935%E2%80%931945)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Film_industry
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ball_lightning
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mexican%E2%80%93American_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chester
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Super_heavy-lift_launch_vehicle
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Star_Wars_(film)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_sulfide
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Violin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_Dien_Bien_Phu
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reservation_Dogs
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daguerreotype
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Street_Fighter
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Armature_(electrical)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/6060_aluminium_alloy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modern_paganism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earring
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metallic_fiber
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schematic
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thorium
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Printed_circuit_board#Solder_resist_application
Solder mask, solder stop mask or solder resist is a thin lacquer-like layer of polymer that is usually applied to the copper traces of a printed circuit board (PCB) for protection against oxidation and to prevent solder bridges from forming between closely spaced solder pads. A solder bridge is an unintended electrical connection between two conductors by means of a small blob of solder. PCBs use solder masks to prevent this from happening. Solder mask is not always used for hand soldered assemblies, but is essential for mass-produced boards that are soldered automatically using reflow or wave soldering techniques. Once applied, openings must be made in the solder mask wherever components are soldered, which is accomplished using photolithography.[1] Solder mask is traditionally green, but is also available in many other colors.[2]
Solder mask comes in different media depending upon the demands of the application. The lowest-cost solder mask is epoxy liquid that is silkscreened through the pattern onto the PCB. Other types are the liquid photoimageable solder mask (LPSM or LPI) inks and dry-film photoimageable solder mask (DFSM). LPSM can be silkscreened or sprayed on the PCB, exposed to the pattern and developed to provide openings in the pattern for parts to be soldered to the copper pads. DFSM is vacuum-laminated on the PCB then exposed and developed. All three processes typically go through a thermal cure of some type after the pattern is defined although LPI solder masks are also available in ultraviolet (UV) cure.
The solder stop layer on a flexible board is also called coverlay or coverfilm.[3]
In electronic design automation, the solder mask is treated as part of the layer stack of the printed circuit board, and is described in individual Gerber files for the top and bottom side of the PCB like any other layer (such as the copper and silk-screen layers).[4] Typical names for these layers include tStop/bStop aka STC/STS[5][nb 1] or TSM/BSM (EAGLE), F.Mask/B.Mask (KiCad), StopTop/StopBot (TARGET), maskTop/maskBottom (Fritzing), SMT/SMB (OrCAD), MT.PHO/MB.PHO (PADS), LSMVS/LSMRS (WEdirekt)[6] or GTS/GBS (Gerber and many others[7]).
Notes
- The letters 'C' and 'S' in EAGLE's old Gerber filename extensions
.STC/.STSfor the top and bottom solder stop mask layers have their origin in times when printed circuit boards were typically equipped with components populated on one side of the board only, the so called "component side" (top) versus the opposite "solder side" (bottom) where these components were soldered (at least in the case of through-hole components).
References
- "Gerber Output Options" (PDF). 1.3. Altium Limited. 2011-07-27 [2008-03-26, 2005-12-05]. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-08-29. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
Further reading
- Zühlke, Karin (2017-12-12). "Forschungsallianz Fela und Würth - "s.mask" - der erste Schritte zur digitalen Leiterplatte". Elektroniknet.de (in German). Markt & Technik. Archived from the original on 2018-06-17.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Printed_circuit_board#Solder_resist_application
Solder resist application
Areas that should not be soldered may be covered with solder resist (solder mask). The solder mask is what gives PCBs their characteristic green color, although it is also available in several other colors, such as red, blue, purple, yellow, black and white. One of the most common solder resists used today is called "LPI" (liquid photoimageable solder mask).[48] A photo-sensitive coating is applied to the surface of the PWB, then exposed to light through the solder mask image film, and finally developed where the unexposed areas are washed away. Dry film solder mask is similar to the dry film used to image the PWB for plating or etching. After being laminated to the PWB surface it is imaged and developed as LPI. Once but no longer commonly used, because of its low accuracy and resolution, is to screen print epoxy ink. In addition to repelling solder, solder resist also provides protection from the environment to the copper that would otherwise be exposed.
Legend / silkscreen
A legend (also known as silk or silkscreen) is often printed on one or both sides of the PCB. It contains the component designators, switch settings, test points and other indications helpful in assembling, testing, servicing, and sometimes using the circuit board.
There are three methods to print the legend:
- Silkscreen printing epoxy ink was the established method, resulting in the alternative name.
- Liquid photo imaging is a more accurate method than screen printing.
- Ink jet printing is increasingly used. Ink jet can print variable data, unique to each PWB unit, such as text or a bar code with a serial number.
Bare-board test
Boards with no components installed are usually bare-board tested for "shorts" and "opens". This is called electrical test or PCB e-test. A short is a connection between two points that should not be connected. An open is a missing connection between points that should be connected. For high-volume production, a fixture such as a "bed of nails" in a rigid needle adapter makes contact with copper lands on the board. The fixture or adapter is a significant fixed cost and this method is only economical for high-volume or high-value production. For small or medium volume production flying probe testers are used where test probes are moved over the board by an XY drive to make contact with the copper lands. There is no need for a fixture and hence the fixed costs are much lower. The CAM system instructs the electrical tester to apply a voltage to each contact point as required and to check that this voltage appears on the appropriate contact points and only on these.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Printed_circuit_board#Solder_resist_application
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Printed_circuit_board#Solder_resist_application
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rigid_needle_adapter
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reference_designator
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Through-hole_technology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surface-mount_technology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pick-and-place_machine
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reflow_oven
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automated_optical_inspection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-volatile_memory
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boundary_scan
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Desoldering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conformal_coating
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antistatic_bag
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fuze
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Through-hole_technology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monoboard
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prototype#Electronics_prototyping
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lab-on-a-chip
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_waste
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restriction_of_Hazardous_Substances_Directive
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breadboard
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microphonics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-chip_module
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Occam_process
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Point-to-point_construction
A stamped circuit board (SCB) is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. This technology is used for small circuits, for instance in the production of LEDs.[1]
Similar to printed circuit boards this layer structure may comprise glass-fibre reinforced epoxy resin and copper. Basically, in the case of LED substrates three variations are possible:
- the PCB (printed circuit board),
- plastic-injection molding and
- the SCB.
Using the SCB technology it is possible to structure and laminate the most widely differing material combinations in a reel-to-reel production process.[2] As the layers are structured separately, improved design concepts are able to be implemented. Consequently, a far better and quicker heat dissipation from within the chip is achieved.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stamped_circuit_board
Stripboard is the generic name for a widely used type of electronics prototyping material for circuit boards characterized by a pre-formed 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) regular (rectangular) grid of holes, with wide parallel strips of copper cladding running in one direction all the way across one side of on an insulating bonded paper board. It is commonly also known by the name of the original product Veroboard, which is a trademark, in the UK, of British company Vero Technologies Ltd and Canadian company Pixel Print Ltd. It was originated and developed in the early 1960s by the Electronics Department of Vero Precision Engineering Ltd (VPE). It was introduced as a general-purpose material for use in constructing electronic circuits - differing from purpose-designed printed circuit boards (PCBs) in that a variety of electronics circuits may be constructed using a standard wiring board.[citation needed]
In using the board, breaks are made in the tracks, usually around holes, to divide the strips into multiple electrical nodes. With care, it is possible to break between holes to allow for components that have two pin rows only one position apart such as twin row headers for IDCs.
Stripboard is not designed for surface-mount components, though it is possible to mount many such components on the track side, particularly if tracks are cut/shaped with a knife or small cutting disc in a rotary tool.
The first single-size Veroboard product was the forerunner of the numerous types of prototype wiring board which, with worldwide use over five decades, have become known as stripboard.[citation needed]
The generic terms 'veroboard' and 'stripboard' are now taken to be synonymous.[citation needed]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stripboard
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire_wrap
Conductive ink is an ink that results in a printed object which conducts electricity. It is typically created by infusing graphite or other conductive materials into ink.[1] There has been a growing interest in replacing metallic materials with nanomaterials due to the emergence of nanotechnology. Among other nanomaterials, graphene, and carbon nanotube-based conductive ink are gaining immense popularity due to their high electrical conductivity and high surface area.[2] Recently, more attention has been paid on using eco-friendly conductive ink using water as a solvent as compared to organic solvents since they are harmful to the environment. However, the high surface tension of water prevents its applicability. Various natural and synthetic surfactants are now used to reduce the surface tension of water and ensure uniform nanomaterials dispersibility for smooth printing and wide application.[3]
Silver inks have multiple uses today including printing RFID tags as used in modern transit tickets, they can be used to improvise or repair circuits on printed circuit boards. Computer keyboards contain membranes with printed circuits that sense when a key is pressed. Windshield defrosters consisting of resistive traces applied to the glass are also printed.
See also
References
- Khan, Junaid; Mariatti, M. (20 November 2022). "Effect of natural surfactant on the performance of reduced graphene oxide conductive ink". Journal of Cleaner Production. 376: 134254. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134254. ISSN 0959-6526. S2CID 252524219.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conductive_ink
Teledeltos paper is an electrically conductive paper. It is formed by a coating of carbon on one side of a sheet of paper, giving one black and one white side. Western Union developed Teledeltos paper in the late 1940s (several decades after it was already in use for mathematical modelling) for use in spark printer based fax machines and chart recorders.[1]
Teledeltos paper has several uses within engineering that are far removed from its original use in spark printers. Many of these use the paper to model the distribution of electric and other scalar fields.
Use
Teledeltos provides a sheet of a uniform resistor, with isotropic resistivity in each direction. As it is cheap and easily cut to shape, it may be used to make one-off resistors of any shape needed. The paper backing also forms a convenient insulator from the bench. These are usually made to represent or model some real-world example of a two-dimensional scalar field, where is it is necessary to study the field's distribution. This field may be an electric field, or some other field following the same linear distribution rules.
The resistivity of Teledeltos is around 6 kilohms / square.[2][i] This is low enough that it may be used with safe low voltages, yet high enough that the currents remain low, avoiding problems with contact resistance.
Connections are made to the paper by painting on areas of silver-loaded conductive paint and attaching wires to these, usually with spring clips.[2][3] Each painted area has a low resistivity (relative to the carbon) and so may be assumed to be at a constant voltage. With the voltages applied, the current flow through the sheet will emulate the field distribution. Voltages may be measured within the sheet by applying a voltmeter probe (relative to one of the known electrodes) or current flows may be measured. As the sheet's resistivity is constant, the simplest way to measure a current flow is to use a small two-probe voltmeter to measure the voltage difference between the probes. As their spacing is known, and the resistivity, the resistance between them and (by Ohm's law) the current flow can be easily determined.
An assumption in some cases is that the surrounding field is 'infinite', this would also require an infinite sheet of Teledeltos. Provided that the sheet is merely 'large' in comparison to the experimental area, a sheet of finite size is sufficient for most experimental practice.[3]
Field plotting
The basic technique for plotting a field is to first construct a model of the independent variables, then to use voltage meter probes to measure the dependent variables. Typically this means applying known voltages at certain points, then measuring voltages and currents within the model. The two basic approaches are to either applying electrodes and a voltage at known points within a large sheet of Teledeltos (modelling an infinite field) or else to cut a shape from Teledeltos and then apply voltages to its edges (modelling a bounded field).[2][3] There is a common practical association that electrical field models are usually infinite and thermal models are usually bounded.
Modelling fields by analogy
Although the modelling of electric fields is itself directly useful in some fields such as thermionic valve design,[4] the main practical use of the broader technique is for modelling fields of other quantities. This technique may be applied to any field that follows the same linear rules as Ohm's law for bulk resistivity. This includes heat flow, some optics and some aspects of Newtonian mechanics. It is not usually applicable to fluid dynamics, owing to viscosity and compressibility effects, or to high-intensity optics where non-linear effects become apparent. It may be applicable to some mechanical problems involving homogeneous and isotropic materials such as metals, but not to composites.
Before the use of Teledeltos, a similar technique had been used for modelling gas flows, where a shallow tray of copper sulphate solution was used as the medium, with copper electrodes at each side. Barriers within the model could be sculpted from wax. Being a liquid, this was far less convenient. Stanley Hooker describes its use pre-war, although he also notes that compressibility effects could be modelled in this way, by sculpting the base of the tank to give additional depth and thus conductivity locally.[5]
One of the most important applications is for thermal modelling. Voltage is the analog of temperature and current flow that of heat flow. If the boundaries of a heatsink model are both painted with conductive paint to form two separate electrodes, each may be held at a voltage to represent the temperatures of some internal heat source (such as a microprocessor chip) and the external ambient temperature. Potentials within the heatsink represent internal temperatures and current flows represent heat flow. In many cases the internal heat source may be modelled with a constant current source, rather than a voltage, giving a better analogy of power loss as heat, rather than assuming a simple constant temperature. If the external airflow is restricted, the 'ambient' electrode may be subdivided and each section connected to a common voltage supply through a resistor or current limiter, representing the proportionate or maximum heatflow capacity of that airstream.
As heatsinks are commonly manufactured from extruded aluminium sections, the two-dimensional paper is not usually a serious limitation. In some cases, such as pistons for internal combustion engines, three-dimensional modelling may be required. This has been performed, in a manner analogous to Teledeltos paper, by using volume tanks of a conductive electrolyte.[6]
This thermal modelling technique is useful in many branches of mechanical engineering such as heatsink or radiator design and die casting.[7]
The development of computational modelling and finite element analysis has reduced the use of Teledeltos, such that the technique is now obscure and the materials can be hard to obtain.[2] Its use is still highly valuable in teaching, as the technique gives a very obvious method for measuring fields and offers immediate feedback as the shape of an experimental setup is changed, encouraging a more fundamental understanding.[3][4]
Sensors
Teledeltos can also be used to make sensors, either directly as an embedded resistive element or indirectly, as part of their design process.
Resistive sensors
A piece of Teledeltos with conductive electrodes at each end makes a simple resistor. Its resistance is slightly sensitive to applied mechanical strain by bending or compression, but the paper substrate is not robust enough to make a reliable sensor for long-term use.
A more common resistive sensor is in the form of a potentiometer. A long, thin resistor with an applied voltage may have a conductive probe slid along its surface. The voltage at the probe depends on its position between the two end contacts. Such a sensor may form the keyboard for a simple electronic musical instrument like a Tannerin or Stylophone.
A similar linear sensor uses two strips of Teledeltos, placed face to face. Pressure on the back of one (finger pressure is enough) presses the two conductive faces together to form a lower resistance contact. This may be used in similar potentiometric fashion to the conductive probe, but without requiring the special probe. This may be used as a classroom demonstration for another electronic musical instrument, with a ribbon controller keyboard, such as the Monotron. If crossed electrodes are used on each piece of Teledeltos, a two-dimensional resistive touchpad may be demonstrated.
Capacitive sensors
Although Teledeltos is not used to manufacture capacitive sensors, its field modelling abilities also allow it to be used to determine the capacitance of arbitrarily shaped electrodes during sensor design.[2]
See also
Notes
- Note that the resistivity units for a two-dimensional sheet are ohms / square (), not the ohm metre (Ω⋅m)s that would be used for the resistivity of a bulk resistor.
References
- John L., Jorstad (September 2006). "Aluminum Future Technology in Die Casting" (PDF). Die Casting Engineering: 19. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-06-14.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teledeltos
Category:Analog computers
Subcategories
This category has only the following subcategory.
O
- Optical bombsights (10 P)
Pages in category "Analog computers"
The following 55 pages are in this category, out of 55 total. This list may not reflect recent changes.
R
T
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Analog_computers
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (analog signals) to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude (digital signals).
Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated.[1] Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions.
Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were typically much faster, but they started to become obsolete as early as the 1950s and 1960s, although they remained in use in some specific applications, such as aircraft flight simulators, the flight computer in aircraft, and for teaching control systems in universities. Perhaps the most relatable example of analog computers are mechanical watches where the continuous and periodic rotation of interlinked gears drives the second, minute and hour needles in the clock. More complex applications, such as aircraft flight simulators and synthetic-aperture radar, remained the domain of analog computing (and hybrid computing) well into the 1980s, since digital computers were insufficient for the task.[2]
Timeline of analog computers
Precursors
This is a list of examples of early computation devices considered precursors of the modern computers. Some of them may even have been dubbed 'computers' by the press, though they may fail to fit modern definitions.
The Antikythera mechanism, a type of device used to determine the positions of heavenly bodies known as an orrery, was described as an early mechanical analog computer by British physicist, information scientist, and historian of science Derek J. de Solla Price.[3] It was discovered in 1901, in the Antikythera wreck off the Greek island of Antikythera, between Kythera and Crete, and has been dated to c. 150~100 BC, during the Hellenistic period. Devices of a level of complexity comparable to that of the Antikythera mechanism would not reappear until a thousand years later.
Many mechanical aids to calculation and measurement were constructed for astronomical and navigation use. The planisphere was first described by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD. The astrolabe was invented in the Hellenistic world in either the 1st or 2nd centuries BC and is often attributed to Hipparchus. A combination of the planisphere and dioptra, the astrolabe was effectively an analog computer capable of working out several different kinds of problems in spherical astronomy. An astrolabe incorporating a mechanical calendar computer[4][5] and gear-wheels was invented by Abi Bakr of Isfahan, Persia in 1235.[6] Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī invented the first mechanical geared lunisolar calendar astrolabe,[7] an early fixed-wired knowledge processing machine[8] with a gear train and gear-wheels,[9] c. AD 1000.
The sector, a calculating instrument used for solving problems in proportion, trigonometry, multiplication and division, and for various functions, such as squares and cube roots, was developed in the late 16th century and found application in gunnery, surveying and navigation.
The planimeter was a manual instrument to calculate the area of a closed figure by tracing over it with a mechanical linkage.
The slide rule was invented around 1620–1630, shortly after the publication of the concept of the logarithm. It is a hand-operated analog computer for doing multiplication and division. As slide rule development progressed, added scales provided reciprocals, squares and square roots, cubes and cube roots, as well as transcendental functions such as logarithms and exponentials, circular and hyperbolic trigonometry and other functions. Aviation is one of the few fields where slide rules are still in widespread use, particularly for solving time–distance problems in light aircraft.
In 1831–1835, mathematician and engineer Giovanni Plana devised a perpetual-calendar machine, which, through a system of pulleys and cylinders, could predict the perpetual calendar for every year from AD 0 (that is, 1 BC) to AD 4000, keeping track of leap years and varying day length.[10]
The tide-predicting machine invented by Sir William Thomson in 1872 was of great utility to navigation in shallow waters. It used a system of pulleys and wires to automatically calculate predicted tide levels for a set period at a particular location.
The differential analyser, a mechanical analog computer designed to solve differential equations by integration, used wheel-and-disc mechanisms to perform the integration. In 1876 James Thomson had already discussed the possible construction of such calculators, but he had been stymied by the limited output torque of the ball-and-disk integrators. A number of similar systems followed, notably those of the Spanish engineer Leonardo Torres y Quevedo, who built several machines for solving real and complex roots of polynomials; and Michelson and Stratton, whose Harmonic Analyser performed Fourier analysis, but using an array of 80 springs rather than Kelvin integrators. This work led to the mathematical understanding of the Gibbs phenomenon of overshoot in Fourier representation near discontinuities.[11] In a differential analyzer, the output of one integrator drove the input of the next integrator, or a graphing output. The torque amplifier was the advance that allowed these machines to work. Starting in the 1920s, Vannevar Bush and others developed mechanical differential analyzers.
Modern era
The Dumaresq was a mechanical calculating device invented around 1902 by Lieutenant John Dumaresq of the Royal Navy. It was an analog computer that related vital variables of the fire control problem to the movement of one's own ship and that of a target ship. It was often used with other devices, such as a Vickers range clock to generate range and deflection data so the gun sights of the ship could be continuously set. A number of versions of the Dumaresq were produced of increasing complexity as development proceeded.
By 1912, Arthur Pollen had developed an electrically driven mechanical analog computer for fire-control systems, based on the differential analyser. It was used by the Imperial Russian Navy in World War I.[citation needed][12]
Starting in 1929, AC network analyzers were constructed to solve calculation problems related to electrical power systems that were too large to solve with numerical methods at the time.[13] These were essentially scale models of the electrical properties of the full-size system. Since network analyzers could handle problems too large for analytic methods or hand computation, they were also used to solve problems in nuclear physics and in the design of structures. More than 50 large network analyzers were built by the end of the 1950s.
World War II era gun directors, gun data computers, and bomb sights used mechanical analog computers. In 1942 Helmut Hölzer built a fully electronic analog computer at Peenemünde Army Research Center[14][15][16] as an embedded control system (mixing device) to calculate V-2 rocket trajectories from the accelerations and orientations (measured by gyroscopes) and to stabilize and guide the missile.[17][18] Mechanical analog computers were very important in gun fire control in World War II, the Korean War and well past the Vietnam War; they were made in significant numbers.
In the period 1930–1945 in the Netherlands, Johan van Veen developed an analogue computer to calculate and predict tidal currents when the geometry of the channels are changed. Around 1950, this idea was developed into the Deltar, a hydraulic analogy computer supporting the closure of estuaries in the southwest of the Netherlands (the Delta Works).
The FERMIAC was an analog computer invented by physicist Enrico Fermi in 1947 to aid in his studies of neutron transport.[19] Project Cyclone was an analog computer developed by Reeves in 1950 for the analysis and design of dynamic systems.[20] Project Typhoon was an analog computer developed by RCA in 1952. It consisted of over 4,000 electron tubes and used 100 dials and 6,000 plug-in connectors to program.[21] The MONIAC Computer was a hydraulic analogy of a national economy first unveiled in 1949.[22]
Computer Engineering Associates was spun out of Caltech in 1950 to provide commercial services using the "Direct Analogy Electric Analog Computer" ("the largest and most impressive general-purpose analyzer facility for the solution of field problems") developed there by Gilbert D. McCann, Charles H. Wilts, and Bart Locanthi.[23][24]
Educational analog computers illustrated the principles of analog calculation. The Heathkit EC-1, a $199 educational analog computer, was made by the Heath Company, US c. 1960.[25] It was programmed using patch cords that connected nine operational amplifiers and other components.[26] General Electric also marketed an "educational" analog computer kit of a simple design in the early 1960s consisting of a two transistor tone generators and three potentiometers wired such that the frequency of the oscillator was nulled when the potentiometer dials were positioned by hand to satisfy an equation. The relative resistance of the potentiometer was then equivalent to the formula of the equation being solved. Multiplication or division could be performed, depending on which dials were inputs and which was the output. Accuracy and resolution was limited and a simple slide rule was more accurate. However, the unit did demonstrate the basic principle.
Analog computer designs were published in electronics magazines. One example is the PEAC (Practical Electronics analogue computer), published in Practical Electronics in the January 1968 edition.[27] Another more modern hybrid computer design was published in Everyday Practical Electronics in 2002.[28] An example described in the EPE hybrid computer was the flight of a VTOL aircraft such as the Harrier jump jet.[28] The altitude and speed of the aircraft were calculated by the analog part of the computer and sent to a PC via a digital microprocessor and displayed on the PC screen.
In industrial process control, analog loop controllers were used to automatically regulate temperature, flow, pressure, or other process conditions. The technology of these controllers ranged from purely mechanical integrators, through vacuum-tube and solid-state devices, to emulation of analog controllers by microprocessors.
Electronic analog computers
The similarity between linear mechanical components, such as springs and dashpots (viscous-fluid dampers), and electrical components, such as capacitors, inductors, and resistors is striking in terms of mathematics. They can be modeled using equations of the same form.
However, the difference between these systems is what makes analog computing useful. Complex systems often are not amenable to pen-and-paper analysis, and require some form of testing or simulation. Complex mechanical systems, such as suspensions for racing cars, are expensive to fabricate and hard to modify. And taking precise mechanical measurements during high-speed tests adds further difficulty.
By contrast, it is very inexpensive to build an electrical equivalent of a complex mechanical system, to simulate its behavior. Engineers arrange a few operational amplifiers (op amps) and some passive linear components to form a circuit that follows the same equations as the mechanical system being simulated. All measurements can be taken directly with an oscilloscope. In the circuit, the (simulated) stiffness of the spring, for instance, can be changed by adjusting the parameters of an integrator. The electrical system is an analogy to the physical system, hence the name, but it is much less expensive than a mechanical prototype, much easier to modify, and generally safer.
The electronic circuit can also be made to run faster or slower than the physical system being simulated. Experienced users of electronic analog computers said that they offered a comparatively intimate control and understanding of the problem, relative to digital simulations.
Electronic analog computers are especially well-suited to representing situations described by differential equations. Historically, they were often used when a system of differential equations proved very difficult to solve by traditional means. As a simple example, the dynamics of a spring-mass system can be described by the equation , with as the vertical position of a mass , the damping coefficient, the spring constant and the gravity of Earth. For analog computing, the equation is programmed as . The equivalent analog circuit consists of two integrators for the state variables (speed) and (position), one inverter, and three potentiometers.
Electronic analog computers have drawbacks: the value of the circuit's supply voltage limits the range over which the variables may vary (since the value of a variable is represented by a voltage on a particular wire). Therefore, each problem must be scaled so its parameters and dimensions can be represented using voltages that the circuit can supply —e.g., the expected magnitudes of the velocity and the position of a spring pendulum. Improperly scaled variables can have their values "clamped" by the limits of the supply voltage. Or if scaled too small, they can suffer from higher noise levels. Either problem can cause the circuit to produce an incorrect simulation of the physical system. (Modern digital simulations are much more robust to widely varying values of their variables, but are still not entirely immune to these concerns: floating-point digital calculations support a huge dynamic range, but can suffer from imprecision if tiny differences of huge values lead to numerical instability.)
The precision of the analog computer readout was limited chiefly by the precision of the readout equipment used, generally three or four significant figures. (Modern digital simulations are much better in this area. Digital arbitrary-precision arithmetic can provide any desired degree of precision.) However, in most cases the precision of an analog computer is absolutely sufficient given the uncertainty of the model characteristics and its technical parameters.
Many small computers dedicated to specific computations are still part of industrial regulation equipment, but from the 1950s to the 1970s, general-purpose analog computers were the only systems fast enough for real time simulation of dynamic systems, especially in the aircraft, military and aerospace field.
In the 1960s, the major manufacturer was Electronic Associates of Princeton, New Jersey, with its 231R Analog Computer (vacuum tubes, 20 integrators) and subsequently its EAI 8800 Analog Computer (solid state operational amplifiers, 64 integrators).[29] Its challenger was Applied Dynamics of Ann Arbor, Michigan.
Although the basic technology for analog computers is usually operational amplifiers (also called "continuous current amplifiers" because they have no low frequency limitation), in the 1960s an attempt was made in the French ANALAC computer to use an alternative technology: medium frequency carrier and non dissipative reversible circuits.
In the 1970s, every large company and administration concerned with problems in dynamics had an analog computing center, such as:
- In the US: NASA (Huntsville, Houston), Martin Marietta (Orlando), Lockheed, Westinghouse, Hughes Aircraft
- In Europe: CEA (French Atomic Energy Commission), MATRA, Aérospatiale, BAC (British Aircraft Corporation).
Analog–digital hybrids
Analog computing devices are fast, digital computing devices are more versatile and accurate, so the idea is to combine the two processes for the best efficiency. An example of such hybrid elementary device is the hybrid multiplier where one input is an analog signal, the other input is a digital signal and the output is analog. It acts as an analog potentiometer upgradable digitally. This kind of hybrid technique is mainly used for fast dedicated real time computation when computing time is very critical as signal processing for radars and generally for controllers in embedded systems.
In the early 1970s, analog computer manufacturers tried to tie together their analog computer with a digital computer to get the advantages of the two techniques. In such systems, the digital computer controlled the analog computer, providing initial set-up, initiating multiple analog runs, and automatically feeding and collecting data. The digital computer may also participate to the calculation itself using analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters.
The largest manufacturer of hybrid computers was Electronics Associates. Their hybrid computer model 8900 was made of a digital computer and one or more analog consoles. These systems were mainly dedicated to large projects such as the Apollo program and Space Shuttle at NASA, or Ariane in Europe, especially during the integration step where at the beginning everything is simulated, and progressively real components replace their simulated part.[30]
Only one company was known as offering general commercial computing services on its hybrid computers, CISI of France, in the 1970s.
The best reference in this field is the 100,000 simulation runs for each certification of the automatic landing systems of Airbus and Concorde aircraft.[31]
After 1980, purely digital computers progressed more and more rapidly and were fast enough to compete with analog computers. One key to the speed of analog computers was their fully parallel computation, but this was also a limitation. The more equations required for a problem, the more analog components were needed, even when the problem wasn't time critical. "Programming" a problem meant interconnecting the analog operators; even with a removable wiring panel this was not very versatile. Today there are no more big hybrid computers, but only hybrid components.[citation needed]
Implementations
This section needs additional citations for verification. (March 2023) |
Mechanical analog computers
While a wide variety of mechanisms have been developed throughout history, some stand out because of their theoretical importance, or because they were manufactured in significant quantities.
Most practical mechanical analog computers of any significant complexity used rotating shafts to carry variables from one mechanism to another. Cables and pulleys were used in a Fourier synthesizer, a tide-predicting machine, which summed the individual harmonic components. Another category, not nearly as well known, used rotating shafts only for input and output, with precision racks and pinions. The racks were connected to linkages that performed the computation. At least one U.S. Naval sonar fire control computer of the later 1950s, made by Librascope, was of this type, as was the principal computer in the Mk. 56 Gun Fire Control System.
Online, there is a remarkably clear illustrated reference (OP 1140)[32] that describes the fire control computer mechanisms.[32] For adding and subtracting, precision miter-gear differentials were in common use in some computers; the Ford Instrument Mark I Fire Control Computer contained about 160 of them.
Integration with respect to another variable was done by a rotating disc driven by one variable. Output came from a pick-off device (such as a wheel) positioned at a radius on the disc proportional to the second variable. (A carrier with a pair of steel balls supported by small rollers worked especially well. A roller, its axis parallel to the disc's surface, provided the output. It was held against the pair of balls by a spring.)
Arbitrary functions of one variable were provided by cams, with gearing to convert follower movement to shaft rotation.
Functions of two variables were provided by three-dimensional cams. In one good design, one of the variables rotated the cam. A hemispherical follower moved its carrier on a pivot axis parallel to that of the cam's rotating axis. Pivoting motion was the output. The second variable moved the follower along the axis of the cam. One practical application was ballistics in gunnery.
Coordinate conversion from polar to rectangular was done by a mechanical resolver (called a "component solver" in US Navy fire control computers). Two discs on a common axis positioned a sliding block with pin (stubby shaft) on it. One disc was a face cam, and a follower on the block in the face cam's groove set the radius. The other disc, closer to the pin, contained a straight slot in which the block moved. The input angle rotated the latter disc (the face cam disc, for an unchanging radius, rotated with the other (angle) disc; a differential and a few gears did this correction).
Referring to the mechanism's frame, the location of the pin corresponded to the tip of the vector represented by the angle and magnitude inputs. Mounted on that pin was a square block.
Rectilinear-coordinate outputs (both sine and cosine, typically) came from two slotted plates, each slot fitting on the block just mentioned. The plates moved in straight lines, the movement of one plate at right angles to that of the other. The slots were at right angles to the direction of movement. Each plate, by itself, was like a Scotch yoke, known to steam engine enthusiasts.
During World War II, a similar mechanism converted rectilinear to polar coordinates, but it was not particularly successful and was eliminated in a significant redesign (USN, Mk. 1 to Mk. 1A).
Multiplication was done by mechanisms based on the geometry of similar right triangles. Using the trigonometric terms for a right triangle, specifically opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse, the adjacent side was fixed by construction. One variable changed the magnitude of the opposite side. In many cases, this variable changed sign; the hypotenuse could coincide with the adjacent side (a zero input), or move beyond the adjacent side, representing a sign change.
Typically, a pinion-operated rack moving parallel to the (trig.-defined) opposite side would position a slide with a slot coincident with the hypotenuse. A pivot on the rack let the slide's angle change freely. At the other end of the slide (the angle, in trig. terms), a block on a pin fixed to the frame defined the vertex between the hypotenuse and the adjacent side.
At any distance along the adjacent side, a line perpendicular to it intersects the hypotenuse at a particular point. The distance between that point and the adjacent side is some fraction that is the product of 1 the distance from the vertex, and 2 the magnitude of the opposite side.
The second input variable in this type of multiplier positions a slotted plate perpendicular to the adjacent side. That slot contains a block, and that block's position in its slot is determined by another block right next to it. The latter slides along the hypotenuse, so the two blocks are positioned at a distance from the (trig.) adjacent side by an amount proportional to the product.
To provide the product as an output, a third element, another slotted plate, also moves parallel to the (trig.) opposite side of the theoretical triangle. As usual, the slot is perpendicular to the direction of movement. A block in its slot, pivoted to the hypotenuse block positions it.
A special type of integrator, used at a point where only moderate accuracy was needed, was based on a steel ball, instead of a disc. It had two inputs, one to rotate the ball, and the other to define the angle of the ball's rotating axis. That axis was always in a plane that contained the axes of two movement pick-off rollers, quite similar to the mechanism of a rolling-ball computer mouse (in that mechanism, the pick-off rollers were roughly the same diameter as the ball). The pick-off roller axes were at right angles.
A pair of rollers "above" and "below" the pick-off plane were mounted in rotating holders that were geared together. That gearing was driven by the angle input, and established the rotating axis of the ball. The other input rotated the "bottom" roller to make the ball rotate.
Essentially, the whole mechanism, called a component integrator, was a variable-speed drive with one motion input and two outputs, as well as an angle input. The angle input varied the ratio (and direction) of coupling between the "motion" input and the outputs according to the sine and cosine of the input angle.
Although they did not accomplish any computation, electromechanical position servos were essential in mechanical analog computers of the "rotating-shaft" type for providing operating torque to the inputs of subsequent computing mechanisms, as well as driving output data-transmission devices such as large torque-transmitter synchros in naval computers.
Other readout mechanisms, not directly part of the computation, included internal odometer-like counters with interpolating drum dials for indicating internal variables, and mechanical multi-turn limit stops.
Considering that accurately controlled rotational speed in analog fire-control computers was a basic element of their accuracy, there was a motor with its average speed controlled by a balance wheel, hairspring, jeweled-bearing differential, a twin-lobe cam, and spring-loaded contacts (ship's AC power frequency was not necessarily accurate, nor dependable enough, when these computers were designed).
Electronic analog computers
Electronic analog computers typically have front panels with numerous jacks (single-contact sockets) that permit patch cords (flexible wires with plugs at both ends) to create the interconnections that define the problem setup. In addition, there are precision high-resolution potentiometers (variable resistors) for setting up (and, when needed, varying) scale factors. In addition, there is usually a zero-center analog pointer-type meter for modest-accuracy voltage measurement. Stable, accurate voltage sources provide known magnitudes.
Typical electronic analog computers contain anywhere from a few to a hundred or more operational amplifiers ("op amps"), named because they perform mathematical operations. Op amps are a particular type of feedback amplifier with very high gain and stable input (low and stable offset). They are always used with precision feedback components that, in operation, all but cancel out the currents arriving from input components. The majority of op amps in a representative setup are summing amplifiers, which add and subtract analog voltages, providing the result at their output jacks. As well, op amps with capacitor feedback are usually included in a setup; they integrate the sum of their inputs with respect to time.
Integrating with respect to another variable is the nearly exclusive province of mechanical analog integrators; it is almost never done in electronic analog computers. However, given that a problem solution does not change with time, time can serve as one of the variables.
Other computing elements include analog multipliers, nonlinear function generators, and analog comparators.
Electrical elements such as inductors and capacitors used in electrical analog computers had to be carefully manufactured to reduce non-ideal effects. For example, in the construction of AC power network analyzers, one motive for using higher frequencies for the calculator (instead of the actual power frequency) was that higher-quality inductors could be more easily made. Many general-purpose analog computers avoided the use of inductors entirely, re-casting the problem in a form that could be solved using only resistive and capacitive elements, since high-quality capacitors are relatively easy to make.
The use of electrical properties in analog computers means that calculations are normally performed in real time (or faster), at a speed determined mostly by the frequency response of the operational amplifiers and other computing elements. In the history of electronic analog computers, there were some special high-speed types.
Nonlinear functions and calculations can be constructed to a limited precision (three or four digits) by designing function generators—special circuits of various combinations of resistors and diodes to provide the nonlinearity. Typically, as the input voltage increases, progressively more diodes conduct.
When compensated for temperature, the forward voltage drop of a transistor's base-emitter junction can provide a usably accurate logarithmic or exponential function. Op amps scale the output voltage so that it is usable with the rest of the computer.
Any physical process that models some computation can be interpreted as an analog computer. Some examples, invented for the purpose of illustrating the concept of analog computation, include using a bundle of spaghetti as a model of sorting numbers; a board, a set of nails, and a rubber band as a model of finding the convex hull of a set of points; and strings tied together as a model of finding the shortest path in a network. These are all described in Dewdney (1984).
Components
Analog computers often have a complicated framework, but they have, at their core, a set of key components that perform the calculations. The operator manipulates these through the computer's framework.
Key hydraulic components might include pipes, valves and containers.
Key mechanical components might include rotating shafts for carrying data within the computer, miter gear differentials, disc/ball/roller integrators, cams (2-D and 3-D), mechanical resolvers and multipliers, and torque servos.
Key electrical/electronic components might include:
- precision resistors and capacitors
- operational amplifiers
- multipliers
- potentiometers
- fixed-function generators
The core mathematical operations used in an electric analog computer are:
- addition
- integration with respect to time
- inversion
- multiplication
- exponentiation
- logarithm
- division
In some analog computer designs, multiplication is much preferred to division. Division is carried out with a multiplier in the feedback path of an Operational Amplifier.
Differentiation with respect to time is not frequently used, and in practice is avoided by redefining the problem when possible. It corresponds in the frequency domain to a high-pass filter, which means that high-frequency noise is amplified; differentiation also risks instability.
Limitations
In general, analog computers are limited by non-ideal effects. An analog signal is composed of four basic components: DC and AC magnitudes, frequency, and phase. The real limits of range on these characteristics limit analog computers. Some of these limits include the operational amplifier offset, finite gain, and frequency response, noise floor, non-linearities, temperature coefficient, and parasitic effects within semiconductor devices. For commercially available electronic components, ranges of these aspects of input and output signals are always figures of merit.
Decline
In the 1950s to 1970s, digital computers based on first vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits and then micro-processors became more economical and precise. This led digital computers to largely replace analog computers. Even so, some research in analog computation is still being done. A few universities still use analog computers to teach control system theory. The American company Comdyna manufactured small analog computers.[33] At Indiana University Bloomington, Jonathan Mills has developed the Extended Analog Computer based on sampling voltages in a foam sheet.[34] At the Harvard Robotics Laboratory,[35] analog computation is a research topic. Lyric Semiconductor's error correction circuits use analog probabilistic signals. Slide rules are still popular among aircraft personnel.[citation needed]
Resurgence
With the development of very-large-scale integration (VLSI) technology, Yannis Tsividis' group at Columbia University has been revisiting analog/hybrid computers design in standard CMOS process. Two VLSI chips have been developed, an 80th-order analog computer (250 nm) by Glenn Cowan[36] in 2005[37] and a 4th-order hybrid computer (65 nm) developed by Ning Guo in 2015,[38] both targeting at energy-efficient ODE/PDE applications. Glenn's chip contains 16 macros, in which there are 25 analog computing blocks, namely integrators, multipliers, fanouts, few nonlinear blocks. Ning's chip contains one macro block, in which there are 26 computing blocks including integrators, multipliers, fanouts, ADCs, SRAMs and DACs. Arbitrary nonlinear function generation is made possible by the ADC+SRAM+DAC chain, where the SRAM block stores the nonlinear function data. The experiments from the related publications revealed that VLSI analog/hybrid computers demonstrated about 1–2 orders magnitude of advantage in both solution time and energy while achieving accuracy within 5%, which points to the promise of using analog/hybrid computing techniques in the area of energy-efficient approximate computing.[citation needed] In 2016, a team of researchers developed a compiler to solve differential equations using analog circuits.[39]
Analog computers are also used in neuromorphic computing, and in 2021 a group of researchers have shown that a specific type of artificial neural network called a spiking neural network was able to work with analog neuromorphic computers.[40]
Practical examples
These are examples of analog computers that have been constructed or practically used:
- Boeing B-29 Superfortress Central Fire Control System
- Deltar
- E6B flight computer
- Kerrison Predictor
- Leonardo Torres y Quevedo's Analogue Calculating Machines based on "fusee sans fin"
- Librascope, aircraft weight and balance computer
- Mechanical computer
- Mechanical integrators, for example, the planimeter
- Nomogram
- Norden bombsight
- Rangekeeper, and related fire control computers
- Scanimate
- Torpedo Data Computer
- Torquetum
- Water integrator
- MONIAC, economic modelling
- Ishiguro Storm Surge Computer
Analog (audio) synthesizers can also be viewed as a form of analog computer, and their technology was originally based in part on electronic analog computer technology. The ARP 2600's Ring Modulator was actually a moderate-accuracy analog multiplier.
The Simulation Council (or Simulations Council) was an association of analog computer users in US. It is now known as The Society for Modeling and Simulation International. The Simulation Council newsletters from 1952 to 1963 are available online and show the concerns and technologies at the time, and the common use of analog computers for missilry.[41]
See also
- Analog neural network
- Analogical models
- Chaos theory
- Differential equation
- Dynamical system
- Field-programmable analog array
- General purpose analog computer
- Lotfernrohr 7 series of WW II German bombsights
- Signal (electrical engineering)
- Voskhod Spacecraft "Globus" IMP navigation instrument
- XY-writer
Notes
- "Simulation Council newsletter". Archived from the original on 28 May 2013.
References
- A.K. Dewdney. "On the Spaghetti Computer and Other Analog Gadgets for Problem Solving", Scientific American, 250(6):19–26, June 1984. Reprinted in The Armchair Universe, by A.K. Dewdney, published by W.H. Freeman & Company (1988), ISBN 0-7167-1939-8.
- Universiteit van Amsterdam Computer Museum. (2007). Analog Computers.
- Jackson, Albert S., "Analog Computation". London & New York: McGraw-Hill, 1960. OCLC 230146450
External links
- Biruni's eight-geared lunisolar calendar in "Archaeology: High tech from Ancient Greece", François Charette, Nature 444, 551–552(30 November 2006), doi:10.1038/444551a
- The first computers
- Large collection of electronic analog computers with lots of pictures, documentation and samples of implementations (some in German)
- Large collection of old analog and digital computers at Old Computer Museum
- A great disappearing act: the electronic analogue computer Chris Bissell, The Open University, Milton Keynes, UK Accessed February 2007
- German computer museum with still runnable analog computers
- Analog computer basics Archived 6 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- Analog computer trumps Turing model
- Harvard Robotics Laboratory Analog Computation
- The Enns Power Network Computer – an analog computer for the analysis of electric power systems (advertisement from 1955)
- Librascope Development Company – Type LC-1 WWII Navy PV-1 "Balance Computor"
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analog_computer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shadow_square
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deltar
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minoan_Moulds_of_Palaikastro
Resistance paper,[1][2] also known as conductive paper and by the trade name Teledeltos paper is paper impregnated or coated with a conductive substance such that the paper exhibits a uniform and known surface resistivity. Resistance paper and conductive ink were commonly used as an analog two-dimensional[3] electromagnetic field solver. Teledeltos paper is a particular type of resistance paper.
References
- "Resistance paper is very simple to use for two-dimensional problems..." Ramo, Simon; Whinnery, John R.; van Duzer, Theodore (1965). Fields and Waves in Communication Electronics. John Wiley. p. 168–170. ISBN 9780471707202.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistance_paper
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AN/MPQ-2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battenberg_course_indicator
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BT-Epoxy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Composite_epoxy_material
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanate_ester
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polyimide
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polytetrafluoroethylene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FR-4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FR-2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_EDA_companies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Electronics_substrates
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barcode
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serial_number
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents,[1]: ch1 [2] and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field.[1]: ch13 [3]: 278 A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, called a vector field.
In electromagnetics, the term "magnetic field" is used for two distinct but closely related vector fields denoted by the symbols B and H. In the International System of Units, the unit of H, magnetic field strength, is the ampere per meter (A/m).[4]: 22 The unit of B, the magnetic flux density, is the tesla (in SI base units: kilogram per second2 per ampere),[4]: 21 which is equivalent to newton per meter per ampere. H and B differ in how they account for magnetization. In vacuum, the two fields are related through the vacuum permeability, ; but in a magnetized material, the quantities on each side of this equation differ by the magnetization field of the material.
Magnetic fields are produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin.[5][1]: ch1 Magnetic fields and electric fields are interrelated and are both components of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
Magnetic fields are used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is conceptualized and investigated as magnetic circuits. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which shields the Earth's ozone layer from the solar wind and is important in navigation using a compass.
Description
The force on an electric charge depends on its location, speed, and direction; two vector fields are used to describe this force.[1]: ch1 The first is the electric field, which describes the force acting on a stationary charge and gives the component of the force that is independent of motion. The magnetic field, in contrast, describes the component of the force that is proportional to both the speed and direction of charged particles.[1]: ch13 The field is defined by the Lorentz force law and is, at each instant, perpendicular to both the motion of the charge and the force it experiences.
There are two different, but closely related vector fields which are both sometimes called the "magnetic field" written B and H.[note 1] While both the best names for these fields and exact interpretation of what these fields represent has been the subject of long running debate, there is wide agreement about how the underlying physics work.[6] Historically, the term "magnetic field" was reserved for H while using other terms for B, but many recent textbooks use the term "magnetic field" to describe B as well as or in place of H.[note 2] There are many alternative names for both (see sidebar).
The B-field
| Alternative names for B[7] |
|---|
The magnetic field vector B at any point can be defined as the vector that, when used in the Lorentz force law, correctly predicts the force on a charged particle at that point:[9][10]: 204
Here F is the force on the particle, q is the particle's electric charge, v, is the particle's velocity, and × denotes the cross product. The direction of force on the charge can be determined by a mnemonic known as the right-hand rule (see the figure).[note 3] Using the right hand, pointing the thumb in the direction of the current, and the fingers in the direction of the magnetic field, the resulting force on the charge points outwards from the palm. The force on a negatively charged particle is in the opposite direction. If both the speed and the charge are reversed then the direction of the force remains the same. For that reason a magnetic field measurement (by itself) cannot distinguish whether there is a positive charge moving to the right or a negative charge moving to the left. (Both of these cases produce the same current.) On the other hand, a magnetic field combined with an electric field can distinguish between these, see Hall effect below.
The first term in the Lorentz equation is from the theory of electrostatics, and says that a particle of charge q in an electric field E experiences an electric force:
The second term is the magnetic force:[10]
Using the definition of the cross product, the magnetic force can also be written as a scalar equation:[9]: 357
where Fmagnetic, v, and B are the scalar magnitude of their respective vectors, and θ is the angle between the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field. The vector B is defined as the vector field necessary to make the Lorentz force law correctly describe the motion of a charged particle. In other words,[9]: 173–4
[T]he command, "Measure the direction and magnitude of the vector B at such and such a place," calls for the following operations: Take a particle of known charge q. Measure the force on q at rest, to determine E. Then measure the force on the particle when its velocity is v; repeat with v in some other direction. Now find a B that makes the Lorentz force law fit all these results—that is the magnetic field at the place in question.
The B field can also be defined by the torque on a magnetic dipole, m.[11]: 174
The SI unit of B is tesla (symbol: T).[note 4] The Gaussian-cgs unit of B is the gauss (symbol: G). (The conversion is 1 T ≘ 10000 G.[12][13]) One nanotesla corresponds to 1 gamma (symbol: γ).[13]
The H-field
| Alternative names for H[7] |
|---|
The magnetic H field is defined:[10]: 269 [11]: 192 [1]: ch36
Where is the vacuum permeability, and M is the magnetization vector. In a vacuum, B and H are proportional to each other. Inside a material they are different (see H and B inside and outside magnetic materials). The SI unit of the H-field is the ampere per metre (A/m),[14] and the CGS unit is the oersted (Oe).[12][9]: 286
Measurement
An instrument used to measure the local magnetic field is known as a magnetometer. Important classes of magnetometers include using induction magnetometers (or search-coil magnetometers) which measure only varying magnetic fields, rotating coil magnetometers, Hall effect magnetometers, NMR magnetometers, SQUID magnetometers, and fluxgate magnetometers. The magnetic fields of distant astronomical objects are measured through their effects on local charged particles. For instance, electrons spiraling around a field line produce synchrotron radiation that is detectable in radio waves. The finest precision for a magnetic field measurement was attained by Gravity Probe B at 5 aT (5×10−18 T).[15]
Visualization
Right: compass needles point in the direction of the local magnetic field, towards a magnet's south pole and away from its north pole.
The field can be visualized by a set of magnetic field lines, that follow the direction of the field at each point. The lines can be constructed by measuring the strength and direction of the magnetic field at a large number of points (or at every point in space). Then, mark each location with an arrow (called a vector) pointing in the direction of the local magnetic field with its magnitude proportional to the strength of the magnetic field. Connecting these arrows then forms a set of magnetic field lines. The direction of the magnetic field at any point is parallel to the direction of nearby field lines, and the local density of field lines can be made proportional to its strength. Magnetic field lines are like streamlines in fluid flow, in that they represent a continuous distribution, and a different resolution would show more or fewer lines.
An advantage of using magnetic field lines as a representation is that many laws of magnetism (and electromagnetism) can be stated completely and concisely using simple concepts such as the "number" of field lines through a surface. These concepts can be quickly "translated" to their mathematical form. For example, the number of field lines through a given surface is the surface integral of the magnetic field.[9]: 237
Various phenomena "display" magnetic field lines as though the field lines were physical phenomena. For example, iron filings placed in a magnetic field form lines that correspond to "field lines".[note 5] Magnetic field "lines" are also visually displayed in polar auroras, in which plasma particle dipole interactions create visible streaks of light that line up with the local direction of Earth's magnetic field.
Field lines can be used as a qualitative tool to visualize magnetic forces. In ferromagnetic substances like iron and in plasmas, magnetic forces can be understood by imagining that the field lines exert a tension, (like a rubber band) along their length, and a pressure perpendicular to their length on neighboring field lines. "Unlike" poles of magnets attract because they are linked by many field lines; "like" poles repel because their field lines do not meet, but run parallel, pushing on each other.
Magnetic field of permanent magnets
Permanent magnets are objects that produce their own persistent magnetic fields. They are made of ferromagnetic materials, such as iron and nickel, that have been magnetized, and they have both a north and a south pole.
The magnetic field of permanent magnets can be quite complicated, especially near the magnet. The magnetic field of a small[note 6] straight magnet is proportional to the magnet's strength (called its magnetic dipole moment m). The equations are non-trivial and also depend on the distance from the magnet and the orientation of the magnet. For simple magnets, m points in the direction of a line drawn from the south to the north pole of the magnet. Flipping a bar magnet is equivalent to rotating its m by 180 degrees.
The magnetic field of larger magnets can be obtained by modeling them as a collection of a large number of small magnets called dipoles each having their own m. The magnetic field produced by the magnet then is the net magnetic field of these dipoles; any net force on the magnet is a result of adding up the forces on the individual dipoles.
There were two simplified models for the nature of these dipoles. These two models produce two different magnetic fields, H and B. Outside a material, though, the two are identical (to a multiplicative constant) so that in many cases the distinction can be ignored. This is particularly true for magnetic fields, such as those due to electric currents, that are not generated by magnetic materials.
A realistic model of magnetism is more complicated than either of these models; neither model fully explains why materials are magnetic. The monopole model has no experimental support. Ampere's model explains some, but not all of a material's magnetic moment. Like Ampere's model predicts, the motion of electrons within an atom are connected to those electrons' orbital magnetic dipole moment, and these orbital moments do contribute to the magnetism seen at the macroscopic level. However, the motion of electrons is not classical, and the spin magnetic moment of electrons (which is not explained by either model) is also a significant contribution to the total moment of magnets.
Magnetic pole model
Historically, early physics textbooks would model the force and torques between two magnets as due to magnetic poles repelling or attracting each other in the same manner as the Coulomb force between electric charges. At the microscopic level, this model contradicts the experimental evidence, and the pole model of magnetism is no longer the typical way to introduce the concept.[10]: 204 However, it is still sometimes used as a macroscopic model for ferromagnetism due to its mathematical simplicity.[16]
In this model, a magnetic H-field is produced by fictitious magnetic charges that are spread over the surface of each pole. These magnetic charges are in fact related to the magnetization field M. The H-field, therefore, is analogous to the electric field E, which starts at a positive electric charge and ends at a negative electric charge. Near the north pole, therefore, all H-field lines point away from the north pole (whether inside the magnet or out) while near the south pole all H-field lines point toward the south pole (whether inside the magnet or out). Too, a north pole feels a force in the direction of the H-field while the force on the south pole is opposite to the H-field.
In the magnetic pole model, the elementary magnetic dipole m is formed by two opposite magnetic poles of pole strength qm separated by a small distance vector d, such that m = qm d. The magnetic pole model predicts correctly the field H both inside and outside magnetic materials, in particular the fact that H is opposite to the magnetization field M inside a permanent magnet.
Since it is based on the fictitious idea of a magnetic charge density, the pole model has limitations. Magnetic poles cannot exist apart from each other as electric charges can, but always come in north–south pairs. If a magnetized object is divided in half, a new pole appears on the surface of each piece, so each has a pair of complementary poles. The magnetic pole model does not account for magnetism that is produced by electric currents, nor the inherent connection between angular momentum and magnetism.
The pole model usually treats magnetic charge as a mathematical abstraction, rather than a physical property of particles. However, a magnetic monopole is a hypothetical particle (or class of particles) that physically has only one magnetic pole (either a north pole or a south pole). In other words, it would possess a "magnetic charge" analogous to an electric charge. Magnetic field lines would start or end on magnetic monopoles, so if they exist, they would give exceptions to the rule that magnetic field lines neither start nor end. Some theories (such as Grand Unified Theories) have predicted the existence of magnetic monopoles, but so far, none have been observed.
Amperian loop model
In the model developed by Ampere, the elementary magnetic dipole that makes up all magnets is a sufficiently small Amperian loop with current I and loop area A. The dipole moment of this loop is m = IA.
These magnetic dipoles produce a magnetic B-field.
The magnetic field of a magnetic dipole is depicted in the figure. From outside, the ideal magnetic dipole is identical to that of an ideal electric dipole of the same strength. Unlike the electric dipole, a magnetic dipole is properly modeled as a current loop having a current I and an area a. Such a current loop has a magnetic moment of
Interactions with magnets
Force between magnets
Specifying the force between two small magnets is quite complicated because it depends on the strength and orientation of both magnets and their distance and direction relative to each other. The force is particularly sensitive to rotations of the magnets due to magnetic torque. The force on each magnet depends on its magnetic moment and the magnetic field[note 7] of the other.
To understand the force between magnets, it is useful to examine the magnetic pole model given above. In this model, the H-field of one magnet pushes and pulls on both poles of a second magnet. If this H-field is the same at both poles of the second magnet then there is no net force on that magnet since the force is opposite for opposite poles. If, however, the magnetic field of the first magnet is nonuniform (such as the H near one of its poles), each pole of the second magnet sees a different field and is subject to a different force. This difference in the two forces moves the magnet in the direction of increasing magnetic field and may also cause a net torque.
This is a specific example of a general rule that magnets are attracted (or repulsed depending on the orientation of the magnet) into regions of higher magnetic field. Any non-uniform magnetic field, whether caused by permanent magnets or electric currents, exerts a force on a small magnet in this way.
The details of the Amperian loop model are different and more complicated but yield the same result: that magnetic dipoles are attracted/repelled into regions of higher magnetic field. Mathematically, the force on a small magnet having a magnetic moment m due to a magnetic field B is:[18]: Eq. 11.42
where the gradient ∇ is the change of the quantity m · B per unit distance and the direction is that of maximum increase of m · B. The dot product m · B = mBcos(θ), where m and B represent the magnitude of the m and B vectors and θ is the angle between them. If m is in the same direction as B then the dot product is positive and the gradient points "uphill" pulling the magnet into regions of higher B-field (more strictly larger m · B). This equation is strictly only valid for magnets of zero size, but is often a good approximation for not too large magnets. The magnetic force on larger magnets is determined by dividing them into smaller regions each having their own m then summing up the forces on each of these very small regions.
Magnetic torque on permanent magnets
If two like poles of two separate magnets are brought near each other, and one of the magnets is allowed to turn, it promptly rotates to align itself with the first. In this example, the magnetic field of the stationary magnet creates a magnetic torque on the magnet that is free to rotate. This magnetic torque τ tends to align a magnet's poles with the magnetic field lines. A compass, therefore, turns to align itself with Earth's magnetic field.
In terms of the pole model, two equal and opposite magnetic charges experiencing the same H also experience equal and opposite forces. Since these equal and opposite forces are in different locations, this produces a torque proportional to the distance (perpendicular to the force) between them. With the definition of m as the pole strength times the distance between the poles, this leads to τ = μ0 m H sin θ, where μ0 is a constant called the vacuum permeability, measuring 4π×10−7 V·s/(A·m) and θ is the angle between H and m.
Mathematically, the torque τ on a small magnet is proportional both to the applied magnetic field and to the magnetic moment m of the magnet:
where × represents the vector cross product. This equation includes all of the qualitative information included above. There is no torque on a magnet if m is in the same direction as the magnetic field, since the cross product is zero for two vectors that are in the same direction. Further, all other orientations feel a torque that twists them toward the direction of magnetic field.
Interactions with electric currents
Currents of electric charges both generate a magnetic field and feel a force due to magnetic B-fields.
Magnetic field due to moving charges and electric currents
All moving charged particles produce magnetic fields. Moving point charges, such as electrons, produce complicated but well known magnetic fields that depend on the charge, velocity, and acceleration of the particles.[19]
Magnetic field lines form in concentric circles around a cylindrical current-carrying conductor, such as a length of wire. The direction of such a magnetic field can be determined by using the "right-hand grip rule" (see figure at right). The strength of the magnetic field decreases with distance from the wire. (For an infinite length wire the strength is inversely proportional to the distance.)
Bending a current-carrying wire into a loop concentrates the magnetic field inside the loop while weakening it outside. Bending a wire into multiple closely spaced loops to form a coil or "solenoid" enhances this effect. A device so formed around an iron core may act as an electromagnet, generating a strong, well-controlled magnetic field. An infinitely long cylindrical electromagnet has a uniform magnetic field inside, and no magnetic field outside. A finite length electromagnet produces a magnetic field that looks similar to that produced by a uniform permanent magnet, with its strength and polarity determined by the current flowing through the coil.
The magnetic field generated by a steady current I (a constant flow of electric charges, in which charge neither accumulates nor is depleted at any point)[note 8] is described by the Biot–Savart law:[20]: 224
A slightly more general[21][note 9] way of relating the current to the B-field is through Ampère's law:
In a modified form that accounts for time varying electric fields, Ampère's law is one of four Maxwell's equations that describe electricity and magnetism.
Force on moving charges and current
Force on a charged particle
A charged particle moving in a B-field experiences a sideways force that is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field, the component of the velocity that is perpendicular to the magnetic field and the charge of the particle. This force is known as the Lorentz force, and is given by
The Lorentz force is always perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field that created it. When a charged particle moves in a static magnetic field, it traces a helical path in which the helix axis is parallel to the magnetic field, and in which the speed of the particle remains constant. Because the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the motion, the magnetic field can do no work on an isolated charge.[22][23] It can only do work indirectly, via the electric field generated by a changing magnetic field. It is often claimed that the magnetic force can do work to a non-elementary magnetic dipole, or to charged particles whose motion is constrained by other forces, but this is incorrect[24] because the work in those cases is performed by the electric forces of the charges deflected by the magnetic field.
Force on current-carrying wire
The force on a current carrying wire is similar to that of a moving charge as expected since a current carrying wire is a collection of moving charges. A current-carrying wire feels a force in the presence of a magnetic field. The Lorentz force on a macroscopic current is often referred to as the Laplace force. Consider a conductor of length ℓ, cross section A, and charge q due to electric current i. If this conductor is placed in a magnetic field of magnitude B that makes an angle θ with the velocity of charges in the conductor, the force exerted on a single charge q is
Relation between H and B
The formulas derived for the magnetic field above are correct when dealing with the entire current. A magnetic material placed inside a magnetic field, though, generates its own bound current, which can be a challenge to calculate. (This bound current is due to the sum of atomic sized current loops and the spin of the subatomic particles such as electrons that make up the material.) The H-field as defined above helps factor out this bound current; but to see how, it helps to introduce the concept of magnetization first.
Magnetization
The magnetization vector field M represents how strongly a region of material is magnetized. It is defined as the net magnetic dipole moment per unit volume of that region. The magnetization of a uniform magnet is therefore a material constant, equal to the magnetic moment m of the magnet divided by its volume. Since the SI unit of magnetic moment is A⋅m2, the SI unit of magnetization M is ampere per meter, identical to that of the H-field.
The magnetization M field of a region points in the direction of the average magnetic dipole moment in that region. Magnetization field lines, therefore, begin near the magnetic south pole and ends near the magnetic north pole. (Magnetization does not exist outside the magnet.)
In the Amperian loop model, the magnetization is due to combining many tiny Amperian loops to form a resultant current called bound current. This bound current, then, is the source of the magnetic B field due to the magnet. Given the definition of the magnetic dipole, the magnetization field follows a similar law to that of Ampere's law:[25]
In the magnetic pole model, magnetization begins at and ends at magnetic poles. If a given region, therefore, has a net positive "magnetic pole strength" (corresponding to a north pole) then it has more magnetization field lines entering it than leaving it. Mathematically this is equivalent to:
H-field and magnetic materials
In SI units, the H-field is related to the B-field by
In terms of the H-field, Ampere's law is
For the differential equivalent of this equation see Maxwell's equations. Ampere's law leads to the boundary condition
Similarly, a surface integral of H over any closed surface is independent of the free currents and picks out the "magnetic charges" within that closed surface:
which does not depend on the free currents.
The H-field, therefore, can be separated into two[note 10] independent parts:
where H0 is the applied magnetic field due only to the free currents and Hd is the demagnetizing field due only to the bound currents.
The magnetic H-field, therefore, re-factors the bound current in terms of "magnetic charges". The H field lines loop only around "free current" and, unlike the magnetic B field, begins and ends near magnetic poles as well.
Magnetism
Most materials respond to an applied B-field by producing their own magnetization M and therefore their own B-fields. Typically, the response is weak and exists only when the magnetic field is applied. The term magnetism describes how materials respond on the microscopic level to an applied magnetic field and is used to categorize the magnetic phase of a material. Materials are divided into groups based upon their magnetic behavior:
- Diamagnetic materials[28] produce a magnetization that opposes the magnetic field.
- Paramagnetic materials[28] produce a magnetization in the same direction as the applied magnetic field.
- Ferromagnetic materials and the closely related ferrimagnetic materials and antiferromagnetic materials[29][30] can have a magnetization independent of an applied B-field with a complex relationship between the two fields.
- Superconductors (and ferromagnetic superconductors)[31][32] are materials that are characterized by perfect conductivity below a critical temperature and magnetic field. They also are highly magnetic and can be perfect diamagnets below a lower critical magnetic field. Superconductors often have a broad range of temperatures and magnetic fields (the so-named mixed state) under which they exhibit a complex hysteretic dependence of M on B.
In the case of paramagnetism and diamagnetism, the magnetization M is often proportional to the applied magnetic field such that:
Stored energy
Energy is needed to generate a magnetic field both to work against the electric field that a changing magnetic field creates and to change the magnetization of any material within the magnetic field. For non-dispersive materials, this same energy is released when the magnetic field is destroyed so that the energy can be modeled as being stored in the magnetic field.
For linear, non-dispersive, materials (such that B = μH where μ is frequency-independent), the energy density is:
If there are no magnetic materials around then μ can be replaced by μ0. The above equation cannot be used for nonlinear materials, though; a more general expression given below must be used.
In general, the incremental amount of work per unit volume δW needed to cause a small change of magnetic field δB is:
Once the relationship between H and B is known this equation is used to determine the work needed to reach a given magnetic state. For hysteretic materials such as ferromagnets and superconductors, the work needed also depends on how the magnetic field is created. For linear non-dispersive materials, though, the general equation leads directly to the simpler energy density equation given above.
Appearance in Maxwell's equations
Like all vector fields, a magnetic field has two important mathematical properties that relates it to its sources. (For B the sources are currents and changing electric fields.) These two properties, along with the two corresponding properties of the electric field, make up Maxwell's Equations. Maxwell's Equations together with the Lorentz force law form a complete description of classical electrodynamics including both electricity and magnetism.
The first property is the divergence of a vector field A, ∇ · A, which represents how A "flows" outward from a given point. As discussed above, a B-field line never starts or ends at a point but instead forms a complete loop. This is mathematically equivalent to saying that the divergence of B is zero. (Such vector fields are called solenoidal vector fields.) This property is called Gauss's law for magnetism and is equivalent to the statement that there are no isolated magnetic poles or magnetic monopoles.
The second mathematical property is called the curl, such that ∇ × A represents how A curls or "circulates" around a given point. The result of the curl is called a "circulation source". The equations for the curl of B and of E are called the Ampère–Maxwell equation and Faraday's law respectively.
Gauss' law for magnetism
One important property of the B-field produced this way is that magnetic B-field lines neither start nor end (mathematically, B is a solenoidal vector field); a field line may only extend to infinity, or wrap around to form a closed curve, or follow a never-ending (possibly chaotic) path.[33] Magnetic field lines exit a magnet near its north pole and enter near its south pole, but inside the magnet B-field lines continue through the magnet from the south pole back to the north.[note 11] If a B-field line enters a magnet somewhere it has to leave somewhere else; it is not allowed to have an end point.
More formally, since all the magnetic field lines that enter any given region must also leave that region, subtracting the "number"[note 12] of field lines that enter the region from the number that exit gives identically zero. Mathematically this is equivalent to Gauss's law for magnetism:
Faraday's Law
A changing magnetic field, such as a magnet moving through a conducting coil, generates an electric field (and therefore tends to drive a current in such a coil). This is known as Faraday's law and forms the basis of many electrical generators and electric motors. Mathematically, Faraday's law is:
where is the electromotive force (or EMF, the voltage generated around a closed loop) and Φ is the magnetic flux—the product of the area times the magnetic field normal to that area. (This definition of magnetic flux is why B is often referred to as magnetic flux density.)[34]: 210 The negative sign represents the fact that any current generated by a changing magnetic field in a coil produces a magnetic field that opposes the change in the magnetic field that induced it. This phenomenon is known as Lenz's law. This integral formulation of Faraday's law can be converted[note 13] into a differential form, which applies under slightly different conditions.
Ampère's Law and Maxwell's correction
Similar to the way that a changing magnetic field generates an electric field, a changing electric field generates a magnetic field. This fact is known as Maxwell's correction to Ampère's law and is applied as an additive term to Ampere's law as given above. This additional term is proportional to the time rate of change of the electric flux and is similar to Faraday's law above but with a different and positive constant out front. (The electric flux through an area is proportional to the area times the perpendicular part of the electric field.)
The full law including the correction term is known as the Maxwell–Ampère equation. It is not commonly given in integral form because the effect is so small that it can typically be ignored in most cases where the integral form is used.
The Maxwell term is critically important in the creation and propagation of electromagnetic waves. Maxwell's correction to Ampère's Law together with Faraday's law of induction describes how mutually changing electric and magnetic fields interact to sustain each other and thus to form electromagnetic waves, such as light: a changing electric field generates a changing magnetic field, which generates a changing electric field again. These, though, are usually described using the differential form of this equation given below.
where J is the complete microscopic current density.
As discussed above, materials respond to an applied electric E field and an applied magnetic B field by producing their own internal "bound" charge and current distributions that contribute to E and B but are difficult to calculate. To circumvent this problem, H and D fields are used to re-factor Maxwell's equations in terms of the free current density Jf:
These equations are not any more general than the original equations (if the "bound" charges and currents in the material are known). They also must be supplemented by the relationship between B and H as well as that between E and D. On the other hand, for simple relationships between these quantities this form of Maxwell's equations can circumvent the need to calculate the bound charges and currents.
Formulation in special relativity and quantum electrodynamics
Relativistic Electrodynamics
As different aspects of the same phenomenon
According to the special theory of relativity, the partition of the electromagnetic force into separate electric and magnetic components is not fundamental, but varies with the observational frame of reference: An electric force perceived by one observer may be perceived by another (in a different frame of reference) as a magnetic force, or a mixture of electric and magnetic forces.
The magnetic field existing as electric field in other frames can be shown by consistency of equations obtained from Lorentz transformation of four force from Coulomb's Law in particle's rest frame with Maxwell's laws considering definition of fields from Lorentz force and for non accelerating condition. The form of magnetic field hence obtained by Lorentz transformation of four-force from the form of Coulomb's law in source's initial frame is given by:[35]
Formally, special relativity combines the electric and magnetic fields into a rank-2 tensor, called the electromagnetic tensor. Changing reference frames mixes these components. This is analogous to the way that special relativity mixes space and time into spacetime, and mass, momentum, and energy into four-momentum.[37] Similarly, the energy stored in a magnetic field is mixed with the energy stored in an electric field in the electromagnetic stress–energy tensor.
Magnetic vector potential
In advanced topics such as quantum mechanics and relativity it is often easier to work with a potential formulation of electrodynamics rather than in terms of the electric and magnetic fields. In this representation, the magnetic vector potential A, and the electric scalar potential φ, are defined using gauge fixing such that:
The vector potential, A given by this form may be interpreted as a generalized potential momentum per unit charge [38] just as φ is interpreted as a generalized potential energy per unit charge. There are multiple choices one can make for the potential fields that satisfy the above condition. However, the choice of potentials is represented by its respective gauge condition.
Maxwell's equations when expressed in terms of the potentials in Lorentz gauge can be cast into a form that agrees with special relativity.[39] In relativity, A together with φ forms a four-potential regardless of the gauge condition, analogous to the four-momentum that combines the momentum and energy of a particle. Using the four potential instead of the electromagnetic tensor has the advantage of being much simpler—and it can be easily modified to work with quantum mechanics.
Propagation of Electric and Magnetic fields
Special theory of relativity imposes the condition for events related by cause and effect to be time-like separated, that is that causal efficacy propagates no faster than light.[40] Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism are found to be in favor of this as electric and magnetic disturbances are found to travel at the speed of light in space. Electric and magnetic fields from classical electrodynamics obey the principle of locality in physics and are expressed in terms of retarded time or the time at which the cause of a measured field originated given that the influence of field travelled at speed of light. The retarded time for a point particle is given as solution of:
where is retarded time or the time at which the source's contribution of the field originated, is the position vector of the particle as function of time, is the point in space, is the time at which fields are measured and is the speed of light. The equation subtracts the time taken for light to travel from particle to the point in space from the time of measurement to find time of origin of the fields. The uniqueness of solution for for given , and is valid for charged particles moving slower than speed of light.[41]
Magnetic field of arbitrary moving point charge
The solution of maxwell's equations for electric and magnetic field of a point charge is expressed in terms of retarded time or the time at which the particle in the past causes the field at the point, given that the influence travels across space at the speed of light.
Any arbitrary motion of point charge causes electric and magnetic fields found by solving maxwell's equations using green's function for retarded potentials and hence finding the fields to be as follows:
where and are electric scalar potential and magnetic vector potential in Lorentz gauge, is the charge of the point source, is a unit vector pointing from charged particle to the point in space, is the velocity of the particle divided by the speed of light and is the corresponding Lorentz factor. Hence by the principle of superposition, the fields of a system of charges also obey principle of locality.
Quantum electrodynamics
In modern physics, the electromagnetic field is understood to be not a classical field, but rather a quantum field; it is represented not as a vector of three numbers at each point, but as a vector of three quantum operators at each point. The most accurate modern description of the electromagnetic interaction (and much else) is quantum electrodynamics (QED),[42] which is incorporated into a more complete theory known as the Standard Model of particle physics.
In QED, the magnitude of the electromagnetic interactions between charged particles (and their antiparticles) is computed using perturbation theory. These rather complex formulas produce a remarkable pictorial representation as Feynman diagrams in which virtual photons are exchanged.
Predictions of QED agree with experiments to an extremely high degree of accuracy: currently about 10−12 (and limited by experimental errors); for details see precision tests of QED. This makes QED one of the most accurate physical theories constructed thus far.
All equations in this article are in the classical approximation, which is less accurate than the quantum description mentioned here. However, under most everyday circumstances, the difference between the two theories is negligible.
Uses and examples
Earth's magnetic field
The Earth's magnetic field is produced by convection of a liquid iron alloy in the outer core. In a dynamo process, the movements drive a feedback process in which electric currents create electric and magnetic fields that in turn act on the currents.[43]
The field at the surface of the Earth is approximately the same as if a giant bar magnet were positioned at the center of the Earth and tilted at an angle of about 11° off the rotational axis of the Earth (see the figure).[44] The north pole of a magnetic compass needle points roughly north, toward the North Magnetic Pole. However, because a magnetic pole is attracted to its opposite, the North Magnetic Pole is actually the south pole of the geomagnetic field. This confusion in terminology arises because the pole of a magnet is defined by the geographical direction it points.[45]
Earth's magnetic field is not constant—the strength of the field and the location of its poles vary.[46] Moreover, the poles periodically reverse their orientation in a process called geomagnetic reversal. The most recent reversal occurred 780,000 years ago.[47]
Rotating magnetic fields
The rotating magnetic field is a key principle in the operation of alternating-current motors. A permanent magnet in such a field rotates so as to maintain its alignment with the external field. This effect was conceptualized by Nikola Tesla, and later utilized in his and others' early AC (alternating current) electric motors.
Magnetic torque is used to drive electric motors. In one simple motor design, a magnet is fixed to a freely rotating shaft and subjected to a magnetic field from an array of electromagnets. By continuously switching the electric current through each of the electromagnets, thereby flipping the polarity of their magnetic fields, like poles are kept next to the rotor; the resultant torque is transferred to the shaft.
A rotating magnetic field can be constructed using two orthogonal coils with 90 degrees phase difference in their AC currents. However, in practice such a system would be supplied through a three-wire arrangement with unequal currents.
This inequality would cause serious problems in standardization of the conductor size and so, to overcome it, three-phase systems are used where the three currents are equal in magnitude and have 120 degrees phase difference. Three similar coils having mutual geometrical angles of 120 degrees create the rotating magnetic field in this case. The ability of the three-phase system to create a rotating field, utilized in electric motors, is one of the main reasons why three-phase systems dominate the world's electrical power supply systems.
Synchronous motors use DC-voltage-fed rotor windings, which lets the excitation of the machine be controlled—and induction motors use short-circuited rotors (instead of a magnet) following the rotating magnetic field of a multicoiled stator. The short-circuited turns of the rotor develop eddy currents in the rotating field of the stator, and these currents in turn move the rotor by the Lorentz force.
In 1882, Nikola Tesla identified the concept of the rotating magnetic field. In 1885, Galileo Ferraris independently researched the concept. In 1888, Tesla gained U.S. Patent 381,968 for his work. Also in 1888, Ferraris published his research in a paper to the Royal Academy of Sciences in Turin.
Hall effect
The charge carriers of a current-carrying conductor placed in a transverse magnetic field experience a sideways Lorentz force; this results in a charge separation in a direction perpendicular to the current and to the magnetic field. The resultant voltage in that direction is proportional to the applied magnetic field. This is known as the Hall effect.
The Hall effect is often used to measure the magnitude of a magnetic field. It is used as well to find the sign of the dominant charge carriers in materials such as semiconductors (negative electrons or positive holes).
Magnetic circuits
An important use of H is in magnetic circuits where B = μH inside a linear material. Here, μ is the magnetic permeability of the material. This result is similar in form to Ohm's law J = σE, where J is the current density, σ is the conductance and E is the electric field. Extending this analogy, the counterpart to the macroscopic Ohm's law (I = V⁄R) is:
where is the magnetic flux in the circuit, is the magnetomotive force applied to the circuit, and Rm is the reluctance of the circuit. Here the reluctance Rm is a quantity similar in nature to resistance for the flux. Using this analogy it is straightforward to calculate the magnetic flux of complicated magnetic field geometries, by using all the available techniques of circuit theory.
Largest magnetic fields
This section needs to be updated. (July 2021) |
As of October 2018, the largest magnetic field produced over a macroscopic volume outside a lab setting is 2.8 kT (VNIIEF in Sarov, Russia, 1998).[48][49] As of October 2018, the largest magnetic field produced in a laboratory over a macroscopic volume was 1.2 kT by researchers at the University of Tokyo in 2018.[49] The largest magnetic fields produced in a laboratory occur in particle accelerators, such as RHIC, inside the collisions of heavy ions, where microscopic fields reach 1014 T.[50][51] Magnetars have the strongest known magnetic fields of any naturally occurring object, ranging from 0.1 to 100 GT (108 to 1011 T).[52]
History
Early developments
While magnets and some properties of magnetism were known to ancient societies, the research of magnetic fields began in 1269 when French scholar Petrus Peregrinus de Maricourt mapped out the magnetic field on the surface of a spherical magnet using iron needles. Noting the resulting field lines crossed at two points he named those points "poles" in analogy to Earth's poles. He also articulated the principle that magnets always have both a north and south pole, no matter how finely one slices them.[53][note 14]
Almost three centuries later, William Gilbert of Colchester replicated Petrus Peregrinus's work and was the first to state explicitly that Earth is a magnet.[54]: 34 Published in 1600, Gilbert's work, De Magnete, helped to establish magnetism as a science.
Mathematical development
In 1750, John Michell stated that magnetic poles attract and repel in accordance with an inverse square law[54]: 56 Charles-Augustin de Coulomb experimentally verified this in 1785 and stated explicitly that north and south poles cannot be separated.[54]: 59 Building on this force between poles, Siméon Denis Poisson (1781–1840) created the first successful model of the magnetic field, which he presented in 1824.[54]: 64 In this model, a magnetic H-field is produced by magnetic poles and magnetism is due to small pairs of north–south magnetic poles.
Three discoveries in 1820 challenged this foundation of magnetism. Hans Christian Ørsted demonstrated that a current-carrying wire is surrounded by a circular magnetic field.[note 15][55] Then André-Marie Ampère showed that parallel wires with currents attract one another if the currents are in the same direction and repel if they are in opposite directions.[54]: 87 [56] Finally, Jean-Baptiste Biot and Félix Savart announced empirical results about the forces that a current-carrying long, straight wire exerted on a small magnet, determining the forces were inversely proportional to the perpendicular distance from the wire to the magnet.[57][54]: 86 Laplace later deduced a law of force based on the differential action of a differential section of the wire,[57][58] which became known as the Biot–Savart law, as Laplace did not publish his findings.[59]
Extending these experiments, Ampère published his own successful model of magnetism in 1825. In it, he showed the equivalence of electrical currents to magnets[54]: 88 and proposed that magnetism is due to perpetually flowing loops of current instead of the dipoles of magnetic charge in Poisson's model.[note 16] Further, Ampère derived both Ampère's force law describing the force between two currents and Ampère's law, which, like the Biot–Savart law, correctly described the magnetic field generated by a steady current. Also in this work, Ampère introduced the term electrodynamics to describe the relationship between electricity and magnetism.[54]: 88–92
In 1831, Michael Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction when he found that a changing magnetic field generates an encircling electric field, formulating what is now known as Faraday's law of induction.[54]: 189–192 Later, Franz Ernst Neumann proved that, for a moving conductor in a magnetic field, induction is a consequence of Ampère's force law.[54]: 222 In the process, he introduced the magnetic vector potential, which was later shown to be equivalent to the underlying mechanism proposed by Faraday.[54]: 225
In 1850, Lord Kelvin, then known as William Thomson, distinguished between two magnetic fields now denoted H and B. The former applied to Poisson's model and the latter to Ampère's model and induction.[54]: 224 Further, he derived how H and B relate to each other and coined the term permeability.[54]: 245 [60]
Between 1861 and 1865, James Clerk Maxwell developed and published Maxwell's equations, which explained and united all of classical electricity and magnetism. The first set of these equations was published in a paper entitled On Physical Lines of Force in 1861. These equations were valid but incomplete. Maxwell completed his set of equations in his later 1865 paper A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field and demonstrated the fact that light is an electromagnetic wave. Heinrich Hertz published papers in 1887 and 1888 experimentally confirming this fact.[61][62]
Modern developments
In 1887, Tesla developed an induction motor that ran on alternating current. The motor used polyphase current, which generated a rotating magnetic field to turn the motor (a principle that Tesla claimed to have conceived in 1882).[63][64][65] Tesla received a patent for his electric motor in May 1888.[66][67] In 1885, Galileo Ferraris independently researched rotating magnetic fields and subsequently published his research in a paper to the Royal Academy of Sciences in Turin, just two months before Tesla was awarded his patent, in March 1888.[68]
The twentieth century showed that classical electrodynamics is already consistent with special relativity, and extended classical electrodynamics to work with quantum mechanics. Albert Einstein, in his paper of 1905 that established relativity, showed that both the electric and magnetic fields are part of the same phenomena viewed from different reference frames. Finally, the emergent field of quantum mechanics was merged with electrodynamics to form quantum electrodynamics, which first formalized the notion that electromagnetic field energy is quantized in the form of photons.
See also
General
- Magnetohydrodynamics – the study of the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids
- Magnetic hysteresis – application to ferromagnetism
- Magnetic nanoparticles – extremely small magnetic particles that are tens of atoms wide
- Magnetic reconnection – an effect that causes solar flares and auroras
- Magnetic scalar potential
- SI electromagnetism units – common units used in electromagnetism
- Orders of magnitude (magnetic field) – list of magnetic field sources and measurement devices from smallest magnetic fields to largest detected
- Upward continuation
- Moses Effect
Mathematics
- Magnetic helicity – extent to which a magnetic field wraps around itself
Applications
- Dynamo theory – a proposed mechanism for the creation of the Earth's magnetic field
- Helmholtz coil – a device for producing a region of nearly uniform magnetic field
- Magnetic field viewing film – Film used to view the magnetic field of an area
- Magnetic pistol – a device on torpedoes or naval mines that detect the magnetic field of their target
- Maxwell coil – a device for producing a large volume of an almost constant magnetic field
- Stellar magnetic field – a discussion of the magnetic field of stars
- Teltron tube – device used to display an electron beam and demonstrates effect of electric and magnetic fields on moving charges
Notes
- From the outside, the field of a dipole of magnetic charge has exactly the same form as a current loop when both are sufficiently small. Therefore, the two models differ only for magnetism inside magnetic material.
References
Further reading
- Jiles, David (1994). Introduction to Electronic Properties of Materials (1st ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-0-412-49580-9.
- Tipler, Paul (2004). Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Electricity, Magnetism, Light, and Elementary Modern Physics (5th ed.). W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-0810-0. OCLC 51095685.
External links
 Media related to Magnetic fields at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Magnetic fields at Wikimedia Commons- Crowell, B., "Electromagnetism".
- Nave, R., "Magnetic Field". HyperPhysics.
- "Magnetism", The Magnetic Field (archived 9 July 2006). theory.uwinnipeg.ca.
- Hoadley, Rick, "What do magnetic fields look like?" 17 July 2005.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_field#Force_on_current-carrying_wire
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ[1]) is a common type of alternating current (AC) used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution.[2] It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral return wire) and is the most common method used by electrical grids worldwide to transfer power.
Three-phase electrical power was developed in the 1880s by several people. In three-phase power, the voltage on each wire is 120 degrees phase shifted relative to each of the other wires. Because it is an AC system, it allows the voltages to be easily stepped-up using transformers to high voltage for transmission and back down for distribution, giving high efficiency.
A three-wire three-phase circuit is usually more economical than an equivalent two-wire single-phase circuit at the same line to ground voltage because it uses less conductor material to transmit a given amount of electrical power.[3] Three-phase power is mainly used directly to power large induction motors, other electric motors and other heavy loads. Small loads often use only a two-wire single-phase circuit, which may be derived from a three-phase system.
Terminology
The conductors between a voltage source and a load are called lines, and the voltage between any two lines is called line voltage. The voltage measured between any line and neutral is called phase voltage.[4] For example, for a 208/120 volt service, the line voltage is 208 Volts, and the phase voltage is 120 Volts.
History
Polyphase power systems were independently invented by Galileo Ferraris, Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky, Jonas Wenström, John Hopkinson, William Stanley Jr., and Nikola Tesla in the late 1880s.[5]
Three phase power evolved out of electric motor development. In 1885, Galileo Ferraris was doing research on rotating magnetic fields. Ferraris experimented with different types of asynchronous electric motors. The research and his studies resulted in the development of an alternator, which may be thought of as an alternating-current motor operating in reverse, so as to convert mechanical (rotating) power into electric power (as alternating current). On 11 March 1888, Ferraris published his research in a paper to the Royal Academy of Sciences in Turin.
Two months later Nikola Tesla gained U.S. Patent 381,968 for a three-phase electric motor design, application filed October 12, 1887. Figure 13 of this patent shows that Tesla envisaged his three-phase motor being powered from the generator via six wires.
These alternators operated by creating systems of alternating currents displaced from one another in phase by definite amounts, and depended on rotating magnetic fields for their operation. The resulting source of polyphase power soon found widespread acceptance. The invention of the polyphase alternator is key in the history of electrification, as is the power transformer. These inventions enabled power to be transmitted by wires economically over considerable distances. Polyphase power enabled the use of water-power (via hydroelectric generating plants in large dams) in remote places, thereby allowing the mechanical energy of the falling water to be converted to electricity, which then could be fed to an electric motor at any location where mechanical work needed to be done. This versatility sparked the growth of power-transmission network grids on continents around the globe.
Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky developed a three-phase electrical generator and a three-phase electric motor in 1888 and studied star and delta connections. His three-phase three-wire transmission system was displayed in Europe at the International Electro-Technical Exhibition of 1891, where Dolivo-Dobrovolsky used the system to transmit electric power at the distance of 176 km with 75% efficiency. In 1891 he also created a three-phase transformer and short-circuited (squirrel-cage) induction motor.[6][7] He designed the world's first three-phase hydroelectric power plant in 1891. Inventor Jonas Wenström received in 1890 a Swedish patent on the same three-phase system.[8]
Principle
In a symmetric three-phase power supply system, three conductors each carry an alternating current of the same frequency and voltage amplitude relative to a common reference, but with a phase difference of one third of a cycle (i.e., 120 degrees out of phase) between each. The common reference is usually connected to ground and often to a current-carrying conductor called the neutral. Due to the phase difference, the voltage on any conductor reaches its peak at one third of a cycle after one of the other conductors and one third of a cycle before the remaining conductor. This phase delay gives constant power transfer to a balanced linear load. It also makes it possible to produce a rotating magnetic field in an electric motor and generate other phase arrangements using transformers (for instance, a two phase system using a Scott-T transformer). The amplitude of the voltage difference between two phases is (1.732...) times the amplitude of the voltage of the individual phases.
The symmetric three-phase systems described here are simply referred to as three-phase systems because, although it is possible to design and implement asymmetric three-phase power systems (i.e., with unequal voltages or phase shifts), they are not used in practice because they lack the most important advantages of symmetric systems.
In a three-phase system feeding a balanced and linear load, the sum of the instantaneous currents of the three conductors is zero. In other words, the current in each conductor is equal in magnitude to the sum of the currents in the other two, but with the opposite sign. The return path for the current in any phase conductor is the other two phase conductors.
Constant power transfer and cancelling phase currents are possible with any number (greater than one) of phases, maintaining the capacity-to-conductor material ratio that is twice that of single-phase power. However, two phases result in a less smooth (pulsating) current to the load (making smooth power transfer a challenge), and more than three phases complicate infrastructure unnecessarily.[9]
Three-phase systems may have a fourth wire, common in low-voltage distribution. This is the neutral wire. The neutral allows three separate single-phase supplies to be provided at a constant voltage and is commonly used for supplying multiple single-phase loads. The connections are arranged so that, as far as possible in each group, equal power is drawn from each phase. Further up the distribution system, the currents are usually well balanced. Transformers may be wired to have a four-wire secondary and a three-wire primary, while allowing unbalanced loads and the associated secondary-side neutral currents.
Phase sequence
Wiring for three phases is typically identified by colors that vary by country. The phases must be connected in the correct order to achieve the intended direction of rotation of three-phase motors. For example, pumps and fans do not work in reverse. Maintaining the identity of phases is required if two sources could be connected at the same time. A direct connection between two different phases is a short circuit.
Advantages
As compared to a single-phase AC power supply that uses two conductors (phase and neutral), a three-phase supply with no neutral and the same phase-to-ground voltage and current capacity per phase can transmit three times as much power using just 1.5 times as many wires (i.e., three instead of two). Thus, the ratio of capacity to conductor material is doubled.[10] The ratio of capacity to conductor material increases to 3:1 with an ungrounded three-phase and center-grounded single-phase system (or 2.25:1 if both employ grounds of the same gauge as the conductors). This leads to higher efficiency, lower weight, and cleaner waveforms.
Three-phase supplies have properties that make them desirable in electric power distribution systems:
- The phase currents tend to cancel out one another, summing to zero in the case of a linear balanced load. This makes it possible to reduce the size of the neutral conductor because it carries little or no current. With a balanced load, all the phase conductors carry the same current and so can be the same size.
- Power transfer into a linear balanced load is constant. In motor/generator applications, this helps to reduce vibrations.
- Three-phase systems can produce a rotating magnetic field with a specified direction and constant magnitude, which simplifies the design of electric motors, as no starting circuit is required.
Most household loads are single-phase. In North American residences, three-phase power might feed an apartment block, while the household loads are connected as single phase. In lower-density areas, a single phase might be used for distribution. Some high-power domestic appliances such as electric stoves and clothes dryers are powered by a split phase system at 240 volts or from two phases of a three phase system at 208 volts.
Generation and distribution
At the power station, an electrical generator converts mechanical power into a set of three AC electric currents, one from each coil (or winding) of the generator. The windings are arranged such that the currents are at the same frequency but with the peaks and troughs of their wave forms offset to provide three complementary currents with a phase separation of one-third cycle (120° or 2π⁄3 radians). The generator frequency is typically 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the country.
At the power station, transformers change the voltage from generators to a level suitable for transmission in order to minimize losses.
After further voltage conversions in the transmission network, the voltage is finally transformed to the standard utilization before power is supplied to customers.
Most automotive alternators generate three-phase AC and rectify it to DC with a diode bridge.[13]
Transformer connections
A "delta" connected transformer winding is connected between phases of a three-phase system. A "wye" transformer connects each winding from a phase wire to a common neutral point.
A single three-phase transformer can be used, or three single-phase transformers.
In an "open delta" or "V" system, only two transformers are used. A closed delta made of three single-phase transformers can operate as an open delta if one of the transformers has failed or needs to be removed.[14] In open delta, each transformer must carry current for its respective phases as well as current for the third phase, therefore capacity is reduced to 87%. With one of three transformers missing and the remaining two at 87% efficiency, the capacity is 58% (2⁄3 of 87%).[15][16]
Where a delta-fed system must be grounded for detection of stray current to ground or protection from surge voltages, a grounding transformer (usually a zigzag transformer) may be connected to allow ground fault currents to return from any phase to ground. Another variation is a "corner grounded" delta system, which is a closed delta that is grounded at one of the junctions of transformers.[17]
Three-wire and four-wire circuits
There are two basic three-phase configurations: wye (Y) and delta (Δ). As shown in the diagram, a delta configuration requires only three wires for transmission but a wye (star) configuration may have a fourth wire. The fourth wire, if present, is provided as a neutral and is normally grounded. The three-wire and four-wire designations do not count the ground wire present above many transmission lines, which is solely for fault protection and does not carry current under normal use.
A four-wire system with symmetrical voltages between phase and neutral is obtained when the neutral is connected to the "common star point" of all supply windings. In such a system, all three phases will have the same magnitude of voltage relative to the neutral. Other non-symmetrical systems have been used.
The four-wire wye system is used when a mixture of single-phase and three-phase loads are to be served, such as mixed lighting and motor loads. An example of application is local distribution in Europe (and elsewhere), where each customer may be only fed from one phase and the neutral (which is common to the three phases). When a group of customers sharing the neutral draw unequal phase currents, the common neutral wire carries the currents resulting from these imbalances. Electrical engineers try to design the three-phase power system for any one location so that the power drawn from each of three phases is the same, as far as possible at that site.[18] Electrical engineers also try to arrange the distribution network so the loads are balanced as much as possible, since the same principles that apply to individual premises also apply to the wide-scale distribution system power. Hence, every effort is made by supply authorities to distribute the power drawn on each of the three phases over a large number of premises so that, on average, as nearly as possible a balanced load is seen at the point of supply.
For domestic use, some countries such as the UK may supply one phase and neutral at a high current (up to 100 A) to one property, while others such as Germany may supply 3 phases and neutral to each customer, but at a lower fuse rating, typically 40–63 A per phase, and "rotated" to avoid the effect that more load tends to be put on the first phase.[citation needed]
Based on wye (Y) and delta (Δ) connection. Generally, there are four different types of three-phase transformer winding connections for transmission and distribution purposes.
- wye (Y) - wye (Y) is used for small current and high voltage.
- Delta (Δ) - Delta (Δ) is used for large currents and low voltages.
- Delta (Δ) - wye (Y) is used for step-up transformers i.e., at generating stations.
- wye (Y) - Delta (Δ) is used for step-down transformers i.e., at the end of the transmission.
In North America, a high-leg delta supply is sometimes used where one winding of a delta-connected transformer feeding the load is center-tapped and that center tap is grounded and connected as a neutral as shown in the second diagram. This setup produces three different voltages: If the voltage between the center tap (neutral) and each of the top and bottom taps (phase and anti-phase) is 120 V (100%), the voltage across the phase and anti-phase lines is 240 V (200%), and the neutral to "high leg" voltage is ≈ 208 V (173%).[14]
The reason for providing the delta connected supply is usually to power large motors requiring a rotating field. However, the premises concerned will also require the "normal" North American 120 V supplies, two of which are derived (180 degrees "out of phase") between the "neutral" and either of the center tapped phase points.
Balanced circuits
In the perfectly balanced case all three lines share equivalent loads. Examining the circuits we can derive relationships between line voltage and current, and load voltage and current for wye and delta connected loads.
In a balanced system each line will produce equal voltage magnitudes at phase angles equally spaced from each other. With V1 as our reference and V3 lagging V2 lagging V1, using angle notation, and VLN the voltage between the line and the neutral we have:[19]
These voltages feed into either a wye or delta connected load.
Wye (or, star; Y)
The voltage seen by the load will depend on the load connection; for the wye case, connecting each load to a phase (line-to-neutral) voltages gives:[19]
where Ztotal is the sum of line and load impedances (Ztotal = ZLN + ZY), and θ is the phase of the total impedance (Ztotal).
The phase angle difference between voltage and current of each phase is not necessarily 0 and is dependent on the type of load impedance, Zy. Inductive and capacitive loads will cause current to either lag or lead the voltage. However, the relative phase angle between each pair of lines (1 to 2, 2 to 3, and 3 to 1) will still be −120°.
- Vab = (1∠α − 1∠α + 120°) √3 |V|∠α + 30°
- Vbc = √3 |V|∠α − 90°
- Vca = √3 |V|∠α + 150°
By applying Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) to the neutral node, the three phase currents sum to the total current in the neutral line. In the balanced case:
Delta (Δ)
In the delta circuit, loads are connected across the lines, and so loads see line-to-line voltages:[19]
(Φv1 is the phase shift for the first voltage, commonly taken to be 0°; in this case, Φv2 = −120° and Φv3 = −240° or 120°.)
Further:
where θ is the phase of delta impedance (ZΔ).
Relative angles are preserved, so I31 lags I23 lags I12 by 120°. Calculating line currents by using KCL at each delta node gives:
and similarly for each other line:
where, again, θ is the phase of delta impedance (ZΔ).
- Ia = Iab − Ica = √3 Iab∠−30°
- Ib = Ibc − Iab
- Ic = Ica − Ibc
- S3Φ = 3VphaseI*phase
Inspection of a phasor diagram, or conversion from phasor notation to complex notation, illuminates how the difference between two line-to-neutral voltages yields a line-to-line voltage that is greater by a factor of √3. As a delta configuration connects a load across phases of a transformer, it delivers the line-to-line voltage difference, which is √3 times greater than the line-to-neutral voltage delivered to a load in the wye configuration. As the power transferred is V2/Z, the impedance in the delta configuration must be 3 times what it would be in a wye configuration for the same power to be transferred.
Single-phase loads
Except in a high-leg delta system and a corner grounded delta system, single-phase loads may be connected across any two phases, or a load can be connected from phase to neutral.[20] Distributing single-phase loads among the phases of a three-phase system balances the load and makes most economical use of conductors and transformers.
In a symmetrical three-phase four-wire, wye system, the three phase conductors have the same voltage to the system neutral. The voltage between line conductors is √3 times the phase conductor to neutral voltage:[21]
The currents returning from the customers' premises to the supply transformer all share the neutral wire. If the loads are evenly distributed on all three phases, the sum of the returning currents in the neutral wire is approximately zero. Any unbalanced phase loading on the secondary side of the transformer will use the transformer capacity inefficiently.
If the supply neutral is broken, phase-to-neutral voltage is no longer maintained. Phases with higher relative loading will experience reduced voltage, and phases with lower relative loading will experience elevated voltage, up to the phase-to-phase voltage.
A high-leg delta provides phase-to-neutral relationship of VLL = 2 VLN , however, LN load is imposed on one phase.[14] A transformer manufacturer's page suggests that LN loading not exceed 5% of transformer capacity.[22]
Since √3 ≈ 1.73, defining VLN as 100% gives VLL ≈ 100% × 1.73 = 173%. If VLL was set as 100%, then VLN ≈ 57.7%.
Unbalanced loads
When the currents on the three live wires of a three-phase system are not equal or are not at an exact 120° phase angle, the power loss is greater than for a perfectly balanced system. The method of symmetrical components is used to analyze unbalanced systems.
Non-linear loads
With linear loads, the neutral only carries the current due to imbalance between the phases. Gas-discharge lamps and devices that utilize rectifier-capacitor front-end such as switch-mode power supplies, computers, office equipment and such produce third-order harmonics that are in-phase on all the supply phases. Consequently, such harmonic currents add in the neutral in a wye system (or in the grounded (zigzag) transformer in a delta system), which can cause the neutral current to exceed the phase current.[20][23]
Three-phase loads
An important class of three-phase load is the electric motor. A three-phase induction motor has a simple design, inherently high starting torque and high efficiency. Such motors are applied in industry for many applications. A three-phase motor is more compact and less costly than a single-phase motor of the same voltage class and rating, and single-phase AC motors above 10 HP (7.5 kW) are uncommon. Three-phase motors also vibrate less and hence last longer than single-phase motors of the same power used under the same conditions.[24]
Resistance heating loads such as electric boilers or space heating may be connected to three-phase systems. Electric lighting may also be similarly connected.
Line frequency flicker in light is detrimental to high speed cameras used in sports event broadcasting for slow motion replays. It can be reduced by evenly spreading line frequency operated light sources across the three phases so that the illuminated area is lit from all three phases. This technique was applied successfully at the 2008 Beijing Olympics.[25]
Rectifiers may use a three-phase source to produce a six-pulse DC output.[26] The output of such rectifiers is much smoother than rectified single phase and, unlike single-phase, does not drop to zero between pulses. Such rectifiers may be used for battery charging, electrolysis processes such as aluminium production or for operation of DC motors. "Zig-zag" transformers may make the equivalent of six-phase full-wave rectification, twelve pulses per cycle, and this method is occasionally employed to reduce the cost of the filtering components, while improving the quality of the resulting DC.
One example of a three-phase load is the electric arc furnace used in steelmaking and in refining of ores.
In many European countries electric stoves are usually designed for a three-phase feed with permanent connection. Individual heating units are often connected between phase and neutral to allow for connection to a single-phase circuit if three-phase is not available.[27] Other usual three-phase loads in the domestic field are tankless water heating systems and storage heaters. Homes in Europe and the UK have standardized on a nominal 230 V between any phase and ground. (Existing supplies remain near 240 V in the UK.) Most groups of houses are fed from a three-phase street transformer so that individual premises with above-average demand can be fed with a second or third phase connection.
Phase converters
Phase converters are used when three-phase equipment needs to be operated on a single-phase power source. They are used when three-phase power is not available or cost is not justifiable. Such converters may also allow the frequency to be varied, allowing speed control. Some railway locomotives use a single-phase source to drive three-phase motors fed through an electronic drive.[28]
A rotary phase converter is a three-phase motor with special starting arrangements and power factor correction that produces balanced three-phase voltages. When properly designed, these rotary converters can allow satisfactory operation of a three-phase motor on a single-phase source. In such a device, the energy storage is performed by the inertia (flywheel effect) of the rotating components. An external flywheel is sometimes found on one or both ends of the shaft.
A three-phase generator can be driven by a single-phase motor. This motor-generator combination can provide a frequency changer function as well as phase conversion, but requires two machines with all their expenses and losses. The motor-generator method can also form an uninterruptible power supply when used in conjunction with a large flywheel and a battery-powered DC motor; such a combination will deliver nearly constant power compared to the temporary frequency drop experienced with a standby generator set gives until the standby generator kicks in.
Capacitors and autotransformers can be used to approximate a three-phase system in a static phase converter, but the voltage and phase angle of the additional phase may only be useful for certain loads.
Variable-frequency drives and digital phase converters use power electronic devices to synthesize a balanced three-phase supply from single-phase input power.
Testing
Verification of the phase sequence in a circuit is of considerable practical importance. Two sources of three-phase power must not be connected in parallel unless they have the same phase sequence, for example, when connecting a generator to an energized distribution network or when connecting two transformers in parallel. Otherwise, the interconnection will behave like a short circuit, and excess current will flow. The direction of rotation of three-phase motors can be reversed by interchanging any two phases; it may be impractical or harmful to test a machine by momentarily energizing the motor to observe its rotation. Phase sequence of two sources can be verified by measuring voltage between pairs of terminals and observing that terminals with very low voltage between them will have the same phase, whereas pairs that show a higher voltage are on different phases.
Where the absolute phase identity is not required, phase rotation test instruments can be used to identify the rotation sequence with one observation. The phase rotation test instrument may contain a miniature three-phase motor, whose direction of rotation can be directly observed through the instrument case. Another pattern uses a pair of lamps and an internal phase-shifting network to display the phase rotation. Another type of instrument can be connected to a de-energized three-phase motor and can detect the small voltages induced by residual magnetism, when the motor shaft is rotated by hand. A lamp or other indicator lights to show the sequence of voltages at the terminals for the given direction of shaft rotation.[29]
Alternatives to three-phase
- Split-phase electric power
- Used when three-phase power is not available and allows double the normal utilization voltage to be supplied for high-power loads.
- Two-phase electric power
- Uses two AC voltages, with a 90-electrical-degree phase shift between them. Two-phase circuits may be wired with two pairs of conductors, or two wires may be combined, requiring only three wires for the circuit. Currents in the common conductor add to 1.4 times the current in the individual phases, so the common conductor must be larger. Two-phase and three-phase systems can be interconnected by a Scott-T transformer, invented by Charles F. Scott.[30] Very early AC machines, notably the first generators at Niagara Falls, used a two-phase system, and some remnant two-phase distribution systems still exist, but three-phase systems have displaced the two-phase system for modern installations.
- Monocyclic power
- An asymmetrical modified two-phase power system used by General Electric around 1897, championed by Charles Proteus Steinmetz and Elihu Thomson. This system was devised to avoid patent infringement. In this system, a generator was wound with a full-voltage single-phase winding intended for lighting loads and with a small fraction (usually 1/4 of the line voltage) winding that produced a voltage in quadrature with the main windings. The intention was to use this "power wire" additional winding to provide starting torque for induction motors, with the main winding providing power for lighting loads. After the expiration of the Westinghouse patents on symmetrical two-phase and three-phase power distribution systems, the monocyclic system fell out of use; it was difficult to analyze and did not last long enough for satisfactory energy metering to be developed.
- High-phase-order systems
- Have been built and tested for power transmission. Such transmission lines typically would use six or twelve phases. High-phase-order transmission lines allow transfer of slightly less than proportionately higher power through a given volume without the expense of a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) converter at each end of the line. However, they require correspondingly more pieces of equipment.
- DC
- AC was historically used because it could be easily transformed to higher voltages for long distance transmission. However modern electronics can raise the voltage of DC with high efficiency, and DC lacks skin effect which permits transmission wires to be lighter and cheaper and so high-voltage direct current gives lower losses over long distances.
Color codes
Conductors of a three-phase system are usually identified by a color code, to allow for balanced loading and to assure the correct phase rotation for motors. Colors used may adhere to International Standard IEC 60446 (later IEC 60445), older standards or to no standard at all and may vary even within a single installation. For example, in the U.S. and Canada, different color codes are used for grounded (earthed) and ungrounded systems.
| Country | Phases[note 1] | Neutral, N[note 2] |
Protective earth, PE[note 3] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | ||||||||||
| Australia and New Zealand (AS/NZS 3000:2007 Figure 3.2, or IEC 60446 as approved by AS:3000) | Red, or brown[note 4] | White;[note 4] prev. yellow | Dark blue, or grey[note 4] | Black, or blue[note 4] | Green/Yellow-striped; (Installations prior to 1966, Green.) | |||||||
| Canada | Mandatory[31] | Red[note 5] | Black | Blue | White, or grey | Green perhaps yellow-striped, or uninsulated | ||||||
| Isolated systems[32] | Orange | Brown | Yellow | White, or grey | Green perhaps yellow-striped | |||||||
| European CENELEC (European Union and others; since April 2004, IEC 60446, later IEC 60445-2017), United Kingdom (since 31 March 2004), Hong Kong (from July 2007), Singapore (from March 2009), Russia (since 2009; GOST R 50462), Argentina, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, South Korea (from Jan. 2021) | Brown | Black | Grey | Blue | Green/yellow-striped[note 6] | |||||||
| Older European (prior to IEC 60446, varied by country)[note 7] | ||||||||||||
| UK (before April 2006), Hong Kong (before April 2009), South Africa, Malaysia, Singapore (before February 2011) | Red | Yellow | Blue | Black | Green/yellow-striped; before c. 1970, green | |||||||
| India | Red | Yellow | Blue | Black | Green perhaps yellow-striped | |||||||
| Chile - NCH 4/2003 | Blue | Black | Red | White | Green perhaps yellow-striped | |||||||
| Former USSR (Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan; before 2009), People's Republic of China[note 8] (GB 50303-2002 Section 15.2.2) | Yellow | Green | Red | Sky blue | Green/yellow-striped | |||||||
| Norway (before CENELEC adoption) | Black | White/grey | Brown | Blue | Yellow/green-striped; prev. yellow, or uninsulated | |||||||
| United States | Common practice[note 9] | Black | Red | Blue | White, or grey | Green perhaps yellow-striped,[note 10] or uninsulated | ||||||
| Alternative practice[note 11] | Brown | Orange (delta[note 12]) | Yellow | Grey, or white | Green | |||||||
| Violet (wye) | ||||||||||||
See also
Notes
- Must be the high leg, if it is present.
References
We also stated one rationale for this three-phase system; namely, that a three-phase generator experiences a constant torque on its rotor as opposed to the pulsating torque that appears in a single- or two-phase machine, which is obviously preferable from a mechanical engineering standpoint.
- C22.1-15—Canadian Electrical Code, Part I: Safety Standard for Electrical Installations (23rd ed.). Canadian Standards Association. 2015. Rule 24–208(c). ISBN 978-1-77139-718-6.
External links
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three-phase_electric_power
In electrical engineering, ground and neutral are circuit conductors used in alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The ground circuit is connected to earth, and neutral circuit is usually connected to ground. As the neutral point of an electrical supply system is often connected to earth ground, ground and neutral are closely related. Under certain conditions, a conductor used to connect to a system neutral is also used for grounding (earthing) of equipment and structures. Current carried on a grounding conductor can result in objectionable or dangerous voltages appearing on equipment enclosures, so the installation of grounding conductors and neutral conductors is carefully defined in electrical regulations. Where a neutral conductor is used also to connect equipment enclosures to earth, care must be taken that the neutral conductor never rises to a high voltage with respect to local ground.
Definitions
Ground or earth in a mains (AC power) electrical wiring system is a conductor that provides a low-impedance path to the earth to prevent hazardous voltages from appearing on equipment (high voltage spikes).[citation needed] The terms ground and earth are used synonymously in this section; ground is more common in North American English, and earth is more common in British English. Under normal conditions, a grounding conductor does not carry current. Grounding is also an integral path for home wiring because it causes circuit breakers to trip more quickly (ie, GFCI), which is safer. Adding new grounds requires a qualified electrician with knowledge particular to a power distribution region.
Neutral is a circuit conductor that normally completes the circuit back to the source. Neutral is usually connected to ground (earth) at the main electrical panel, street drop, or meter, and also at the final step-down transformer of the supply[citation needed]. That is for simple single panel installations; for multiple panels the situation is more complex. In a polyphase (usually three-phase) AC system, the neutral conductor is intended to have similar voltages to each of the other circuit conductors, but may carry very little current if the phases are balanced.
All neutral wires of the same earthed (grounded) electrical system should have the same electrical potential, because they are all connected through the system ground. Neutral conductors are usually insulated for the same voltage as the line conductors, with interesting exceptions.[1]
Circuitry
Neutral wires are usually connected at a neutral bus within panelboards or switchboards, and are "bonded" to earth ground at either the electrical service entrance, or at transformers within the system. For electrical installations with split-phase (three-wire single-phase) service, the neutral point of the system is at the center-tap on the secondary side of the service transformer. For larger electrical installations, such as those with polyphase service, the neutral point is usually at the common connection on the secondary side of delta/wye connected transformers. Other arrangements of polyphase transformers may result in no neutral point, and no neutral conductors.
Grounding systems
The IEC standard (IEC 60364) codifies methods of installing neutral and ground conductors in a building, where these earthing systems are designated with letter symbols. The letter symbols are common in countries using IEC standards, but North American practices rarely refer to the IEC symbols. The differences are that the conductors may be separate over their entire run from equipment to earth ground, or may be combined all or part of their length. Different systems are used to minimize the voltage difference between neutral and local earth ground. Current flowing in a grounding conductor will produce a voltage drop along the conductor, and grounding systems seek to ensure this voltage does not reach unsafe levels.
In the TN-S system, separate neutral and protective earth conductors are installed between the equipment and the source of supply (generator or electric utility transformer). Normal circuit currents flow only in the neutral, and the protective earth conductor bonds all equipment cases to earth to intercept any leakage current due to insulation failure. The neutral conductor is connected to earth at the building point of supply, but no common path to ground exists for circuit current and the protective conductor.
In the TN-C system, a common conductor provides both the neutral and protective grounding. The neutral conductor is connected to earth ground at the point of supply, and equipment cases are connected to the neutral. The danger exists that a broken neutral connection will allow all the equipment cases to rise to a dangerous voltage if any leakage or insulation fault exists in any equipment. This can be mitigated with special cables but the cost is then higher.
In the TN-C-S system, each piece of electrical equipment has both a protective ground connection to its case, and a neutral connection. These are all brought back to some common point in the building system, and a common connection is then made from that point back to the source of supply and to the earth.
In a TT system, no lengthy common protective ground conductor is used, instead each article of electrical equipment (or building distribution system) has its own connection to earth ground.
Indian CEAR, Rule 41, makes the following provisions:
- The neutral conductor of a 3-phase, 4-wire system and the middle conductor of a 2- phase, 3-wire system must have at least 2 separate and distinct earth connections with a minimum of 2 different earth electrodes to have a satisfactory earth resistance
- The earth electrodes must be interconnected to reduce earth resistance
- The neutral conductor shall also be earthed at one or more points along the distribution system or service line in addition to any connection at the user end
Combining neutral with ground
Stray voltages created in grounding (earthing) conductors by currents flowing in the supply utility neutral conductors can be troublesome. For example, special measures may be required in barns used for milking dairy cattle. Very small voltages, not usually perceptible to humans, may cause low milk yield, or even mastitis (inflammation of the udder).[2] So-called "tingle voltage filters" may be required in the electrical distribution system for a milking parlour.
Connecting the neutral to the equipment case provides some protection against faults, but may produce a dangerous voltage on the case if the neutral connection is broken.
Combined neutral and ground conductors are commonly used in electricity supply companies' wiring and occasionally for fixed wiring in buildings and for some specialist applications where there is little alternative, such as railways and trams. Since normal circuit currents in the neutral conductor can lead to objectionable or dangerous differences between local earth potential and the neutral, and to protect against neutral breakages, special precautions such as frequent rodding down to earth (multiple ground rod connections), use of cables where the combined neutral and earth completely surrounds the phase conductor(s), and thicker than normal equipotential bonding must be considered to ensure the system is safe.
Fixed appliances on three-wire circuits
In the United States, the cases of some kitchen stoves (ranges, ovens), cook tops, clothes dryers and other specifically listed appliances were grounded through their neutral wires as a measure to conserve copper from copper cables during World War II. This practice was removed from the NEC in the 1996 edition, but existing installations (called "old work") may still allow the cases of such listed appliances to be connected to the neutral conductor for grounding. (Canada did not adopt this system and instead during this time and into the present uses separate neutral and ground wires.)
This practice arose from the three-wire system used to supply both 120 volt and 240 volt loads. Because these listed appliances often have components that use either 120, or both 120 and 240 volts, there is often some current on the neutral wire. This differs from the protective grounding wire, which only carries current under fault conditions. Using the neutral conductor for grounding the equipment enclosure was considered safe since the devices were permanently wired to the supply and so the neutral was unlikely to be broken without also breaking both supply conductors. Also, the unbalanced current due to lamps and small motors in the appliances was small compared to the rating of the conductors and therefore unlikely to cause a large voltage drop in the neutral conductor.
Portable appliances
In North American and European practice, small portable equipment connected by a cord set is permitted under certain conditions to have merely two conductors in the attachment plug. A polarized plug can be used to maintain the identity of the neutral conductor into the appliance but neutral is never used as a chassis/case ground. The small cords to lamps, etc., often have one or more molded ridges or embedded strings to identify the neutral conductor, or may be identified by colour. Portable appliances never use the neutral conductor for case grounding, and often feature "double-insulated" construction.
In places where the design of the plug and socket cannot ensure that a system neutral conductor is connected to particular terminals of the device ("unpolarized" plugs), portable appliances must be designed on the assumption that either pole of each circuit may reach full main voltage with respect to the ground.
Technical equipment
In North American practice, equipment connected by a cord set must have three wires if supplied exclusively by 240 volts, or must have four wires (including neutral and ground), if supplied by 120/240 volts.
There are special provisions in the NEC for so-called technical equipment, mainly professional grade audio and video equipment supplied by so-called "balanced" 120 volt circuits. The center tap of a transformer is connected to ground, and the equipment is supplied by two line wires each 60 volts to ground (and 120 volts between line conductors). The center tap is not distributed to the equipment and no neutral conductor is used. These cases generally use a grounding conductor which is separated from the safety grounding conductor specifically for the purposes of noise and "hum" reduction.
Another specialized distribution system was formerly specified in patient care areas of hospitals. An isolated power system was furnished, from a special isolation transformer, with the intention of minimizing any leakage current that could pass through equipment directly connected to a patient (for example, an electrocardiograph for monitoring the heart). The neutral of the circuit was not connected to ground. The leakage current was due to the distributed capacitance of the wiring and capacitance of the supply transformer. [3] Such distribution systems were monitored by permanently installed instruments to give an alarm when high leakage current was detected.
A shared neutral is a connection in which a plurality of circuits use the same neutral connection. This is also known as a common neutral, and the circuits and neutral together are sometimes referred to as an Edison circuit.
Three-phase circuits
In a three-phase circuit, a neutral is shared between all three phases. Commonly the system neutral is connected to the star point on the feeding transformer. This is the reason that the secondary side of most three-phase distribution transformers is wye- or star-wound. Three-phase transformers and their associated neutrals are usually found in industrial distribution environments.
A system could be made entirely ungrounded. In this case a fault between one phase and ground would not cause any significant current. Commonly the neutral is grounded (earthed) through a bond between the neutral bar and the earth bar. It is common on larger systems to monitor any current flowing through the neutral-to-earth link and use this as the basis for neutral fault protection.
The connection between neutral and earth allows any phase-to-earth fault to develop enough current flow to "trip" the circuit overcurrent protection device. In some jurisdictions, calculations are required to ensure the fault loop impedance is low enough so that fault current will trip the protection (In Australia, this is referred to in AS3000:2007 Fault loop impedance calculation). This may limit the length of a branch circuit.
In the case of two phases sharing one neutral and the third phase is disconnected, the worst-case current draw is one side has zero load and the other has full load, or when both sides have full load. The latter case results in , or where is the magnitude of the current. In other words the magnitude of the current in the neutral equals that of the other two wires.
In a three-phase linear circuit with three identical resistive or reactive loads, the neutral carries no current. The neutral carries current if the loads on each phase are not identical. In some jurisdictions, the neutral is allowed to be reduced in size if no unbalanced current flow is expected. If the neutral is smaller than the phase conductors, it can be overloaded if a large unbalanced load occurs.
The current drawn by non-linear loads, such as fluorescent & HID lighting and electronic equipment containing switching power supplies, often contains harmonics. Triplen harmonic currents (odd multiples of the third harmonic) are additive, resulting in more current in the shared neutral conductor than in any of the phase conductors. In the absolute worst case, the current in the shared neutral conductor can be triple that in each phase conductor. Some jurisdictions prohibit the use of shared neutral conductors when feeding single-phase loads from a three-phase source; others require that the neutral conductor be substantially larger than the phase conductors. It is good practice to use four-pole circuit breakers (as opposed to the standard three-pole) where the fourth pole is the neutral phase, and is hence protected against overcurrent on the neutral conductor.
Split phase
In split-phase wiring, for example a duplex receptacle in a North American kitchen, devices may be connected with a cable that has three conductors, in addition to ground. The three conductors are usually coloured red, black, and white. The white serves as a common neutral, while the red and black each feed, separately, the top and bottom hot sides of the receptacle. Typically such receptacles are supplied from two circuit breakers in which the handles of two poles are tied together for a common trip. If two large appliances are used at once, current passes through both and the neutral only carries the difference in current. The advantage is that only three wires are required to serve these loads, instead of four. If one kitchen appliance overloads the circuit, the other side of the duplex receptacle will be shut off as well. This is called a multiwire branch circuit. Common trip is required when the connected load uses more than one phase simultaneously. The common trip prevents overloading of the shared neutral if one device draws more than rated current.
Grounding problems
A ground connection that is missing or of inadequate capacity may not provide the protective functions as intended during a fault in the connected equipment. Extra connections between ground and circuit neutral may result in circulating current in the ground path, stray current introduced in the earth or in a structure, and stray voltage.[citation needed] Extra ground connections on a neutral conductor may bypass the protection provided by a ground-fault circuit interrupter. Signal circuits that rely on a ground connection will not function or will have erratic function if the ground connection is missing.
See also
- Appliance classes
- Electrical bonding
- Electrical wiring
- Electrical wiring (UK)
- Electrical wiring (United States)
- Earthing arrangements
- Ground (electricity)
References
- Leslie A. Geddes Handbook of Electrical Hazards and Accidents, CRC Press, 1995 ISBN 0849394317, pp. 90-91
Further reading
- Rick Gilmour et al., editor, Canadian Electrical Code Part I, Nineteenth Edition, C22.1-02 Safety Standard for Electrical Installations, Canadian Standards Association, Toronto, Ontario Canada (2002) ISBN 1-55324-690-X
- NFPA 70, National Electrical Code 2002, National Fire Protection Association, Inc., Quincy, Massachusetts USA, (2002). no ISBN
- IEE Wiring Regulations Regulations for Electrical Installations Fifteenth Edition 1981, The Institution of Electrical Engineers, (1981) Hitchin, Herts. United Kingdom
- Electrical Safety chapter from Lessons In Electric Circuits Vol 1 DC book and series.
- EDISON CIRCUITS POSE SAFETY HAZARD
- The Complete Guide To Home Wiring (link dead but multiple sources via Google search)
- Advanced Home Wiring
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_and_neutral
The hot-wire barretter was a demodulating detector, invented in 1902 by Reginald Fessenden, that found limited use in early radio receivers. In effect, it was a highly sensitive thermoresistor, which could demodulate amplitude-modulated signals, something that the coherer (the standard detector of the time) could not do.[1]
The first device used to demodulate amplitude modulated signals, it was later superseded by the electrolytic detector, also generally attributed to Fessenden. The barretter principle is still used as a detector for microwave radiation, similar to a bolometer.
Description and construction
Fessenden's 1902 patent describes the construction of the device. A fine platinum wire, about 0.003 inches (0.08 mm) in diameter, is embedded in the middle of a silver tube having a diameter of about 0.1 inches (2.5 mm). This compound wire is then drawn until the silver wire has a diameter of about 0.002 inches (0.05 mm); as the platinum wire within it is reduced in the same ratio, it is drawn down to a final diameter of 0.00006 inches (1.5 μm). The result is called Wollaston wire.
The silver cladding is etched off a short piece of the composite wire, leaving an extremely fine platinum wire; this is supported, on two heavier silver wires, in a loop inside a glass bulb. The leads are taken out through the glass envelope, and the whole device is put under vacuum and then sealed.
Operation
The hot-wire barretter depends upon the increase of a metal resistivity with increasing temperature. The device is biased by a direct current adjusted to heat the wire to its most sensitive temperature. When there is an oscillating current from the antenna through the extremely fine platinum wire loop, the wire is further heated as the current increases and cools as the current decreases again. As the wire heats and cools, it varies its resistance in response to the signals passing through it. Because of the low thermal mass of the wire, it is capable of responding quickly enough to vary its resistance in response to audio signals. However, it cannot vary its resistance fast enough to respond to the much higher radio frequencies. The signal is demodulated because the current supplied by the biasing source varies with the changing wire resistance. Headphones are connected in series with the DC circuit, and the variations in the current are rendered as sound.
See also
- Electrolytic detector a development of the barretter detector.
- Iron-hydrogen resistor
References
- Tapan K. Sarkar, Robert Mailloux, Arthur A. Oliner, Magdalena Salazar-Palma, Dipak L. Sengupta, "History of Wireless", ISBN 978-0-471-78301-5, January 2006, Wiley-IEEE Press, page 369.
External links
Patents
- US 706744, "Current Actuated Wave Responsive Device" – August, 1902 ("barretter" detector)
- US 727331, "Receiver for Electromagnetic Waves" – May, 1903 (improved "barretter")
Other
- Detectors of electrical oscillations
- Tech Definitions – Radio Concepts
- United States Early Radio History
- Secor, H. Winfield (January, 1917). Radio Detector Development. The Electrical Experimenter, pages 652+, accessed 2007-12-20.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hot-wire_barretter
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both.[1]
Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses pre-determined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved.[2] To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: protocols are to communication what programming languages are to computations.[3] An alternate formulation states that protocols are to communication what algorithms are to computation.[4]
Multiple protocols often describe different aspects of a single communication. A group of protocols designed to work together is known as a protocol suite; when implemented in software they are a protocol stack.
Internet communication protocols are published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) handles wired and wireless networking and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) handles other types. The ITU-T handles telecommunications protocols and formats for the public switched telephone network (PSTN). As the PSTN and Internet converge, the standards are also being driven towards convergence.
Communicating systems
History
One of the first uses of the term protocol in a data-commutation context occurs in a memorandum entitled A Protocol for Use in the NPL Data Communications Network written by Roger Scantlebury and Keith Bartlett in April 1967.[5][6]
On the ARPANET, the starting point for host-to-host communication in 1969 was the 1822 protocol, which defined the transmission of messages to an IMP.[7] The Network Control Protocol (NCP) for the ARPANET was first implemented in 1970.[8] The NCP interface allowed application software to connect across the ARPANET by implementing higher-level communication protocols, an early example of the protocol layering concept.[9]
Networking research in the early 1970s by Robert E. Kahn and Vint Cerf led to the formulation of the Transmission Control Program (TCP).[10] Its RFC 675 specification was written by Cerf with Yogen Dalal and Carl Sunshine in December 1974, still a monolithic design at this time.
The International Networking Working Group agreed a connectionless datagram standard which was presented to the CCIT in 1975 but was not adopted by the ITU or by the ARPANET.[11] International research, particularly the work of Rémi Després, contributed to the development of the X.25 standard, based on virtual circuits by the ITU-T in 1976.[12][13] Computer manufacturers developed proprietary protocols such as IBM's Systems Network Architecture (SNA), Digital Equipment Corporation's DECnet and Xerox Network Systems.[14]
TCP software was redesigned as a modular protocol stack. Originally referred to as IP/TCP, it was installed on SATNET in 1982 and on the ARPANET in January 1983. The development of a complete protocol suite by 1989, as outlined in RFC 1122 and RFC 1123, laid the foundation for the growth of TCP/IP as a comprehensive protocol suite as the core component of the emerging Internet.[15]
International work on a reference model for communication standards led to the OSI model, published in 1984. For a period in the late 1980s and early 1990s, engineers, organizations and nations became polarized over the issue of which standard, the OSI model or the Internet protocol suite, would result in the best and most robust computer networks.[16][17][18]
Concept
The information exchanged between devices through a network or other media is governed by rules and conventions that can be set out in communication protocol specifications. The nature of communication, the actual data exchanged and any state-dependent behaviors, is defined by these specifications. In digital computing systems, the rules can be expressed by algorithms and data structures. Protocols are to communication what algorithms or programming languages are to computations.[3][4]
Operating systems usually contain a set of cooperating processes that manipulate shared data to communicate with each other. This communication is governed by well-understood protocols, which can be embedded in the process code itself.[19][20] In contrast, because there is no shared memory, communicating systems have to communicate with each other using a shared transmission medium. Transmission is not necessarily reliable, and individual systems may use different hardware or operating systems.
To implement a networking protocol, the protocol software modules are interfaced with a framework implemented on the machine's operating system. This framework implements the networking functionality of the operating system.[21] When protocol algorithms are expressed in a portable programming language the protocol software may be made operating system independent. The best-known frameworks are the TCP/IP model and the OSI model.
At the time the Internet was developed, abstraction layering had proven to be a successful design approach for both compiler and operating system design and, given the similarities between programming languages and communication protocols, the originally monolithic networking programs were decomposed into cooperating protocols.[22] This gave rise to the concept of layered protocols which nowadays forms the basis of protocol design.[23]
Systems typically do not use a single protocol to handle a transmission. Instead they use a set of cooperating protocols, sometimes called a protocol suite.[24] Some of the best-known protocol suites are TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, X.25, AX.25 and AppleTalk.
The protocols can be arranged based on functionality in groups, for instance, there is a group of transport protocols. The functionalities are mapped onto the layers, each layer solving a distinct class of problems relating to, for instance: application-, transport-, internet- and network interface-functions.[25] To transmit a message, a protocol has to be selected from each layer. The selection of the next protocol is accomplished by extending the message with a protocol selector for each layer.[26]
Types
There are two types of communication protocols, based on their representation of the content being carried: text-based and binary.[27]
Text-based
A text-based protocol or plain text protocol represents its content in human-readable format, often in plain text.
The immediate human readability stands in contrast to binary protocols which have inherent benefits for use in a computer environment (such as ease of mechanical parsing and improved bandwidth utilization).
Network applications have various methods of encapsulating data. One method very common with Internet protocols is a text oriented representation that transmits requests and responses as lines of ASCII text, terminated by a newline character (and usually a carriage return character). Examples of protocols that use plain, human-readable text for its commands are FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), and the finger protocol.[28]
Text-based protocols are typically optimized for human parsing and interpretation and are therefore suitable whenever human inspection of protocol contents is required, such as during debugging and during early protocol development design phases.
To be clear, all digital communication is fundamentally binary. The "Text" based protocols mentioned here use only binary content, which is made "humanly readable" by a text editor (or other such software).
Binary
A binary protocol utilizes all values of a byte, as opposed to a text-based protocol which only uses values corresponding to human-readable characters in ASCII encoding. Binary protocols are intended to be read by a machine rather than a human being. Binary protocols have the advantage of terseness, which translates into speed of transmission and interpretation.[29]
Binary have been used in the normative documents describing modern standards like EbXML, HTTP/2, HTTP/3 and EDOC.[30] An interface in UML[31] may also be considered a binary protocol.
Basic requirements
Getting the data across a network is only part of the problem for a protocol. The data received has to be evaluated in the context of the progress of the conversation, so a protocol must include rules describing the context. These kinds of rules are said to express the syntax of the communication. Other rules determine whether the data is meaningful for the context in which the exchange takes place. These kinds of rules are said to express the semantics of the communication.
Messages are sent and received on communicating systems to establish communication. Protocols should therefore specify rules governing the transmission. In general, much of the following should be addressed:[32]
- Data formats for data exchange
- Digital message bitstrings are exchanged. The bitstrings are divided in fields and each field carries information relevant to the protocol. Conceptually the bitstring is divided into two parts called the header and the payload. The actual message is carried in the payload. The header area contains the fields with relevance to the operation of the protocol. Bitstrings longer than the maximum transmission unit (MTU) are divided in pieces of appropriate size.[33]
- Address formats for data exchange
- Addresses are used to identify both the sender and the intended receiver(s). The addresses are carried in the header area of the bitstrings, allowing the receivers to determine whether the bitstrings are of interest and should be processed or should be ignored. A connection between a sender and a receiver can be identified using an address pair (sender address, receiver address). Usually, some address values have special meanings. An all-1s address could be taken to mean an addressing of all stations on the network, so sending to this address would result in a broadcast on the local network. The rules describing the meanings of the address value are collectively called an addressing scheme.[34]
- Address mapping
- Sometimes protocols need to map addresses of one scheme on addresses of another scheme. For instance, to translate a logical IP address specified by the application to an Ethernet MAC address. This is referred to as address mapping.[35]
- Routing
- When systems are not directly connected, intermediary systems along the route to the intended receiver(s) need to forward messages on behalf of the sender. On the Internet, the networks are connected using routers. The interconnection of networks through routers is called internetworking.
- Detection of transmission errors
- Error detection is necessary on networks where data corruption is possible. In a common approach, a CRC of the data area is added to the end of packets, making it possible for the receiver to detect differences caused by corruption. The receiver rejects the packets on CRC differences and arranges somehow for retransmission.[36]
- Acknowledgements
- Acknowledgement of correct reception of packets is required for connection-oriented communication. Acknowledgments are sent from receivers back to their respective senders.[37]
- Loss of information - timeouts and retries
- Packets may be lost on the network or be delayed in transit. To cope with this, under some protocols, a sender may expect an acknowledgment of correct reception from the receiver within a certain amount of time. Thus, on timeouts, the sender may need to retransmit the information.[a] In case of a permanently broken link, the retransmission has no effect, so the number of retransmissions is limited. Exceeding the retry limit is considered an error.[38]
- Direction of information flow
- Direction needs to be addressed if transmissions can only occur in one direction at a time as on half-duplex links or from one sender at a time as on a shared medium. This is known as media access control. Arrangements have to be made to accommodate the case of collision or contention where two parties respectively simultaneously transmit or wish to transmit.[39]
- Sequence control
- If long bitstrings are divided into pieces and then sent on the network individually, the pieces may get lost or delayed or, on some types of networks, take different routes to their destination. As a result, pieces may arrive out of sequence. Retransmissions can result in duplicate pieces. By marking the pieces with sequence information at the sender, the receiver can determine what was lost or duplicated, ask for necessary retransmissions and reassemble the original message.[40]
- Flow control
- Flow control is needed when the sender transmits faster than the receiver or intermediate network equipment can process the transmissions. Flow control can be implemented by messaging from receiver to sender.[41]
- Queueing
- Communicating processes or state machines employ queues (or "buffers"), usually FIFO queues, to deal with the messages in the order sent, and may sometimes have multiple queues with different prioritization.
Protocol design
Systems engineering principles have been applied to create a set of common network protocol design principles. The design of complex protocols often involves decomposition into simpler, cooperating protocols. Such a set of cooperating protocols is sometimes called a protocol family or a protocol suite,[24] within a conceptual framework.
Communicating systems operate concurrently. An important aspect of concurrent programming is the synchronization of software for receiving and transmitting messages of communication in proper sequencing. Concurrent programming has traditionally been a topic in operating systems theory texts.[42] Formal verification seems indispensable because concurrent programs are notorious for the hidden and sophisticated bugs they contain.[43] A mathematical approach to the study of concurrency and communication is referred to as communicating sequential processes (CSP).[44] Concurrency can also be modeled using finite state machines, such as Mealy and Moore machines. Mealy and Moore machines are in use as design tools in digital electronics systems encountered in the form of hardware used in telecommunication or electronic devices in general.[45][better source needed]
The literature presents numerous analogies between computer communication and programming. In analogy, a transfer mechanism of a protocol is comparable to a central processing unit (CPU). The framework introduces rules that allow the programmer to design cooperating protocols independently of one another.
Layering
In modern protocol design, protocols are layered to form a protocol stack. Layering is a design principle that divides the protocol design task into smaller steps, each of which accomplishes a specific part, interacting with the other parts of the protocol only in a small number of well-defined ways. Layering allows the parts of a protocol to be designed and tested without a combinatorial explosion of cases, keeping each design relatively simple.
The communication protocols in use on the Internet are designed to function in diverse and complex settings. Internet protocols are designed for simplicity and modularity and fit into a coarse hierarchy of functional layers defined in the Internet Protocol Suite.[46] The first two cooperating protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) resulted from the decomposition of the original Transmission Control Program, a monolithic communication protocol, into this layered communication suite.
The OSI model was developed internationally based on experience with networks that predated the internet as a reference model for general communication with much stricter rules of protocol interaction and rigorous layering.
Typically, application software is built upon a robust data transport layer. Underlying this transport layer is a datagram delivery and routing mechanism that is typically connectionless in the Internet. Packet relaying across networks happens over another layer that involves only network link technologies, which are often specific to certain physical layer technologies, such as Ethernet. Layering provides opportunities to exchange technologies when needed, for example, protocols are often stacked in a tunneling arrangement to accommodate the connection of dissimilar networks. For example, IP may be tunneled across an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network.
Protocol layering
Protocol layering forms the basis of protocol design.[23] It allows the decomposition of single, complex protocols into simpler, cooperating protocols.[46] The protocol layers each solve a distinct class of communication problems. Together, the layers make up a layering scheme or model.
Computations deal with algorithms and data; Communication involves protocols and messages; So the analog of a data flow diagram is some kind of message flow diagram.[4] To visualize protocol layering and protocol suites, a diagram of the message flows in and between two systems, A and B, is shown in figure 3. The systems, A and B, both make use of the same protocol suite. The vertical flows (and protocols) are in-system and the horizontal message flows (and protocols) are between systems. The message flows are governed by rules, and data formats specified by protocols. The blue lines mark the boundaries of the (horizontal) protocol layers.
Software layering
The software supporting protocols has a layered organization and its relationship with protocol layering is shown in figure 5.
To send a message on system A, the top-layer software module interacts with the module directly below it and hands over the message to be encapsulated. The lower module fills in the header data in accordance with the protocol it implements and interacts with the bottom module which sends the message over the communications channel to the bottom module of system B. On the receiving system B the reverse happens, so ultimately the message gets delivered in its original form to the top module of system B.[47]
Program translation is divided into subproblems. As a result, the translation software is layered as well, allowing the software layers to be designed independently. The same approach can be seen in the TCP/IP layering.[48]
The modules below the application layer are generally considered part of the operating system. Passing data between these modules is much less expensive than passing data between an application program and the transport layer. The boundary between the application layer and the transport layer is called the operating system boundary.[49]
Strict layering
Strictly adhering to a layered model, a practice known as strict layering, is not always the best approach to networking.[50] Strict layering can have a negative impact on the performance of an implementation.[51]
While the use of protocol layering is today ubiquitous across the field of computer networking, it has been historically criticized by many researchers[52] as abstracting the protocol stack in this way may cause a higher layer to duplicate the functionality of a lower layer, a prime example being error recovery on both a per-link basis and an end-to-end basis.[53]
Design patterns
Commonly recurring problems in the design and implementation of communication protocols can be addressed by software design patterns.[54][55][56][57][58]
Formal specification
Popular formal methods of describing communication syntax are Abstract Syntax Notation One (an ISO standard) and augmented Backus–Naur form (an IETF standard).
Finite-state machine models are used to formally describe the possible interactions of the protocol.[59][60] and communicating finite-state machines[61]
Protocol development
For communication to occur, protocols have to be selected. The rules can be expressed by algorithms and data structures. Hardware and operating system independence is enhanced by expressing the algorithms in a portable programming language. Source independence of the specification provides wider interoperability.
Protocol standards are commonly created by obtaining the approval or support of a standards organization, which initiates the standardization process. The members of the standards organization agree to adhere to the work result on a voluntary basis. Often the members are in control of large market shares relevant to the protocol and in many cases, standards are enforced by law or the government because they are thought to serve an important public interest, so getting approval can be very important for the protocol.
The need for protocol standards
The need for protocol standards can be shown by looking at what happened to the Binary Synchronous Communications (BSC) protocol invented by IBM. BSC is an early link-level protocol used to connect two separate nodes. It was originally not intended to be used in a multinode network, but doing so revealed several deficiencies of the protocol. In the absence of standardization, manufacturers and organizations felt free to enhance the protocol, creating incompatible versions on their networks. In some cases, this was deliberately done to discourage users from using equipment from other manufacturers. There are more than 50 variants of the original bi-sync protocol. One can assume, that a standard would have prevented at least some of this from happening.[21]
In some cases, protocols gain market dominance without going through a standardization process. Such protocols are referred to as de facto standards. De facto standards are common in emerging markets, niche markets, or markets that are monopolized (or oligopolized). They can hold a market in a very negative grip, especially when used to scare away competition. From a historical perspective, standardization should be seen as a measure to counteract the ill-effects of de facto standards. Positive exceptions exist; a de facto standard operating system like Linux does not have this negative grip on its market, because the sources are published and maintained in an open way, thus inviting competition.
Standards organizations
Some of the standards organizations of relevance for communication protocols are the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The IETF maintains the protocols in use on the Internet. The IEEE controls many software and hardware protocols in the electronics industry for commercial and consumer devices. The ITU is an umbrella organization of telecommunication engineers designing the public switched telephone network (PSTN), as well as many radio communication systems. For marine electronics the NMEA standards are used. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) produces protocols and standards for Web technologies.
International standards organizations are supposed to be more impartial than local organizations with a national or commercial self-interest to consider. Standards organizations also do research and development for standards of the future. In practice, the standards organizations mentioned, cooperate closely with each other.[62]
Multiple standards bodies may be involved in the development of a protocol. If they are uncoordinated, then the result may be multiple, incompatible definitions of a protocol, or multiple, incompatible interpretations of messages; important invariants in one definition (e.g., that time-to-live values are monotone decreasing to prevent stable routing loops) may not be respected in another.[63]
The standardization process
In the ISO, the standardization process starts off with the commissioning of a sub-committee workgroup. The workgroup issues working drafts and discussion documents to interested parties (including other standards bodies) in order to provoke discussion and comments. This will generate a lot of questions, much discussion and usually some disagreement. These comments are taken into account and a draft proposal is produced by the working group. After feedback, modification, and compromise the proposal reaches the status of a draft international standard, and ultimately an international standard. International standards are reissued periodically to handle the deficiencies and reflect changing views on the subject.[64]
OSI standardization
A lesson learned from ARPANET, the predecessor of the Internet, was that protocols need a framework to operate. It is therefore important to develop a general-purpose, future-proof framework suitable for structured protocols (such as layered protocols) and their standardization. This would prevent protocol standards with overlapping functionality and would allow clear definition of the responsibilities of a protocol at the different levels (layers).[65] This gave rise to the Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model), which is used as a framework for the design of standard protocols and services conforming to the various layer specifications.[66]
In the OSI model, communicating systems are assumed to be connected by an underlying physical medium providing a basic transmission mechanism. The layers above it are numbered. Each layer provides service to the layer above it using the services of the layer immediately below it. The top layer provides services to the application process. The layers communicate with each other by means of an interface, called a service access point. Corresponding layers at each system are called peer entities. To communicate, two peer entities at a given layer use a protocol specific to that layer which is implemented by using services of the layer below.[67] For each layer, there are two types of standards: protocol standards defining how peer entities at a given layer communicate, and service standards defining how a given layer communicates with the layer above it.
In the OSI model, the layers and their functionality are (from highest to lowest layer):
- The Application layer may provide the following services to the application processes: identification of the intended communication partners, establishment of the necessary authority to communicate, determination of availability and authentication of the partners, agreement on privacy mechanisms for the communication, agreement on responsibility for error recovery and procedures for ensuring data integrity, synchronization between cooperating application processes, identification of any constraints on syntax (e.g. character sets and data structures), determination of cost and acceptable quality of service, selection of the dialogue discipline, including required logon and logoff procedures.[68]
- The presentation layer may provide the following services to the application layer: a request for the establishment of a session, data transfer, negotiation of the syntax to be used between the application layers, any necessary syntax transformations, formatting and special purpose transformations (e.g., data compression and data encryption).[69]
- The session layer may provide the following services to the presentation layer: establishment and release of session connections, normal and expedited data exchange, a quarantine service which allows the sending presentation entity to instruct the receiving session entity not to release data to its presentation entity without permission, interaction management so presentation entities can control whose turn it is to perform certain control functions, resynchronization of a session connection, reporting of unrecoverable exceptions to the presentation entity.[70]
- The transport layer provides reliable and transparent data transfer in a cost-effective way as required by the selected quality of service. It may support the multiplexing of several transport connections on to one network connection or split one transport connection into several network connections.[71]
- The network layer does the setup, maintenance and release of network paths between transport peer entities. When relays are needed, routing and relay functions are provided by this layer. The quality of service is negotiated between network and transport entities at the time the connection is set up. This layer is also responsible for network congestion control.[72]
- The data link layer does the setup, maintenance and release of data link connections. Errors occurring in the physical layer are detected and may be corrected. Errors are reported to the network layer. The exchange of data link units (including flow control) is defined by this layer.[73]
- The physical layer describes details like the electrical characteristics of the physical connection, the transmission techniques used, and the setup, maintenance and clearing of physical connections.[74]
In contrast to the TCP/IP layering scheme, which assumes a connectionless network, RM/OSI assumed a connection-oriented network.[75] Connection-oriented networks are more suitable for wide area networks and connectionless networks are more suitable for local area networks. Connection-oriented communication requires some form of session and (virtual) circuits, hence the (in the TCP/IP model lacking) session layer. The constituent members of ISO were mostly concerned with wide area networks, so the development of RM/OSI concentrated on connection-oriented networks and connectionless networks were first mentioned in an addendum to RM/OSI[76][77] and later incorporated into an update to RM/OSI.[78]
At the time,[when?] the IETF had to cope with this and the fact that the Internet needed protocols that simply were not there.[citation needed] As a result, the IETF developed its own standardization process based on "rough consensus and running code".[79] The standardization process is described by RFC 2026.
Nowadays, the IETF has become a standards organization for the protocols in use on the Internet. RM/OSI has extended its model to include connectionless services and because of this, both TCP and IP could be developed into international standards.[citation needed]
Wire image
The wire image of a protocol is the information that a non-participant observer is able to glean from observing the protocol messages, including both information explicitly given meaning by the protocol, but also inferences made by the observer.[80] Unencrypted protocol metadata is one source making up the wire image, and side-channels including packet timing also contribute.[81] Different observers with different vantages may see different wire images.[82] The wire image is relevant to end-user privacy and the extensibility of the protocol.[83]
If some portion of the wire image is not cryptographically authenticated, it is subject to modification by intermediate parties (i.e., middleboxes), which can influence protocol operation.[81] Even if authenticated, if a portion is not encrypted, it will form part of the wire image, and intermediate parties may intervene depending on its content (e.g., dropping packets with particular flags). Signals deliberately intended for intermediary consumption may be left authenticated but unencrypted.[84]
The wire image can be deliberately engineered, encrypting parts that intermediaries should not be able to observe and providing signals for what they should be able to.[85] If provided signals are decoupled from the protocol's operation, they may become untrustworthy.[86] Benign network management and research are affected by metadata encryption; protocol designers must balance observability for operability and research against ossification resistance and end-user privacy.[83] The IETF announced in 2014 that it had determined that large-scale surveillance of protocol operations is an attack due to the ability to infer information from the wire image about users and their behaviour,[87] and that the IETF would "work to mitigate pervasive monitoring" in its protocol designs;[88] this had not been done systematically previously.[88]
Ossification
Protocol ossification is the loss of flexibility, extensibility and evolvability of network protocols. This is largely due to middleboxes that are sensitive to the wire image of the protocol, and which can interrupt or interfere with messages that are valid but which the middlebox does not correctly recognize.[89] This is a violation of the end-to-end principle.[90] Secondary causes include inflexibility in endpoint implementations of protocols.[91]
Ossification is a major issue in Internet protocol design and deployment, as it can prevent new protocols or extensions from being deployed on the Internet, or place strictures on the design of new protocols; new protocols may have to be encapsulated in an already-deployed protocol or mimic the wire image of another protocol.[92] Because of ossification, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are the only practical choices for transport protocols on the Internet,[93] and TCP itself has significantly ossified, making extension or modification of the protocol difficult.[94]
Recommended methods of preventing ossification include encrypting protocol metadata,[95] and ensuring that extension points are exercised and wire image variability is exhibited as fully as possible;[96] remedying existing ossification requires coordination across protocol participants.[97] QUIC is the first IETF transport protocol to have been designed with deliberate anti-ossification properties.[80]
Taxonomies
Classification schemes for protocols usually focus on the domain of use and function. As an example of domain of use, connection-oriented protocols and connectionless protocols are used on connection-oriented networks and connectionless networks respectively. An example of function is a tunneling protocol, which is used to encapsulate packets in a high-level protocol so that the packets can be passed across a transport system using the high-level protocol.
A layering scheme combines both function and domain of use. The dominant layering schemes are the ones developed by the IETF and by ISO. Despite the fact that the underlying assumptions of the layering schemes are different enough to warrant distinguishing the two, it is a common practice to compare the two by relating common protocols to the layers of the two schemes.[98] The layering scheme from the IETF is called Internet layering or TCP/IP layering. The layering scheme from ISO is called the OSI model or ISO layering.
In networking equipment configuration, a term-of-art distinction is often drawn: The term protocol strictly refers to the transport layer, and the term service refers to protocols utilizing a protocol for transport. In the common case of TCP and UDP, services are distinguished by port numbers. Conformance to these port numbers is voluntary, so in content inspection systems the term service strictly refers to port numbers, and the term application is often used to refer to protocols identified through inspection signatures.
See also
Notes
- Failure to receive an acknowledgment indicates that either the original transmission or the acknowledgment was lost. The sender has no means to distinguish these cases and therefore, to ensure all data is received, must make the conservative assumption that the original transmission was lost.
References
The authors wish to thank a number of colleagues for helpful comments during early discussions of international network protocols, especially R. Metcalfe, R. Scantlebury, D. Walden, and H. Zimmerman; D. Davies and L. Pouzin who constructively commented on the fragmentation and accounting issues; and S. Crocker who commented on the creation and destruction of associations.
This Basic Reference Model of Open Systems Interconnection is based on the assumption that a connection is required for the transfer of data.
- Comer 2000, Sect. 11.5.1 - The TCP/IP 5-Layer Reference Model, p. 183, states the same.
Bibliography
- Radia Perlman (1999). Interconnections: Bridges, Routers, Switches, and Internetworking Protocols (2nd ed.). Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-63448-1.. In particular Ch. 18 on "network design folklore", which is also available online
- Gerard J. Holzmann (1991). Design and Validation of Computer Protocols. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-539925-4.
- Douglas E. Comer (2000). Internetworking with TCP/IP - Principles, Protocols and Architecture (4th ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-018380-6. In particular Ch.11 Protocol layering. Also has a RFC guide and a Glossary of Internetworking Terms and Abbreviations.
- R. Braden, ed. (1989). Requirements for Internet Hosts -- Communication Layers. Internet Engineering Task Force abbr. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1122. RFC 1122. Describes TCP/IP to the implementors of protocolsoftware. In particular the introduction gives an overview of the design goals of the suite.
- M. Ben-ari (1982). Principles of concurrent programming (10th Print ed.). Prentice Hall International. ISBN 0-13-701078-8.
- C.A.R. Hoare (1985). Communicating sequential processes (10th Print ed.). Prentice Hall International. ISBN 0-13-153271-5.
- R.D. Tennent (1981). Principles of programming languages (10th Print ed.). Prentice Hall International. ISBN 0-13-709873-1.
- Brian W Marsden (1986). Communication network protocols (2nd ed.). Chartwell Bratt. ISBN 0-86238-106-1.
- Andrew S. Tanenbaum (1984). Structured computer organization (10th Print ed.). Prentice Hall International. ISBN 0-13-854605-3.
- Bryant, Stewart; Morrow, Monique, eds. (November 2009). Uncoordinated Protocol Development Considered Harmful. doi:10.17487/RFC5704. RFC 5704.
- Farrell, Stephen; Tschofenig, Hannes (May 2014). Pervasive Monitoring Is an Attack. doi:10.17487/RFC7258. RFC 7258.
- Trammell, Brian; Kuehlewind, Mirja (April 2019). The Wire Image of a Network Protocol. doi:10.17487/RFC8546. RFC 8546.
- Hardie, Ted, ed. (April 2019). Transport Protocol Path Signals. doi:10.17487/RFC8558. RFC 8558.
- Fairhurst, Gorry; Perkins, Colin (July 2021). Considerations around Transport Header Confidentiality, Network Operations, and the Evolution of Internet Transport Protocols. doi:10.17487/RFC9065. RFC 9065.
- Thomson, Martin; Pauly, Tommy (December 2021). Long-Term Viability of Protocol Extension Mechanisms. doi:10.17487/RFC9170. RFC 9170.
- McQuistin, Stephen; Perkins, Colin; Fayed, Marwan (July 2016). Implementing Real-Time Transport Services over an Ossified Network. 2016 Applied Networking Research Workshop. doi:10.1145/2959424.2959443. hdl:1893/26111.
- Papastergiou, Giorgos; Fairhurst, Gorry; Ros, David; Brunstrom, Anna; Grinnemo, Karl-Johan; Hurtig, Per; Khademi, Naeem; Tüxen, Michael; Welzl, Michael; Damjanovic, Dragana; Mangiante, Simone (2017). "De-Ossifying the Internet Transport Layer: A Survey and Future Perspectives". IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. 19: 619–639. doi:10.1109/COMST.2016.2626780. hdl:2164/8317. S2CID 1846371.
External links
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communication_protocol#Wire_image
Tube drawing is a process to size a tube by shrinking a large diameter tube into a smaller one, by drawing the tube through a die. This process produces high-quality tubing with precise dimensions, good surface finish, and the added strength of cold working.[1] For this reason this process is established for many materials, mainly metalworking but also glass. Because it is so versatile, tube drawing is suitable for both large- and small-scale production.[2] The large-scale production of glass typically uses a one step process where glass is directly drawn into a tube from a melting tank.
There are five types of tube drawing: tube sinking, mandrel drawing, stationary mandrel, moving mandrel, and floating mandrel. A mandrel is used in many of the types to prevent buckling or wrinkling in the workpiece.
Processes
Tube sinking
Tube sinking, also known as free tube drawing, reduces the diameter of the tube without a mandrel inside the tube. The inner diameter is determined by the inner and outer diameter of the stock tube, the outer diameter of the final product, the length of the die landing, the amount of back tension, and the friction between the tube and the die.[3] This type of drawing operation is the most economical, especially on thick-walled tubes and tubes smaller than 12 mm (0.47 in) in diameter,[1] but does not give the best surface finish. As the tube thickness increases the surface finish quality decreases. This process is often used for the tubing on low-cost lawn furniture.[4]
Rod drawing
Rod drawing is the process that draws the tube with a mandrel inside the tube; the mandrel is drawn with the tube. The advantage to this process is that the mandrel defines the inner diameter and the surface finish and has a quick setup time for short runs. The disadvantages are that lengths are limited by the length of the mandrel, usually no more than 100 feet (30 m), and that a second operation is required to remove the mandrel, called reeling. This type of process is usually used on heavy walled or small (inner diameter) tubes. Common applications include super-high pressure tubing and hydraulic tubing (with the addition of a finishing tube sinking operation).[4] This process is also used for precision manufacturing of trombone handslides.[5]
Fixed plug drawing
Fixed plug drawing, also known as stationary mandrel drawing,[3] uses a mandrel at the end of the die to shape the inner diameter of the tube. This process is slow and the area reductions are limited, but it gives the best inner surface finish of any of the processes. This is the oldest tube drawing method.[4]
Floating plug drawing
Floating plug drawing, also known as floating mandrel drawing,[3] uses a mandrel that is not anchored whatsoever to shape the inner diameter of the tube. The mandrel is held in by the friction forces between the mandrel and the tube. This axial force is given by friction and pressure. The greatest advantage of this is that it can be used on extremely long lengths, sometimes up to 1,000 feet (300 m). The disadvantage is it requires a precise design otherwise it will give inadequate results. This process is often used for oil-well tubing.[4]
Tethered plug drawing
Tethered plug drawing, also known as semi-floating mandrel drawing, is a mix between floating plug drawing and fixed plug drawing. The mandrel is allowed to float, but is still anchored via a tether. This process gives similar results to the floating plug process, except that it is designed for straight tubes. It gives a better inner surface finish than rod drawing.[4]
See also
References
Notes
- See, for example, this video of the process of making Getzen trombones: "Slide Stretching". Getzen Co.
Bibliography
- Degarmo, E. Paul; Black, J T.; Kohser, Ronald A. (2003), Materials and Processes in Manufacturing (9th ed.), Wiley, ISBN 0-471-65653-4.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tube_drawing
Tube bending is any metal forming processes used to permanently form pipes or tubing. Tube bending may be form-bound or use freeform-bending procedures, and it may use heat supported or cold forming procedures.
Form bound bending procedures like “press bending” or “rotary draw bending” are used to form the work piece into the shape of a die. Straight tube stock can be formed using a bending machine to create a variety of single or multiple bends and to shape the piece into the desired form. These processes can be used to form complex shapes out of different types of ductile metal tubing.[1] Freeform-bending processes, like three-roll-pushbending, shape the workpiece kinematically, thus the bending contour is not dependent on the tool geometry.
Generally, round stock is used in tube bending. However, square and rectangular tubes and pipes may also be bent to meet job specifications. Other factors involved in the bending process are the wall thickness, tooling and lubricants needed by the pipe and tube bender to best shape the material, and the different ways the tube may be used (tube, pipe wires).
In 1995, Uk-based Unison Ltd developed the first three ‘all-electric’ tube bending machines with; 20mm, 40mm and 65mm tube capacity. The very first machine went into service in 1996 and is still in production.
Geometry
A tube can be bent in multiple directions and angles. Common simple bends consist of forming elbows, which are 90° bends, and U-bends, which are 180° bends. More complex geometries include multiple two-dimensional (2D) bends and three-dimensional (3D) bends. A 2D tube has the openings on the same plane; a 3D has openings on different planes.
A two plane bend or compound bend is defined as a compound bend that has a bend in the plan view and a bend in the elevation. When calculating a two plane bend, one must know the bend angle and rotation (dihedral angle).
One side effect of bending the workpiece is the wall thickness changes; the wall along the inner radius of the tube becomes thicker and the outer wall becomes thinner. To reduce this the tube may be supported internally and or externally to preserve the cross section. Depending on the bend angle, wall thickness, and bending process the inside of the wall may wrinkle.
Processes
Tube bending as a process starts with loading a tube into a tube or pipe bender and clamping it into place between two dies, the clamping block and the forming die. The tube is also loosely held by two other dies, the wiper die and the pressure die.
The process of tube bending involves using mechanical force to push stock material pipe or tubing against a die, forcing the pipe or tube to conform to the shape of the die. Often, stock tubing is held firmly in place while the end is rotated and rolled around the die. Other forms of processing including pushing stock through rollers that bend it into a simple curve.[2] For some tube bending processing, a mandrel is placed inside the tube to prevent collapsing. The tube is held in tension by a wiper die to prevent any creasing during stress. A wiper die is usually made of a softer alloy such as aluminum or brass to avoid scratching or damaging the material being bent.
Much of the tooling is made of hardened steel or tool steel to maintain and prolong the tool's life. However, when there is a concern of scratching or gouging the work piece, a softer material such as aluminum or bronze is utilized. For example, the clamping block, rotating form block and pressure die are often formed from hardened steel because the tubing is not moving past these parts of the machine. The pressure die and the wiping die are formed from aluminum or bronze to maintain the shape and surface of the work piece as it slides by.
Pipe bending machines are typically human powered, pneumatic powered, hydraulic assisted, hydraulic driven, or electric servomotor.
Press bending
Press bending is probably the first bending process used on cold pipes and tubing.[clarification needed] In this process a die in the shape of the bend is pressed against the pipe forcing the pipe to fit the shape of the bend. Because the pipe is not supported internally there is some deformation of the shape of the pipe, resulting in an oval cross section. This process is used where a consistent cross section of the pipe is not required. Although a single die can produce various shapes, it only works for one size tube and radius.
Rotary draw bending
Rotary draw bending (RDB) is a precise technology, since it bends using tooling or "die sets" which have a constant center line radius (CLR), alternatively indicated as mean bending radius (Rm). Rotary draw benders can be programmable to store multiple bend jobs with varying degrees of bending. Often a positioning index table (IDX) is attached to the bender allowing the operator to reproduce complex bends which can have multiple bends and differing planes.
Rotary draw benders are the most popular machines for use in bending tube, pipe and solids for applications like: handrails, frames, motor vehicle roll cages, handles, lines and much more. Rotary draw benders create aesthetically pleasing bends when the right tooling is matched to the application. CNC rotary draw bending machines can be very complex and use sophisticated tooling to produce severe bends with high quality requirements.
The complete tooling is required only for high-precision bending of difficult-to-bend tubes with relatively large OD/t (diameter/thickness) ratio and relatively small ratio between the mean bending radius Rm and OD.[3] The use of axial boosting either on the tube free end or on the pressure die is useful to prevent excessive thinning and collapse of the extrados of the tube. The mandrel, with or without ball with spherical links, is mostly used to prevent wrinkles and ovalization. For relatively easy bending processes (that is, as the difficulty factor BF decreases), the tooling can be progressively simplified, eliminating the need for the axial assist, the mandrel, and the wiper die (which mostly prevents wrinkling). Furthermore, in some particular cases, the standard tooling must be modified in order to meet specific requirements of the products.
Roll bending
During the roll bending process the pipe, extrusion, or solid is passed through a series of rollers (typically three) that apply pressure to the pipe gradually changing the bend radius in the pipe. The pyramid style roll benders have one moving roll, usually the top roll. Double pinch type roll benders have two adjustable rolls, usually the bottom rolls, and a fixed top roll. This method of bending causes very little deformation in the cross section of the pipe. This process is suited to producing coils of pipe as well as long gentle bends like those used in truss systems.
Three-roll push bending
Three-roll push bending (TRPB) is the most commonly used freeform-bending process to manufacture bending geometries consisting of several plane bending curves. Nevertheless, 3D-shaping is possible. The profile is guided between bending-roll and supporting-roll(s), while being pushed through the tools. The position of the forming-roll defines the bending radius. The bending point is the tangent-point between tube and bending-roll. To change the bending plane, the pusher rotates the tube around its longitudinal axis. Generally, a TRPB tool kit can be applied on a conventional rotary draw bending machine. The process is very flexible since with a unique tool set, several bending radii values Rm can be obtained, although the geometrical precision of the process is not comparable to rotary draw bending.[4] Bending contours defined as spline- or polynomial-functions can be manufactured.[5]
Simple three-roll bending
Three roll bending of tubes and open profiles can also be performed with simpler machines, often semi-automatic and non CNC controlled, able to feed the tube into the bending zone by friction. These machines have often a vertical layout, i.e. the three rolls lie on a vertical plane.
Induction bending
An induction coil is placed around a small section of the pipe at the bend point. It is then induction heated to between 800 and 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit (430 and 1,200 C). While the pipe is hot, pressure is placed on the pipe to bend it. The pipe can then be quenched with either air or water spray or be cooled against ambient air.
Induction bending is used to produce bends for a wide range of applications, such as (thin walled) pipe lines for both the upstream and down stream and on- and off shore segments of the petrochemical industry, large radius structural parts for the construction industry, thick walled, short radius bends for the power generating industry and city heating systems.
Big advantages of induction bending are:
- no need for mandrels
- bend radii and angles (1°-180°) can be freely selected
- highly accurate bend radii and angles
- accurate pipe spools can easily be produced
- significant savings can be obtained on field welds
- wide range of pipe sizes can be accommodated in one machine (1” OD thru 80”OD)
- excellent wall thinning and ovality values
Packing
Ice packing
The pipe is filled with a water solution, frozen, and bent while cold. The solute (soap can be used) makes the ice flexible. This technique is used to make trombones.[6]
Pitch packing
A similar techniques using pitch was formerly used, but discontinued because the pitch was hard to clean out without excessive heat.[6]
Sand-packing/hot-slab forming
In the sand packing process the pipe is filled with fine sand and the ends are capped. The filled pipe is heated in a furnace to 1,600 °F (870 °C) or higher. Then it is placed on a slab with pins set in it, and bent around the pins using a winch, crane, or some other mechanical force. The sand in the pipe minimizes distortion in the pipe cross section.
Mandrels
A mandrel is a steel rod or linked ball inserted into the tube while it is being bent to give the tube extra support to reduce wrinkling and breaking the tube during this process. The different types of mandrels are as follows.
- Plug mandrel: a solid rod used on normal bends
- Form mandrel: a solid rod with curved end used on bend when more support is needed
- Ball mandrel without cable: unlinked steel ball bearings inserted into tube, used on critical and precise bends
- Ball mandrel with cable: linked ball bearings inserted into tube, used on critical bend and precise bends
- Sand: sand packed into tube
In production of a product where the bend is not critical a plug mandrel can be used. A form type tapers the end of the mandrel to provide more support in the bend of the tube. When precise bending is needed a ball mandrel (or ball mandrel with steel cable) should be used. The conjoined ball-like disks are inserted into the tubing to allow for bending while maintaining the same diameter throughout. Other styles include using sand, cerrobend, or frozen water. These allow for a somewhat constant diameter while providing an inexpensive alternative to the aforementioned styles.
Performance automotive or motorcycle exhaust pipe is a common application for a mandrel.
Bending springs
These are strong but flexible springs inserted into a pipe to support the pipe walls during manual bending. They have diameters only slightly less than the internal diameter of the pipe to be bent. They are only suitable for bending 15-and-22 mm (0.6-and-0.9 in) soft copper pipe (typically used in household plumbing) or PVC pipe.
The spring is pushed into the pipe until its center is roughly where the bend is to be. A length of flexible wire can be attached to the end of the spring to facilitate its removal. The pipe is generally held against the flexed knee, and the ends of the pipe are pulled up to create the bend. To make it easier to retrieve the spring from the pipe, it is a good idea to bend the pipe slightly more than required, and then slacken it off a little. Springs are less cumbersome than rotary benders, but are not suitable for bending short lengths of piping when it is difficult to get the required leverage on the pipe ends.
Bending springs for smaller diameter pipes (10 mm copper pipe) slide over the pipe instead of inside.
See also
- Bending (mechanics)
- Bending machine (manufacturing)
- Brake (sheet metal bending)
- Spring Back Compensation
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tube_bending
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring voltage or 'potential difference' by comparison of an unknown voltage with a known reference voltage. If a sensitive indicating instrument is used, very little current is drawn from the source of the unknown voltage. Since the reference voltage can be produced from an accurately calibrated voltage divider, a potentiometer can provide high precision in measurement. The method was described by Johann Christian Poggendorff around 1841 and became a standard laboratory measuring technique.[1]
In this arrangement, a fraction of a known voltage from a resistive slide wire is compared with an unknown voltage by means of a galvanometer. The sliding contact or wiper of the potentiometer is adjusted and the galvanometer briefly connected between the sliding contact and the unknown voltage. The deflection of the galvanometer is observed and the sliding tap adjusted until the galvanometer no longer deflects from zero. At that point the galvanometer draws no current from the unknown source, and the magnitude of voltage can be calculated from the position of the sliding contact.
This null balance measuring method is still important in electrical metrology and standards work and is also used in other areas of electronics.
Measurement potentiometers are divided into four main classes listed below.
Principle of operation
The principle of a potentiometer is that the potential dropped across a segment of a wire of uniform cross-section carrying a constant current is directly proportional to its length. The potentiometer is a simple device used to measure the electrical potentials (or compare the e.m.f of a cell). One form of potentiometer is a uniform high-resistance wire attached to an insulating support, marked with a linear measuring scale. In use, an adjustable regulated voltage source E, of greater magnitude than the potential to be measured, is connected across the wire so as to pass a steady current through it.
Between the end of the wire and any point along it will be a potential proportional to the length of wire to that point. By comparing the potential at points along the wire with an unknown potential, the magnitude of the unknown potential can be determined. The instrument used for comparison must be sensitive, but need not be particularly well-calibrated or accurate so long as its deflection from zero position can be easily detected.
Constant current potentiometer
In this circuit, the ends of a uniform resistance wire R1 are connected to a regulated DC supply VS for use as a voltage divider. The potentiometer is first calibrated by positioning the wiper (arrow) at the spot on the R1 wire that corresponds to the voltage of a standard cell so that
A standard electrochemical cell is used whose emf is known (e.g. 1.0183 volts for a Weston standard cell).[2][3]
The supply voltage VS is then adjusted until the galvanometer shows zero, indicating the voltage on R2 is equal to the standard cell voltage.
An unknown DC voltage, in series with the galvanometer, is then connected to the sliding wiper, across a variable-length section R3 of the resistance wire. The wiper is moved until no current flows into or out of the source of unknown voltage, as indicated by the galvanometer in series with the unknown voltage. The voltage across the selected R3 section of wire is then equal to the unknown voltage. The final step is to calculate the unknown voltage from the fraction of the length of the resistance wire that was connected to the unknown voltage.
The galvanometer does not need to be calibrated, as its only function is to read zero or not zero. When measuring an unknown voltage and the galvanometer reads zero, no current is drawn from the unknown voltage and so the reading is independent of the source's internal resistance, as if by a voltmeter of infinite resistance.
Because the resistance wire can be made very uniform in cross-section and resistivity, and the position of the wiper can be measured easily, this method can be used to measure unknown DC voltages greater than or less than a calibration voltage produced by a standard cell without drawing any current from the standard cell.
If the potentiometer is attached to a constant voltage DC supply such as a lead–acid battery, then a second variable resistor (not shown) can be used to calibrate the potentiometer by varying the current through the R1 resistance wire.
If the length of the R1 resistance wire is AB, where A is the (-) end and B is the (+) end, and the movable wiper is at point X at a distance AX on the R3 portion of the resistance wire when the galvanometer gives a zero reading for an unknown voltage, the distance AX is measured or read from a pre-printed scale next to the resistance wire. The unknown voltage can then be calculated:
Constant resistance potentiometer
The constant resistance potentiometer is a variation of the basic idea in which a variable current is fed through a fixed resistor. These are used primarily for measurements in the millivolt and microvolt range.
Microvolt potentiometer
This is a form of the constant resistance potentiometer described above but designed to minimize the effects of contact resistance and thermal emf. This equipment is satisfactorily used down to readings of 1000 nV or so.
Thermocouple potentiometer
Another development of the standard types was the 'thermocouple potentiometer' especially adapted for temperature measurement with thermocouples.[4] Potentiometers for use with thermocouples also measure the temperature at which the thermocouple wires are connected, so that cold-junction compensation may be applied to correct the apparent measured EMF to the standard cold-junction temperature of 0 degrees C.
Analytical chemistry
To make a potentiometric determination of an analyte in a solution, the potential of the cell is measured. This measurement must be corrected for the reference and junction potentials. It can also be used in standardisation methods. The concentration of the analyte can then be calculated from the Nernst Equation. Many varieties of this basic principle exist for quantitative measurements.
Metre bridge
A metre bridge is a simple type of potentiometer which may be used in school science laboratories to demonstrate the principle of resistance measurement by potentiometric means. A resistance wire is laid along the length of a metre rule and contact with the wire is made through a galvanometer by a slider. When the galvanometer reads zero, the ratio between the lengths of wire to the left and right of the slider is equal to the ratio between the values of a known and an unknown resistor in a parallel circuit.[5]
See also
References
- "Ian Hickson's Metre Bridge Experiment". Academia.hixie.ch. Retrieved 2013-06-01.
External links
- Pictures of measuring potentiometers
- Electrical calibration equipment including various measurement potentiometers
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potentiometer_(measuring_instrument)
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in art, printed media, simulators, videos and video games. These images are either static (i.e. still images) or dynamic (i.e. moving images). CGI both refers to 2D computer graphics and (more frequently) 3D computer graphics with the purpose of designing characters, virtual worlds, or scenes and special effects (in films, television programs, commercials, etc.). The application of CGI for creating/improving animations is called computer animation, or CGI animation.
History
The first feature film to use CGI as well as the composition of live action film with CGI was Vertigo (1958)[1], which used CGI in the opening credits of the film. The first feature film to make use of CGI with live action in the storyline of the film was the 1973 film Westworld.[2] Other early films that incorporated CGI include Star Wars: Episode IV (1977),[2] Tron (1982),[2] Golgo 13: The Professional (1983),[3] The Last Starfighter (1984),[4] Young Sherlock Holmes (1985)[2] and Flight of the Navigator (1986).[5] The first music video to use CGI was Dire Straits' award-winning "Money for Nothing" (1985), whose success was instrumental in giving the process mainstream exposure.[6]
The evolution of CGI led to the emergence of virtual cinematography in the 1990s, where the vision of the simulated camera is not constrained by the laws of physics. Availability of CGI software and increased computer speeds have allowed individual artists and small companies to produce professional-grade films, games, and fine art from their home computers.
Static images and landscapes
Not only do animated images form part of computer-generated imagery; natural looking landscapes (such as fractal landscapes) are also generated via computer algorithms. A simple way to generate fractal surfaces is to use an extension of the triangular mesh method, relying on the construction of some special case of a de Rham curve, e.g. midpoint displacement.[7] For instance, the algorithm may start with a large triangle, then recursively zoom in by dividing it into four smaller Sierpinski triangles, then interpolate the height of each point from its nearest neighbors.[7] The creation of a Brownian surface may be achieved not only by adding noise as new nodes are created but by adding additional noise at multiple levels of the mesh.[7] Thus a topographical map with varying levels of height can be created using relatively straightforward fractal algorithms. Some typical, easy-to-program fractals used in CGI are the plasma fractal and the more dramatic fault fractal.[8]
Many specific techniques been researched and developed to produce highly focused computer-generated effects — e.g., the use of specific models to represent the chemical weathering of stones to model erosion and produce an "aged appearance" for a given stone-based surface.[9]
Architectural scenes
Modern architects use services from computer graphic firms to create 3-dimensional models for both customers and builders. These computer generated models can be more accurate than traditional drawings. Architectural animation (which provides animated movies of buildings, rather than interactive images) can also be used to see the possible relationship a building will have in relation to the environment and its surrounding buildings. The processing of architectural spaces without the use of paper and pencil tools is now a widely accepted practice with a number of computer-assisted architectural design systems.[10]
Architectural modeling tools allow an architect to visualize a space and perform "walk-throughs" in an interactive manner, thus providing "interactive environments" both at the urban and building levels.[11] Specific applications in architecture not only include the specification of building structures (such as walls and windows) and walk-throughs but the effects of light and how sunlight will affect a specific design at different times of the day.[12][13]
Architectural modeling tools have now become increasingly internet-based. However, the quality of internet-based systems still lags behind that of sophisticated in-house modeling systems.[14]
In some applications, computer-generated images are used to "reverse engineer" historical buildings. For instance, a computer-generated reconstruction of the monastery at Georgenthal in Germany was derived from the ruins of the monastery, yet provides the viewer with a "look and feel" of what the building would have looked like in its day.[15]
Anatomical models
Computer generated models used in skeletal animation are not always anatomically correct. However, organizations such as the Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute have developed anatomically correct computer-based models. Computer generated anatomical models can be used both for instructional and operational purposes. To date, a large body of artist produced medical images continue to be used by medical students, such as images by Frank H. Netter, e.g. Cardiac images. However, a number of online anatomical models are becoming available.
A single patient X-ray is not a computer generated image, even if digitized. However, in applications which involve CT scans a three-dimensional model is automatically produced from many single-slice x-rays, producing "computer generated image". Applications involving magnetic resonance imaging also bring together a number of "snapshots" (in this case via magnetic pulses) to produce a composite, internal image.
In modern medical applications, patient-specific models are constructed in 'computer assisted surgery'. For instance, in total knee replacement, the construction of a detailed patient-specific model can be used to carefully plan the surgery.[16] These three-dimensional models are usually extracted from multiple CT scans of the appropriate parts of the patient's own anatomy. Such models can also be used for planning aortic valve implantations, one of the common procedures for treating heart disease. Given that the shape, diameter, and position of the coronary openings can vary greatly from patient to patient, the extraction (from CT scans) of a model that closely resembles a patient's valve anatomy can be highly beneficial in planning the procedure.[17]
Cloth and skin images
Models of cloth generally fall into three groups:
- The geometric-mechanical structure at yarn crossing
- The mechanics of continuous elastic sheets
- The geometric macroscopic features of cloth.[18]
To date, making the clothing of a digital character automatically fold in a natural way remains a challenge for many animators.[19]
In addition to their use in film, advertising and other modes of public display, computer generated images of clothing are now routinely used by top fashion design firms.[20]
The challenge in rendering human skin images involves three levels of realism:
- Photo realism in resembling real skin at the static level
- Physical realism in resembling its movements
- Function realism in resembling its response to actions.[21]
The finest visible features such as fine wrinkles and skin pores are the size of about 100 µm or 0.1 millimetres. Skin can be modeled as a 7-dimensional bidirectional texture function (BTF) or a collection of bidirectional scattering distribution function (BSDF) over the target's surfaces.
Interactive simulation and visualization
Interactive visualization is the rendering of data that may vary dynamically and allowing a user to view the data from multiple perspectives. The applications areas may vary significantly, ranging from the visualization of the flow patterns in fluid dynamics to specific computer aided design applications.[22] The data rendered may correspond to specific visual scenes that change as the user interacts with the system — e.g. simulators, such as flight simulators, make extensive use of CGI techniques for representing the world.[23]
At the abstract level, an interactive visualization process involves a "data pipeline" in which the raw data is managed and filtered to a form that makes it suitable for rendering. This is often called the "visualization data". The visualization data is then mapped to a "visualization representation" that can be fed to a rendering system. This is usually called a "renderable representation". This representation is then rendered as a displayable image.[23] As the user interacts with the system (e.g. by using joystick controls to change their position within the virtual world) the raw data is fed through the pipeline to create a new rendered image, often making real-time computational efficiency a key consideration in such applications.[23][24]
Computer animation
While computer-generated images of landscapes may be static, computer animation only applies to dynamic images that resemble a movie. However, in general, the term computer animation refers to dynamic images that do not allow user interaction, and the term virtual world is used for the interactive animated environments.
Computer animation is essentially a digital successor to the art of stop motion animation of 3D models and frame-by-frame animation of 2D illustrations. Computer generated animations are more controllable than other more physically based processes, such as constructing miniatures for effects shots or hiring extras for crowd scenes, and because it allows the creation of images that would not be feasible using any other technology. It can also allow a single graphic artist to produce such content without the use of actors, expensive set pieces, or props.
To create the illusion of movement, an image is displayed on the computer screen and repeatedly replaced by a new image which is similar to the previous image, but advanced slightly in the time domain (usually at a rate of 24 or 30 frames/second). This technique is identical to how the illusion of movement is achieved with television and motion pictures.
Text-to-image models
A text-to-image model is a machine learning model which takes an input natural language description and produces an image matching that description. Such models began to be developed in the mid-2010s, as a result of advances in deep neural networks. In 2022, the output of state of the art text-to-image models, such as OpenAI's DALL-E 2, Google Brain's Imagen and StabilityAI's Stable Diffusion began to approach the quality of real photographs and human-drawn art.
Text-to-image models generally combine a language model, which transforms the input text into a latent representation, and a generative image model, which produces an image conditioned on that representation. The most effective models have generally been trained on massive amounts of image and text data scraped from the web.[25]Virtual worlds
A virtual world is an agent-based and simulated environment allowing users to interact with artificially animated characters (e.g software agent) or with other physical users, through the use of avatars. Virtual worlds are intended for its users to inhabit and interact, and the term today has become largely synonymous with interactive 3D virtual environments, where the users take the form of avatars visible to others graphically.[26] These avatars are usually depicted as textual, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional graphical representations, although other forms are possible[27] (auditory[28] and touch sensations for example). Some, but not all, virtual worlds allow for multiple users.
In courtrooms
Computer-generated imagery has been used in courtrooms, primarily since the early 2000s. However, some experts have argued that it is prejudicial. They are used to help judges or the jury to better visualize the sequence of events, evidence or hypothesis.[29] However, a 1997 study showed that people are poor intuitive physicists and easily influenced by computer generated images.[30] Thus it is important that jurors and other legal decision-makers be made aware that such exhibits are merely a representation of one potential sequence of events.
Broadcast and live events
Weather visualizations were the first application of CGI in television. It has now become common in weather casting to display full motion video of images captured in real-time from multiple cameras and other imaging devices. Coupled with 3D graphics symbols and mapped to a common virtual geospatial model, these animated visualizations constitute the first true application of CGI to TV.
CGI has become common in sports telecasting. Sports and entertainment venues are provided with see-through and overlay content through tracked camera feeds for enhanced viewing by the audience. Examples include the yellow "first down" line seen in television broadcasts of American football games showing the line the offensive team must cross to receive a first down. CGI is also used in association with football and other sporting events to show commercial advertisements overlaid onto the view of the playing area. Sections of rugby fields and cricket pitches also display sponsored images. Swimming telecasts often add a line across the lanes to indicate the position of the current record holder as a race proceeds to allow viewers to compare the current race to the best performance. Other examples include hockey puck tracking and annotations of racing car performance[31] and snooker ball trajectories.[32][33] Sometimes CGI on TV with correct alignment to the real world has been referred to as augmented reality.
Motion-capture
Computer-generated imagery is often used in conjunction with motion-capture to better cover the faults that come with CGI and animation. Computer-generated imagery is limited in its practical application by how realistic it can look. Unrealistic, or badly managed computer-generated imagery can result in the Uncanny Valley effect.[34] This effect refers to the human ability to recognize things that look eerily like humans, but are slightly off. Such ability is a fault with normal computer-generated imagery which, due to the complex anatomy of the human-body, can often fail to replicate it perfectly. This is where motion-capture comes into play. Artists can use a motion-capture rig to get footage of a human performing an action and then replicate it perfectly with computer-generated imagery so that it looks normal.
The lack of anatomically correct digital models contributes to the necessity of motion-capture as it is used with computer-generated imagery. Because computer-generated imagery reflects only the outside, or skin, of the object being rendered, it fails to capture the infinitesimally small interactions between interlocking muscle groups used in fine motor-control, like speaking. The constant motion of the face as it makes sounds with shaped lips and tongue movement, along with the facial expressions that go along with speaking are difficult to replicate by hand.[35] Motion capture can catch the underlying movement of facial muscles and better replicate the visual that goes along with the audio, like Josh Brolin's Thanos.
See also
- 3D modeling
- Cinema Research Corporation
- Cel shading
- Anime Studio
- Animation database
- List of computer-animated films
- Digital image
- Parallel rendering
- Photoshop is the industry standard commercial digital photo editing tool.
- GIMP, a FOSS digital photo editing application.
- Poser DIY CGI optimized for soft models
- Ray tracing (graphics)
- Real-time computer graphics
- Shader
- Virtual human
- Virtual studio
- Virtual Physiological Human
References
Citations
- Pelachaud, Catherine; Steedman, Mark; Badler, Norman (1991-06-01). "Linguistic Issues in Facial Animation". Center for Human Modeling and Simulation.
Sources
- Begault, Durand R. (1994). 3-D Sound for Virtual Reality and Multimedia. AP Professional. ISBN 978-0-1208-4735-8.
- Biocca, Frank; Levy, Mark R. (1995). Communication in the Age of Virtual Reality. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. ISBN 978-0-8058-1549-8.
- Peitgen, Heinz-Otto; Jürgens, Hartmut; Saupe, Dietmar (2004). Chaos and Fractals: New Frontiers of Science. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-0-387-20229-7.
- Sondermann, Horst (2008). Light Shadow Space: Architectural Rendering with Cinema 4D. Vienna: Springer. ISBN 978-3-211-48761-7.
External links
| Library resources about Computer-generated imagery |
- A Critical History of Computer Graphics and Animation – a course page at Ohio State University that includes all the course materials and extensive supplementary materials (videos, articles, links).
- CG101: A Computer Graphics Industry Reference ISBN 073570046X Unique and personal histories of early computer graphics production, plus a comprehensive foundation of the industry for all reading levels.
- F/X Gods, by Anne Thompson, Wired, February 2005.
- "History Gets A Computer Graphics Make-Over" Tayfun King, Click, BBC World News (2004-11-19)
- NIH Visible Human Gallery
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer-generated_imagery
Hand Drawn Pressing is a vinyl record pressing company located in Addison, Texas.[1] It opened in 2011 as the world's first fully automated record pressing plant.[2][3]
History
Starting as Dallas-based record label Hand Drawn Records, Hand Drawn Pressing expanded into record brokering in 2011, simplifying the process for artists and pressing records through another record pressing plant. It eventually became independent from the record label by the name of Hand Drawn Pressing under chief creative officer Dustin Blocker and chief operating officer Alex Cushing in 2014.[4] Acquiring two vinyl record presses in 2016, Hand Drawn Pressing began operations in a packaging warehouse.[5][6]
Technology
Hand Drawn Pressing uses the WarmTone press engineered by Canada's Viryl Technologies.[7] Before the introduction of the WarmTone press, all current record pressing facilities used machines exclusively resurfaced from the twentieth century.[8] The resurfaced machines press an average of two records per minute. The WarmTone press averages three records per minute with a smaller percentage for error.[9][10]
See also
Production of phonograph records
References
- Mawajdeh, Hady. "This indie music label is investing in vinyl". Marketplace. Marketplace. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
External links
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hand_Drawn_Pressing
In philosophy, the brain in a vat (BIV) is a scenario used in a variety of thought experiments intended to draw out certain features of human conceptions of knowledge, reality, truth, mind, consciousness, and meaning. It is a modernized version of René Descartes's evil demon thought experiment, originated by Gilbert Harman.[1] Found in many science fiction stories, it outlines a scenario in which a mad scientist, machine, or other entity might remove a person's brain from the body, suspend it in a vat of life-sustaining liquid, and connect its neurons by wires to a supercomputer that would provide it with electrical impulses identical to those a brain normally receives.[2] According to such stories, the computer would then be simulating reality (including appropriate responses to the brain's own output) and the "disembodied" brain would continue to have perfectly normal conscious experiences, such as those of a person with an embodied brain, without these being related to objects or events in the real world.
Uses
The simplest use of brain-in-a-vat scenarios is as an argument for philosophical skepticism[3] and solipsism. A simple version of this runs as follows: since the brain in a vat gives and receives exactly the same impulses as it would if it were in a skull, and since these are its only way of interacting with its environment, then it is not possible to tell, from the perspective of that brain, whether it is in a skull or a vat. Yet in the first case, most of the person's beliefs may be true (if they believe, say, that they are walking down the street, or eating ice-cream); in the latter case, their beliefs are false. Since the argument says if one cannot know whether one is a brain in a vat, then one cannot know whether most of one's beliefs might be completely false. Since, in principle, it is impossible to rule out oneself being a brain in a vat, there cannot be good grounds for believing any of the things one believes; a skeptical argument would contend that one certainly cannot know them, raising issues with the definition of knowledge. Other philosophers have drawn upon sensation and its relationship to meaning in order to question whether brains in vats are really deceived at all,[4] thus raising wider questions concerning perception, metaphysics, and the philosophy of language.
The brain-in-a-vat is a contemporary version of the argument given in Hindu Maya illusion, Plato's Allegory of the Cave, Zhuangzi's "Zhuangzi dreamed he was a butterfly", and the evil demon in René Descartes' Meditations on First Philosophy.
Recently, many contemporary philosophers believe that virtual reality will seriously affect human autonomy as a form of brain in a vat. But another view is that VR will not destroy our cognitive structure or take away our connection with reality. On the contrary, VR will allow us to have more new propositions, new insights and new perspectives to see the world.[5]
Philosophical debates
While the disembodied brain (the brain in a vat) can be seen as a helpful thought experiment, there are several philosophical debates surrounding the plausibility of the thought experiment. If these debates conclude that the thought experiment is implausible, a possible consequence would be that we are no closer to knowledge, truth, consciousness, representation, etc. than we were prior to the experiment.
Argument from biology
One argument against the BIV thought experiment derives from the idea that the BIV is not – and cannot be – biologically similar to that of an embodied brain (that is, a brain found in a person). Since the BIV is dis embodied, it follows that it does not have similar biology to that of an embodied brain. That is, the BIV lacks the connections from the body to the brain, which renders the BIV neither neuroanatomically nor neurophysiologically similar to that of an embodied brain.[6][7] If this is the case, we cannot say that it is even possible for the BIV to have similar experiences to the embodied brain, since the brains are not equal. However, it could be counter-argued that the hypothetical machine could be made to also replicate those types of inputs.
Argument from externalism
A second argument deals directly with the stimuli coming into the brain. This is often referred to as the account from externalism or ultra-externalism.[8] In the BIV, the brain receives stimuli from a machine. In an embodied brain, however, the brain receives the stimuli from the sensors found in the body (via touching, tasting, smelling, etc.) which receive their input from the external environment. This argument oftentimes leads to the conclusion that there is a difference between what the BIV is representing and what the embodied brain is representing. This debate has been hashed out, but remains unresolved, by several philosophers including Uriah Kriegel,[9] Colin McGinn,[10] and Robert D. Rupert,[11] and has ramifications for philosophy of mind discussions on (but not limited to) representation, consciousness, content, cognition, and embodied cognition.[12]
Argument from incoherence
A third argument against BIV comes from a direction of incoherence, which was presented by the philosopher Hilary Putnam. He attempts to demonstrate this through the usage of a transcendental argument, in which he tries to illustrate that the thought experiment's incoherence lies on the basis that it is self-refuting.[13] To do this, Putnam first established a relationship that he refers to as a "causal connection" which is sometimes referred to as "a causal constraint".[14][2] This relationship is further defined, through a theory of reference that suggested reference can not be assumed, and words are not automatically intrinsically connected with what it represents. This theory of reference would later become known as semantic externalism. This concept is further illustrated when Putnam establishes a scenario in which a monkey types out Hamlet by chance; however, this does not mean that the monkey is referring to the play due to the fact that the monkey has no knowledge of Hamlet and therefore can not refer back to it.[15] He then offers the "Twin Earth" example to demonstrate that two identical individuals, one on the Earth and another on a "twin Earth", may possess the exact same mental state and thoughts, yet refer to two different things.[16] For instance, when people think of cats, the referent of their thoughts would be the cats that are found on Earth. However, people's twins on twin Earth, though possessing the same thoughts, would instead be referring not to Earth's cats, but to twin Earth's cats. Bearing this in mind, he writes that a "pure" brain in a vat, i.e., one that has never existed outside of the simulation, could not even truthfully say that it was a brain in a vat. This is because the BIV, when it says "brain" and "vat", can only refer to objects within the simulation, not to things outside the simulation it does not have a relationship with. Putnam refers to this relationship as a "causal connection" which is sometimes referred to as "a causal constraint".[14][2] Therefore, what it says is demonstrably false. Alternatively, if the speaker is not actually a BIV, then the statement is also false. He concludes, then, that the statement "I'm a BIV" is necessarily false and self-refuting.[16] This argument has been explored at length in philosophical literature since its publication. One counter-argument says that, even assuming Putnam's reference theory, a brain on Earth that is "kidnapped", placed into a vat, and subjected to a simulation could still refer to "real" brains and vats, and thus correctly say it is a brain in a vat.[17] However, the notion that the "pure" BIV is incorrect and the reference theory underpinning it remains influential in the philosophy of mind, language and metaphysics.[18][19]
Reconstructions of Putnam's argument
An issue that has arisen with Putnam's argument is that even if the premises he laid out is assumed to be true, the only proven fact is that when a brain in a vat states 'I am a BIV' it would be false due to the causal theory of reference.[20] This does not necessarily provide proof that we are not brains in vats, rather it is an argument that is primarily focused on externalist semantics.[21] In order to combat this issue, various philosophers have taken on the task of reconstructing Putnam's argument. Some philosophers like Anthony L. Brueckner and Crispin Wright have taken on approaches that utilize disquotational principles.[20][14] While others like Ted A. Warfield have taken on approaches that focus on the concepts of self-knowledge and priori.[21]
The Disjunctive Argument
One of the earliest but influential reconstructions of Putnam's transcendental argument was suggested by Anthony L. Brueckner. Brueckner's reconstruction is as follows: "(1) Either I am a BIV (speaking vat-English) or I am a non-BIV (speak- ing English). (2) If I am a BIV (speaking vat-English), then my utterances of 'I am a BIV' are true if I have sense impressions as of being a BIV. (3) If I am a BIV (speaking vat-English), then I do not have sense impressions as of being a BIV. (4) If I am a BIV (speaking vat-English), then my utterances of 'I am a BIV' are false. [(2), (3)] (5) If I am a non-BIV (speaking English), then my utterances of 'I am a BIV' are true if I am a BIV. (6) If I am a non-BIV (speaking English), then my utterances of 'I am a BIV' are false. [(5)] (7) My utterances of 'I am a BIV' are false. [(1), (4), (6)]"[20] A key thing to note is that although these premises further define Putnam's argument, it does not in fact prove ' I am not a BIV', due to the fact that although the premises do lay out the idea that 'I am a BIV' is false, it does not necessarily provide any basis on which false statement the speaker is making. There is no differentiation between the BIV making the statement versus a non-BIV making the statement. Therefore, Brueckner further strengthens his argument by adding a disquotational principle of "My utterances of ‘I am not a BIV’ are true if I am not a BIV."[20]
In fiction
- Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D., Season 4
- Alita: Battle Angel
- Avatar
- Bliss
- "The Brain of Colonel Barham", a 1965 episode of the TV series The Outer Limits
- The Brain of Morbius
- Brain (novel)
- Brainstorm
- Caprica
- Chappie
- The City of Lost Children
- Cold Lazarus
- The Colossus of New York[22]
- Dark Star
- Donovan's Brain
- Existenz
- Fallout series
- Point Lookout, an expansion pack for Fallout 3
- Old World Blues, an expansion pack for Fallout: New Vegas
- Automatron, an expansion pack for Fallout 4
- Futurama
- Gangers in Doctor Who
- Ghost in the Shell
- Inception
- Kavanozdaki Adam
- Lobotomy Corporation
- "Flashes Before Your Eyes", an episode of Lost
- The Man with Two Brains
- The Matrix film series
- "Out of Time", an episode of Red Dwarf
- Possible Worlds
- Psycho-Pass
- Repo Men
- RoboCop
- Saints Row IV
- "Ship in a Bottle", an episode of Star Trek: The Next Generation
- Sid Meier's Alpha Centauri
- Soma
- Source Code
- "Spock's Brain", an episode of Star Trek: The Original Series
- The Star Diaries
- Strange Days
- "The Inner Light", an episode of Star Trek: The Next Generation
- The Thirteenth Floor
- Total Recall
- Transcendence
- Tron
- Tron: Legacy
- "The Vacation Goo", an episode of American Dad!
- The Whisperer in Darkness
- Upload (TV series)
- Where am I?, written by Daniel Dennett
- William and Mary by Roald Dahl
- Adapted into the first episode of Way Out in 1961
- Adapted again for Tales of the Unexpected in 1979
- "White Christmas - Part II", an episode of Black Mirror
- World on a Wire
See also
References
- "The Colossus of New York (1958)". monsterhuntermoviereviews.com. MonsterHunter. 27 September 2013. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
It turns out that Jeremy's brain was sitting in a glass case of water hooked up to an EEG machine which led me to believe that they must have had some kind of clearance sale on set leftovers from Donovan's Brain.
(with photo).
External links
- Philosophy
- Brueckner, Tony. "Skepticism and Content Externalism". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- "Brain in a vat". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- Inverse "brain in a vat"
- Putnam's discussion of the "brains in a vat" in chapter one of Reason, Truth, and History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1981. p. 222. ISBN 978-0-52129776-9.
- 'Where Am I?' by Daniel Dennett
- "Brain in a Vat Brain Teaser" – Harper's Magazine (1996)
- Science
- Adaptive flight control with living neuronal networks on microelectrode arrays
- Architecture for Neuronal Cell Control of a Mobile Robot
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_in_a_vat
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mad_scientist
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Playing_God_(ethics)
| Part of a series of articles on |
| Synthetic biology |
|---|
| Synthetic biological circuits |
| Genome editing |
| Artificial cells |
| Xenobiology |
| Other topics |
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary field of science that focuses on living systems and organisms, and it applies engineering principles to develop new biological parts, devices, and systems or to redesign existing systems found in nature.[1]
It is a branch of science that encompasses a broad range of methodologies from various disciplines, such as biotechnology, biomaterials, material science/engineering, genetic engineering, molecular biology, molecular engineering, systems biology, membrane science, biophysics, chemical and biological engineering, electrical and computer engineering, control engineering and evolutionary biology.
It includes designing and constructing biological modules, biological systems, and biological machines or, re-design of existing biological systems for useful purposes.[2]
Additionally, it is the branch of science that focuses on the new abilities of engineering into existing organisms to redesign them for useful purposes.[3]
In order to produce predictable and robust systems with novel functionalities that do not already exist in nature, it is also necessary to apply the engineering paradigm of systems design to biological systems. According to the European Commission, this possibly involves a molecular assembler based on biomolecular systems such as the ribosome.[4]
History
1910: First identifiable use of the term synthetic biology in Stéphane Leduc's publication Théorie physico-chimique de la vie et générations spontanées.[5] He also noted this term in another publication, La Biologie Synthétique in 1912.[6]
1944: Canadian-American scientist Oswald Avery shows that DNA is the material of which genes and chromosomes are made. This becomes the bedrock on which call subsequent genetic research is built.[7]
1953: Francis Crick and James Watson publish the structure of the DNA in Nature.
1961: Jacob and Monod postulate cellular regulation by molecular networks from their study of the lac operon in E. coli and envisioned the ability to assemble new systems from molecular components.[8]
1973: First molecular cloning and amplification of DNA in a plasmid is published in P.N.A.S. by Cohen, Boyer et al. constituting the dawn of synthetic biology.[9]
1978: Arber, Nathans and Smith win the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of restriction enzymes, leading Szybalski to offer an editorial comment in the journal Gene:
The work on restriction nucleases not only permits us easily to construct recombinant DNA molecules and to analyze individual genes, but also has led us into the new era of synthetic biology where not only existing genes are described and analyzed but also new gene arrangements can be constructed and evaluated.[10]
1988: First DNA amplification by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a thermostable DNA polymerase is published in Science by Mullis et al.[11] This obviated adding new DNA polymerase after each PCR cycle, thus greatly simplifying DNA mutagenesis and assembly.
2000: Two papers in Nature report synthetic biological circuits, a genetic toggle switch and a biological clock, by combining genes within E. coli cells.[12][13]
2003: The most widely used standardized DNA parts, BioBrick plasmids, are invented by Tom Knight.[14] These parts will become central to the International Genetically Engineered Machine (iGEM) competition founded at MIT in the following year.
2003: Researchers engineer an artemisinin precursor pathway in E. coli.[15]
2004: First international conference for synthetic biology, Synthetic Biology 1.0 (SB1.0) is held at MIT.
2005: Researchers develop a light-sensing circuit in E. coli.[16] Another group designs circuits capable of multicellular pattern formation.[17]
2006: Researchers engineer a synthetic circuit that promotes bacterial invasion of tumour cells.[18]
2010: Researchers publish in Science the first synthetic bacterial genome, called M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0.[19][20] The genome is made from chemically-synthesized DNA using yeast recombination.
2011: Functional synthetic chromosome arms are engineered in yeast.[21]
2012: Charpentier and Doudna labs publish in Science the programming of CRISPR-Cas9 bacterial immunity for targeting DNA cleavage.[22] This technology greatly simplified and expanded eukaryotic gene editing.
2019: Scientists at ETH Zurich report the creation of the first bacterial genome, named Caulobacter ethensis-2.0, made entirely by a computer, although a related viable form of C. ethensis-2.0 does not yet exist.[23][24]
2019: Researchers report the production of a new synthetic (possibly artificial) form of viable life, a variant of the bacteria Escherichia coli, by reducing the natural number of 64 codons in the bacterial genome to 59 codons instead, in order to encode 20 amino acids.[25][26]
2020: Scientist created the first xenobot, programmable synthetic organism derived from frog cells and designed by AI.[27]
2021: Scientist reported that xenobots are able to self-replicate by gathering loose cells in the environment and then forming new xenobot.[28]
Perspectives
It is a field whose scope is expanding in terms of systems integration, engineered organisms and practical findings.[1]
Engineers view biology as technology (in other words, a given system includes biotechnology or its biological engineering)[29] Synthetic biology includes the broad redefinition and expansion of biotechnology, with the ultimate goal of being able to design and build engineered live biological systems that process information, manipulate chemicals, fabricate materials and structures, produce energy, provide food, and maintain and enhance human health, as well as advance fundamental knowledge of biological systems and our environment.[30]
Researchers and companies working in synthetic biology are using nature's power to solve issues in agriculture, manufacturing, and medicine.[3]
Due to more powerful genetic engineering capabilities and decreased DNA synthesis and sequencing costs, the field of synthetic biology is rapidly growing. In 2016, more than 350 companies across 40 countries were actively engaged in synthetic biology applications; all these companies had an estimated net worth of $3.9 billion in the global market.[31] Synthetic biology currently has no generally accepted definition. Here are a few examples:
It is the science of emerging genetic and physical engineering to produce new (and, therefore, synthetic) life forms. To develop organisms with novel or enhanced characteristics, this emerging field of study combines biology, engineering, and related disciplines' knowledge and techniques to design chemically synthesised DNA.[32][33]
Biomolecular engineering includes approaches that aim to create a toolkit of functional units that can be introduced to present new technological functions in living cells. Genetic engineering includes approaches to construct synthetic chromosomes or minimal organisms like Mycoplasma laboratorium.
Biomolecular design refers to the general idea of de novo design and additive combination of biomolecular components. Each of these approaches shares a similar task: to develop a more synthetic entity at a higher level of complexity by inventively manipulating a simpler part at the preceding level.[34][35] Optimizing these exogenous pathways in unnatural systems takes iterative fine-tuning of the individual biomolecular components to select the highest concentrations of the desired product.[36]
On the other hand, "re-writers" are synthetic biologists interested in testing the irreducibility of biological systems. Due to the complexity of natural biological systems, it would be simpler to rebuild the natural systems of interest from the ground up; To provide engineered surrogates that are easier to comprehend, control and manipulate.[37] Re-writers draw inspiration from refactoring, a process sometimes used to improve computer software.
Categories of synthetic biology
Bioengineering, synthetic genomics, protocell synthetic biology, unconventional molecular biology, and in silico techniques are the five categories of synthetic biology.[38]
It is necessary to review the distinctions and analogies between the categories of synthetic biology for its social and ethical assessment. To distinguish between issues affecting the whole field and particular to a specific one.[38]
Bioengineering
The subfield of bioengineering concentrates on creating novel metabolic and regulatory pathways and is currently the one that likely draws the attention of most researchers and funding. It is primarily motivated by the desire to establish biotechnology as a legitimate engineering discipline. When referring to this area of synthetic biology, the word "bioengineering" should not be confused with "traditional genetic engineering," which involves introducing a single transgene into the intended organism. Bioengineers adapted Synthetic biology to provide a substantially more integrated perspective on how to alter organisms or metabolic systems.[38]
A typical example of single-gene genetic engineering is the insertion of the human insulin gene into bacteria to create transgenic proteins. The creation of whole new signalling pathways, containing numerous genes and regulatory components, such as an oscillator circuit to initiate the periodic production of green fluorescent protein (GFP) in mammalian cells, is known as bioengineering as part of Synthetic biology.[38]
By utilising simplified and abstracted metabolic and regulatory modules as well as other standardized parts that may be freely combined to create new pathways or creatures, bioengineering aims to create innovative biological systems. In addition to creating infinite opportunities for novel applications, this strategy is anticipated to make bioengineering more predictable and controllable than traditional biotechnology.[38]
Synthetic genomics
The formation of animals with a chemically manufactured (minimal) genome is another facet of synthetic biology that is highlighted by synthetic genomics. This area of synthetic biology has been made possible by ongoing advancements in DNA synthesis technology, which now makes it feasible to produce DNA molecules with thousands of base pairs at a reasonable cost. The goal is to combine these molecules into complete genomes and transplant them into living cells, replacing the host cell's genome and reprogramming its metabolism to perform different functions.[38]
Scientists have previously demonstrated the potential of this approach by creating infectious viruses by synthesising the genomes of multiple viruses. These significant advances in science and technology triggered the initial public concerns concerning the risks associated with this technology.[38]
A simple genome might also work as a "chassis genome" that could be enlarged quickly by gene inclusion created for particular tasks. Such "chassis creatures" would be more suited for the insertion of new functions than wild organisms since they would have fewer biological pathways that could potentially conflict with the new functionalities in addition to having specific insertion sites. Synthetic genomics strives to create creatures with novel "architectures," much like the bioengineering method. It adopts an integrative or holistic perspective of the organism. In this case, the objective is the creation of chassis genomes based on necessary genes and other required DNA sequences rather than the design of metabolic or regulatory pathways based on abstract criteria.[38]
Protocell synthetic biology
The in vitro generation of synthetic cells is the protocell branch of synthetic biology. Lipid vesicles, which have all the necessary components to function as a complete system, can be used to create these artificial cells. In the end, these synthetic cells should meet the requirements for being deemed alive, namely the capacity for self-replication, self-maintenance, and evolution. The protocell technique has this as its end aim, however there are other intermediary steps that fall short of meeting all the criteria for a living cellIn order to carry out a specific function, these lipid vesicles contain cell extracts or more specific sets of biological macromolecules and complex structures, such as enzymes, nucleic acids, or ribosomes. For instance, liposomes may carry out particular polymerase chain reactions or synthesise a particular protein.[38]
Protocell synthetic biology takes artificial life one step closer to reality by eventually synthesizing not only the genome but also every component of the cell in vitro, as opposed to the synthetic genomics approach, which relies on coercing a natural cell to carry out the instructions encoded by the introduced synthetic genome. Synthetic biologists in this field view their work as basic study into the conditions necessary for life to exist and its origin more than in any of the other techniques. The protocell technique, however, also lends itself well to applications; similar to other synthetic biology byproducts, protocells could be employed for the manufacture of biopolymers and medicines.[38]
Unconventional molecular biology
The objective of the "unnatural molecular biology" strategy is to create new varieties of life that are based on a different kind of molecular biology, such as new types of nucleic acids or a new genetic code. The creation of new types of nucleotides that can be built into unique nucleic acids could be accomplished by changing certain DNA or RNA constituents, such as the bases or the backbone sugars.[38]
The normal genetic code is being altered by inserting quadruplet codons or changing some codons to encode new amino acids, which would subsequently permit the use of non-natural amino acids with unique features in protein production. It is a scientific and technological problem to adjust the enzymatic machinery of the cell for both approaches.[38]
A new sort of life would be formed by organisms with a genome built on synthetic nucleic acids or on a totally new coding system for synthetic amino acids. This new style of life would have some benefits but also some new dangers. On release into the environment, there would be no horizontal gene transfer or outcrossing of genes with natural species. Furthermore, these kinds of synthetic organisms might be created to require non-natural materials for protein or nucleic acid synthesis, rendering them unable to thrive in the wild if they accidentally escaped.[38]
On the other hand, if these organisms ultimately were able to survive outside of controlled space, they might have a particular benefit over natural organisms because they would be resistant to predatory living organisms or natural viruses, that could lead to an unmanaged spread of the synthetic organisms.[38]
In silico technique
Synthetic biology in silico and the various strategies are interconnected. The development of complex designs, whether they are metabolic pathways, fundamental cellular processes, or chassis genomes, is one of the major difficulties faced by the four synthetic-biology methods outlined above. Because of this, synthetic biology has a robust in silico branch, similar to systems biology, that aims to create computational models for the design of common biological components or synthetic circuits, which are essentially simulations of synthetic organisms.[38]
The practical application of simulations and models through bioengineering or other fields of synthetic biology is the long-term goal of in silico synthetic biology. Many of the computational simulations of synthetic organisms up to this point possess little to no direct analogy to living things. Due to this, in silico synthetic biology is regarded as a separate group in this article.[38]
It is sensible to integrate the five areas under the umbrella of synthetic biology as an unified area of study. Even though they focus on various facets of life, such as metabolic regulation, essential elements, or biochemical makeup, these five strategies all work toward the same end – creating new types of living organisms. Additionally, the varied methodologies begin with numerous methodological approaches, which leads to the diversity of synthetic biology approaches.[38]
Synthetic biology is an interdisciplinary field that draws from and is inspired by many different scientific disciplines, not one single field or technique. Synthetic biologists all have the same underlying objective of designing and producing new forms of life, despite the fact that they may employ various methodologies, techniques, and research instruments. Any evaluation of synthetic biology, whether it examines ethical, legal, or safety considerations, must take into account the fact that while some questions, risks, and issues are unique to each technique, in other circumstances synthetic biology as a whole must be taken into consideration.[38]
Four engineering approaches
Synthetic biology has traditionally been divided into four different engineering approaches: top down, parallel, orthogonal and bottom up.[39]
To replicate emergent behaviours from natural biology and build artificial life, unnatural chemicals are used. The other looks for interchangeable components from biological systems to put together and create systems that do not work naturally. In either case, a synthetic objective compels researchers to venture into new area in order to engage and resolve issues that cannot be readily resolved by analysis. Due to this, new paradigms are driven to arise in ways that analysis cannot easily do. In addition to equipments that oscillate, creep, and play tic-tac-toe, synthetic biology has produced diagnostic instruments that enhance the treatment of patients with infectious diseases.[40]
Top-down approach
It involves using metabolic and genetic engineering techniques to impart new functions to living cells.[41] By comparing universal genes and eliminating non-essential ones to create a basic genome, this method seeks to lessen the complexity of existing cells. These initiatives are founded on the hypothesis of a single genesis for cellular life, the so-called Last Universal Common Ancestor, which supports the presence of a universal minimal genome that gave rise to all living things. Recent studies, however, raise the possibility that the eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells that make up the tree of life may have evolved from a group of primordial cells rather than from a single cell. As a result, even while the Holy Grail-like pursuit of the "minimum genome" has grown elusive, cutting out a number of non-essential functions impairs an organism's fitness and leads to "fragile" genomes.[39]
Bottom-up approach
This approach involves creating new biological systems in vitro by bringing together 'non-living' biomolecular components,[42] often with the aim of constructing an artificial cell.
Reproduction, replication, and assembly are three crucial self-organizational principles that are taken into account in order to accomplish this. Cells, which are made up of a container and a metabolism, are considered "hardware" in the definition of reproduction, whereas replication occurs when a system duplicates a perfect copy of itself, as in the case of DNA, which is considered "software." When vesicles or containers (such as Oparin's coacervates) formed of tiny droplets of molecules that are organic like lipids or liposomes, membrane-like structures comprising phospholipids, aggregate, assembly occur.[39]
The study of protocells exists alongside with other in vitro synthetic biology initiatives that seek to produce minimum cells, metabolic pathways, or "never-born proteins" as well as to mimic physiological functions including cell division and growth. The in vitro enhancement of synthetic pathways does have the potential to have an effect on some other synthetic biology sectors, including metabolic engineering, despite the fact that it no longer classified as synthetic biology research. This research, which is primarily essential, deserves proper recognition as synthetic biology research.[39]
Parallel approach
Parallel engineering is also known as bioengineering. The basic genetic code is the foundation for parallel engineering research, which uses conventional biomolecules like nucleic acids and the 20 amino acids to construct biological systems. For a variety of applications in biocomputing, bioenergy, biofuels, bioremediation, optogenetics, and medicine, it involves the standardisation of DNA components, engineering of switches, biosensors, genetic circuits, logic gates, and cellular communication operators. For directing the expression of two or more genes and/or proteins, the majority of these applications often rely on the use of one or more vectors (or plasmids). Small, circular, double-strand DNA units known as plasmids, which are primarily found in prokaryotic but can also occasionally be detected in eukaryotic cells, may replicate autonomously of chromosomal DNA.[39]
Orthogonal approach
It is also known as perpendicular engineering. This strategy, also referred to as "chemical synthetic biology," principally seeks to alter or enlarge the genetic codes of living systems utilising artificial DNA bases and/or amino acids. This subfield is also connected to xenobiology, a newly developed field that combines systems chemistry, synthetic biology, exobiology, and research into the origins of life. In recent decades, researchers have created compounds that are structurally similar to the DNA canonical bases to see if those "alien" or xeno (XNA) molecules may be employed as genetic information carriers. Similar to this, noncanonical moieties have taken the place of the DNA sugar (deoxyribose).[39] In order to express information other than the 20 conventional amino acids of proteins, the genetic code can be altered or enlarged. One method involves incorporating a specified unnatural, noncanonical, or xeno amino acid (XAA) into one or more proteins at one or more precise places using orthogonal enzymes and a transfer RNA adaptor from an other organism. By using "directed evolution," which entails repeated cycles of gene mutagenesis (genotypic diversity production), screening or selection (of a specific phenotypic trait), and amplification of a better variant for the following iterative round, orthogonal enzymes are produced Numerous XAAs have been effectively incorporated into proteins in more complex creatures like worms and flies as well as in bacteria, yeast, and human cell lines. As a result of canonical DNA sequence changes, directed evolution also enables the development of orthogonal ribosomes, which make it easier to incorporate XAAs into proteins or create "mirror life," or biological systems that contain biomolecules made up of enantiomers with different chiral orientations.[39]
Enabling technologies
Several novel enabling technologies were critical to the success of synthetic biology. Concepts include standardization of biological parts and hierarchical abstraction to permit using those parts in synthetic systems.[43] DNA serves as the guide for how biological processes should function, like the score to a complex symphony of life. Our ability to comprehend and design biological systems has undergone significant modifications as a result of developments in the previous few decades in both reading (sequencing) and writing (synthesis) DNA sequences. These developments have produced ground-breaking techniques for designing, assembling, and modifying DNA-encoded genes, materials, circuits, and metabolic pathways, enabling an ever-increasing amount of control over biological systems and even entire organisms.[44]
Basic technologies include reading and writing DNA (sequencing and fabrication). Measurements under multiple conditions are needed for accurate modeling and computer-aided design (CAD).
DNA and gene synthesis
Driven by dramatic decreases in costs of oligonucleotide ("oligos") synthesis and the advent of PCR, the sizes of DNA constructions from oligos have increased to the genomic level.[45] In 2000, researchers reported synthesis of the 9.6 kbp (kilo bp) Hepatitis C virus genome from chemically synthesized 60 to 80-mers.[46] In 2002 researchers at Stony Brook University succeeded in synthesizing the 7741 bp poliovirus genome from its published sequence, producing the second synthetic genome, spanning two years.[47] In 2003 the 5386 bp genome of the bacteriophage Phi X 174 was assembled in about two weeks.[48] In 2006, the same team, at the J. Craig Venter Institute, constructed and patented a synthetic genome of a novel minimal bacterium, Mycoplasma laboratorium and were working on getting it functioning in a living cell.[49][50][51]
In 2007 it was reported that several companies were offering synthesis of genetic sequences up to 2000 base pairs (bp) long, for a price of about $1 per bp and a turnaround time of less than two weeks.[52] Oligonucleotides harvested from a photolithographic- or inkjet-manufactured DNA chip combined with PCR and DNA mismatch error-correction allows inexpensive large-scale changes of codons in genetic systems to improve gene expression or incorporate novel amino-acids (see George M. Church's and Anthony Forster's synthetic cell projects.[53][54]) This favors a synthesis-from-scratch approach.
Additionally, the CRISPR/Cas system has emerged as a promising technique for gene editing. It was described as "the most important innovation in the synthetic biology space in nearly 30 years".[55] While other methods take months or years to edit gene sequences, CRISPR speeds that time up to weeks.[55] Due to its ease of use and accessibility, however, it has raised ethical concerns, especially surrounding its use in biohacking.[56][57][58]
Sequencing
DNA sequencing determines the order of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule. Synthetic biologists use DNA sequencing in their work in several ways. First, large-scale genome sequencing efforts continue to provide information on naturally occurring organisms. This information provides a rich substrate from which synthetic biologists can construct parts and devices. Second, sequencing can verify that the fabricated system is as intended. Third, fast, cheap, and reliable sequencing can facilitate rapid detection and identification of synthetic systems and organisms.[59]
Modularity
This is the ability of a system or component to operate without reference to its context.[60]
The most used[61]: 22–23 standardized DNA parts are BioBrick plasmids, invented by Tom Knight in 2003.[14] Biobricks are stored at the Registry of Standard Biological Parts in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The BioBrick standard has been used by tens of thousands of students worldwide in the international Genetically Engineered Machine (iGEM) competition. BioBrick Assembly Standard 10 promotes modularity by allowing BioBrick coding sequences to be spliced out and exchanged using restriction enzymes EcoRI or XbaI (BioBrick prefix) and SpeI and PstI (BioBrick suffix).[61]: 22–23
Sequence overlap between two genetic elements (genes or coding sequences), called overlapping genes, can prevent their individual manipulation.[62] To increase genome modularity, the practice of genome refactoring or improving "the internal structure of an existing system for future use, while simultaneously maintaining external system function"[63] has been adopted across synthetic biology disciplines.[62] Some notable examples of refactoring including the nitrogen fixation cluster[64] and type III secretion system[65] along with bacteriophages T7[63] and ΦX174.[66]
While DNA is most important for information storage, a large fraction of the cell's activities are carried out by proteins. Tools can send proteins to specific regions of the cell and to link different proteins together. The interaction strength between protein partners should be tunable between a lifetime of seconds (desirable for dynamic signaling events) up to an irreversible interaction (desirable for device stability or resilient to harsh conditions). Interactions such as coiled coils,[67] SH3 domain-peptide binding[68] or SpyTag/SpyCatcher[69] offer such control. In addition it is necessary to regulate protein-protein interactions in cells, such as with light (using light-oxygen-voltage-sensing domains) or cell-permeable small molecules by chemically induced dimerization.[70]
In a living cell, molecular motifs are embedded in a bigger network with upstream and downstream components. These components may alter the signaling capability of the modeling module. In the case of ultrasensitive modules, the sensitivity contribution of a module can differ from the sensitivity that the module sustains in isolation.[71][72]
Modeling
Models inform the design of engineered biological systems by better predicting system behavior prior to fabrication. Synthetic biology benefits from better models of how biological molecules bind substrates and catalyze reactions, how DNA encodes the information needed to specify the cell and how multi-component integrated systems behave. Multiscale models of gene regulatory networks focus on synthetic biology applications. Simulations can model all biomolecular interactions in transcription, translation, regulation and induction of gene regulatory networks.[73] [74] [75][76]
Only extensive modelling can enable the exploration of dynamic gene expression in a form suitable for research and design due to the numerous involved species and the intricacy of their relationships. Dynamic simulations of the entire biomolecular interconnection involved in regulation, transport, transcription, induction, and translation enable the molecular level detailing of designs. As opposed to modelling artificial networks a posteriori, this is contrasted.[77]
Microfluidics
Microfluidics, in particular droplet microfluidics, is an emerging tool used to construct new components, and to analyze and characterize them.[78][79] It is widely employed in screening assays.[80]
Synthetic transcription factors
Studies have considered the components of the DNA transcription mechanism. One desire of scientists creating synthetic biological circuits is to be able to control the transcription of synthetic DNA in unicellular organisms (prokaryotes) and in multicellular organisms (eukaryotes). One study tested the adjustability of synthetic transcription factors (sTFs) in areas of transcription output and cooperative ability among multiple transcription factor complexes.[81] Researchers were able to mutate functional regions called zinc fingers, the DNA specific component of sTFs, to decrease their affinity for specific operator DNA sequence sites, and thus decrease the associated site-specific activity of the sTF (usually transcriptional regulation). They further used the zinc fingers as components of complex-forming sTFs, which are the eukaryotic translation mechanisms.[81]
Applications
Synthetic biology initiatives frequently aim to redesign organisms so that they can create a material, such as a drug or fuel, or acquire a new function, such as the ability to sense something in the environment. Examples of what researchers are creating using synthetic biology include:
- Utilizing microorganisms for bioremediation to remove contaminants from our water, soil, and air.
- Beta-carotene, a substance typically associated with carrots that prevents vitamin A deficiency, is produced by rice that has been modified. Every year, between 250,000 and 500,000 children lose their vision due to vitamin A deficiency, which also significantly raises their chance of dying from infectious infections.
- As a sustainable and environmentally benign alternative to the fresh roses that perfumers use to create expensive smells, yeast has been created to produce rose oil.[82]
Biosensors
A biosensor refers to an engineered organism, usually a bacterium, that is capable of reporting some ambient phenomenon such as the presence of heavy metals or toxins. One such system is the Lux operon of Aliivibrio fischeri,[83] which codes for the enzyme that is the source of bacterial bioluminescence, and can be placed after a respondent promoter to express the luminescence genes in response to a specific environmental stimulus.[84] One such sensor created, consisted of a bioluminescent bacterial coating on a photosensitive computer chip to detect certain petroleum pollutants. When the bacteria sense the pollutant, they luminesce.[85] Another example of a similar mechanism is the detection of landmines by an engineered E.coli reporter strain capable of detecting TNT and its main degradation product DNT, and consequently producing a green fluorescent protein (GFP).[86]
Modified organisms can sense environmental signals and send output signals that can be detected and serve diagnostic purposes. Microbe cohorts have been used.[87]
Biosensors could also be used to detect pathogenic signatures – such as of SARS-CoV-2 – and can be wearable.[88][89]
For the purpose of detecting and reacting to various and temporary environmental factors, cells have developed a wide range of regulatory circuits, ranging from transcriptional to post-translational. These circuits are made up of transducer modules that filter the signals and activate a biological response, as well as carefully designed sensitive sections that attach analytes and regulate signal-detection thresholds. Modularity and selectivity are programmed to biosensor circuits at the transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels, to achieve the delicate balancing of the two basic sensing modules.[90]
Food and drink
However, not all synthetic nutrition products are animal food products – for instance, as of 2021 there are also products of synthetic coffee that are reported to be close to commercialization.[98][99][100] Similar fields of research and production based on synthetic biology that can be used for the production of food and drink are:
- Genetically engineered microbial food cultures (e.g. for solar-energy-based protein powder)[101][102]
- Cell-free artificial synthesis (e.g. synthetic starch;[103][104] )
Materials
Photosynthetic microbial cells have been used as a step to synthetic production of spider silk.[105][106]
Biological computers
A biological computer refers to an engineered biological system that can perform computer-like operations, which is a dominant paradigm in synthetic biology. Researchers built and characterized a variety of logic gates in a number of organisms,[107] and demonstrated both analog and digital computation in living cells. They demonstrated that bacteria can be engineered to perform both analog and/or digital computation.[108][109] In human cells research demonstrated a universal logic evaluator that operates in mammalian cells in 2007.[110] Subsequently, researchers utilized this paradigm to demonstrate a proof-of-concept therapy that uses biological digital computation to detect and kill human cancer cells in 2011.[111] Another group of researchers demonstrated in 2016 that principles of computer engineering, can be used to automate digital circuit design in bacterial cells.[112] In 2017, researchers demonstrated the 'Boolean logic and arithmetic through DNA excision' (BLADE) system to engineer digital computation in human cells.[113] In 2019, researchers implemented a perceptron in biological systems opening the way for machine learning in these systems.[114]
Cell transformation
Cells use interacting genes and proteins, which are called gene circuits, to implement diverse function, such as responding to environmental signals, decision making and communication. Three key components are involved: DNA, RNA and Synthetic biologist designed gene circuits that can control gene expression from several levels including transcriptional, post-transcriptional and translational levels.
Traditional metabolic engineering has been bolstered by the introduction of combinations of foreign genes and optimization by directed evolution. This includes engineering E. coli and yeast for commercial production of a precursor of the antimalarial drug, Artemisinin.[115]
Entire organisms have yet to be created from scratch, although living cells can be transformed with new DNA. Several ways allow constructing synthetic DNA components and even entire synthetic genomes, but once the desired genetic code is obtained, it is integrated into a living cell that is expected to manifest the desired new capabilities or phenotypes while growing and thriving.[116] Cell transformation is used to create biological circuits, which can be manipulated to yield desired outputs.[12][13]
By integrating synthetic biology with materials science, it would be possible to use cells as microscopic molecular foundries to produce materials whose properties were genetically encoded. Re-engineering has produced Curli fibers, the amyloid component of extracellular material of biofilms, as a platform for programmable nanomaterial. These nanofibers were genetically constructed for specific functions, including adhesion to substrates, nanoparticle templating and protein immobilization.[117]
Designed proteins
Natural proteins can be engineered, for example, by directed evolution, novel protein structures that match or improve on the functionality of existing proteins can be produced. One group generated a helix bundle that was capable of binding oxygen with similar properties as hemoglobin, yet did not bind carbon monoxide.[119] A similar protein structure was generated to support a variety of oxidoreductase activities [120] while another formed a structurally and sequentially novel ATPase.[121] Another group generated a family of G-protein coupled receptors that could be activated by the inert small molecule clozapine N-oxide but insensitive to the native ligand, acetylcholine; these receptors are known as DREADDs.[122] Novel functionalities or protein specificity can also be engineered using computational approaches. One study was able to use two different computational methods – a bioinformatics and molecular modeling method to mine sequence databases, and a computational enzyme design method to reprogram enzyme specificity. Both methods resulted in designed enzymes with greater than 100 fold specificity for production of longer chain alcohols from sugar.[123]
Another common investigation is expansion of the natural set of 20 amino acids. Excluding stop codons, 61 codons have been identified, but only 20 amino acids are coded generally in all organisms. Certain codons are engineered to code for alternative amino acids including: nonstandard amino acids such as O-methyl tyrosine; or exogenous amino acids such as 4-fluorophenylalanine. Typically, these projects make use of re-coded nonsense suppressor tRNA-Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase pairs from other organisms, though in most cases substantial engineering is required.[124]
Other researchers investigated protein structure and function by reducing the normal set of 20 amino acids. Limited protein sequence libraries are made by generating proteins where groups of amino acids may be replaced by a single amino acid.[125] For instance, several non-polar amino acids within a protein can all be replaced with a single non-polar amino acid.[126] One project demonstrated that an engineered version of Chorismate mutase still had catalytic activity when only nine amino acids were used.[127]
Researchers and companies practice synthetic biology to synthesize industrial enzymes with high activity, optimal yields and effectiveness. These synthesized enzymes aim to improve products such as detergents and lactose-free dairy products, as well as make them more cost effective.[128] The improvements of metabolic engineering by synthetic biology is an example of a biotechnological technique utilized in industry to discover pharmaceuticals and fermentive chemicals. Synthetic biology may investigate modular pathway systems in biochemical production and increase yields of metabolic production. Artificial enzymatic activity and subsequent effects on metabolic reaction rates and yields may develop "efficient new strategies for improving cellular properties ... for industrially important biochemical production".[129]
Designed nucleic acid systems
Scientists can encode digital information onto a single strand of synthetic DNA. In 2012, George M. Church encoded one of his books about synthetic biology in DNA. The 5.3 Mb of data was more than 1000 times greater than the previous largest amount of information to be stored in synthesized DNA.[130] A similar project encoded the complete sonnets of William Shakespeare in DNA.[131] More generally, algorithms such as NUPACK,[132] ViennaRNA,[133] Ribosome Binding Site Calculator,[134] Cello,[135] and Non-Repetitive Parts Calculator[136] enables the design of new genetic systems.
Many technologies have been developed for incorporating unnatural nucleotides and amino acids into nucleic acids and proteins, both in vitro and in vivo. For example, in May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA. By including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, they were able to exchange the bacteria 24 times; they did not generate mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides.[137][138][139]
Space exploration
Synthetic biology raised NASA's interest as it could help to produce resources for astronauts from a restricted portfolio of compounds sent from Earth.[140][141][142] On Mars, in particular, synthetic biology could lead to production processes based on local resources, making it a powerful tool in the development of occupied outposts with less dependence on Earth.[140] Work has gone into developing plant strains that are able to cope with the harsh Martian environment, using similar techniques to those employed to increase resilience to certain environmental factors in agricultural crops.[143]
Synthetic life
One important topic in synthetic biology is synthetic life, that is concerned with hypothetical organisms created in vitro from biomolecules and/or chemical analogues thereof. Synthetic life experiments attempt to either probe the origins of life, study some of the properties of life, or more ambitiously to recreate life from non-living (abiotic) components. Synthetic life biology attempts to create living organisms capable of carrying out important functions, from manufacturing pharmaceuticals to detoxifying polluted land and water.[145] In medicine, it offers prospects of using designer biological parts as a starting point for new classes of therapies and diagnostic tools.[145]
A living "artificial cell" has been defined as a completely synthetic cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate.[146] Nobody has been able to create such a cell.[146]
A completely synthetic bacterial chromosome was produced in 2010 by Craig Venter, and his team introduced it to genomically emptied bacterial host cells.[19] The host cells were able to grow and replicate.[147][148] The Mycoplasma laboratorium is the only living organism with completely engineered genome.
The first living organism with 'artificial' expanded DNA code was presented in 2014; the team used E. coli that had its genome extracted and replaced with a chromosome with an expanded genetic code. The nucleosides added are d5SICS and dNaM.[139]
In May 2019, researchers, in a milestone effort, reported the creation of a new synthetic (possibly artificial) form of viable life, a variant of the bacteria Escherichia coli, by reducing the natural number of 64 codons in the bacterial genome to 59 codons instead, in order to encode 20 amino acids.[25][26]
In 2017 the international Build-a-Cell large-scale open-source research collaboration for the construction of synthetic living cells was started,[149] followed by national synthetic cell organizations in several countries, including FabriCell,[150] MaxSynBio[151] and BaSyC.[152] The European synthetic cell efforts were unified in 2019 as SynCellEU initiative.[153]
Drug delivery platforms
In Therapeutics, Synthetic biology has achieved significant advancements in altering and simplifying the therapeutics scope in a relatively short period of time. In fact, new therapeutic platforms, from the discovery of disease mechanisms and drug targets to the manufacture and transport of small molecules, are made possible by the logical and model-guided design construction of biological components.[60]
Synthetic biology devices have been designed to act as therapies in therapeutic treatment. It is possible to control complete created viruses and organisms to target particular pathogens and diseased pathways. Thus ,in two independent studies 91,92, researchers utilised genetically modified bacteriophages to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria by giving them genetic features that specifically target and hinder bacterial defences against antibiotic activity.[154]
In the therapy of cancer, since conventional medicines frequently indiscriminately target tumours and normal tissues, artificially created viruses and organisms that can identify and connect their therapeutic action to pathological signals may be helpful. For example, p53 pathway activity in human cells was put into adenoviruses to control how they replicated.[154]
Engineered bacteria-based platform
Bacteria have long been used in cancer treatment. Bifidobacterium and Clostridium selectively colonize tumors and reduce their size.[155] Recently synthetic biologists reprogrammed bacteria to sense and respond to a particular cancer state. Most often bacteria are used to deliver a therapeutic molecule directly to the tumor to minimize off-target effects. To target the tumor cells, peptides that can specifically recognize a tumor were expressed on the surfaces of bacteria. Peptides used include an affibody molecule that specifically targets human epidermal growth factor receptor 2[156] and a synthetic adhesin.[157] The other way is to allow bacteria to sense the tumor microenvironment, for example hypoxia, by building an AND logic gate into bacteria.[158] The bacteria then only release target therapeutic molecules to the tumor through either lysis[159] or the bacterial secretion system.[160] Lysis has the advantage that it can stimulate the immune system and control growth. Multiple types of secretion systems can be used and other strategies as well. The system is inducible by external signals. Inducers include chemicals, electromagnetic or light waves.
Multiple species and strains are applied in these therapeutics. Most commonly used bacteria are Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia Coli, Bifidobacteria, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Listeria and Bacillus subtilis. Each of these species have their own property and are unique to cancer therapy in terms of tissue colonization, interaction with immune system and ease of application.
Engineered yeast-based platform
Synthetic biologists are developing genetically modified live yeast that can deliver therapeutic biologic medicines. When orally delivered, these live yeast act like micro-factories and will make therapeutic molecules directly in the gastrointestinal tract. Because yeast are eukaryotic, a key benefit is that they can be administered together with antibiotics. Probiotic yeast expressing human P2Y2 purinergic receptor suppressed intestinal inflammation in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease.[161] A live S. boulardii yeast delivering a tetra-specific anti-toxin that potently neutralizes Toxin A and Toxin B of Clostridioides difficile has been developed. This therapeutic anti-toxin is a fusion of four single-domain antibodies (nanobodies) that potently and broadly neutralize the two major virulence factors of C. difficile at the site of infection in preclinical models. [162] The first in human clinical trial of engineered live yeast for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection is anticipated in 2024 and will be sponsored by the developer Fzata, Inc.
Cell-based platform
The immune system plays an important role in cancer and can be harnessed to attack cancer cells. Cell-based therapies focus on immunotherapies, mostly by engineering T cells.
T cell receptors were engineered and 'trained' to detect cancer epitopes. Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are composed of a fragment of an antibody fused to intracellular T cell signaling domains that can activate and trigger proliferation of the cell. A second generation CAR-based therapy was approved by FDA.[citation needed]
Gene switches were designed to enhance safety of the treatment. Kill switches were developed to terminate the therapy should the patient show severe side effects.[163] Mechanisms can more finely control the system and stop and reactivate it.[164][165] Since the number of T-cells are important for therapy persistence and severity, growth of T-cells is also controlled to dial the effectiveness and safety of therapeutics.[166]
Although several mechanisms can improve safety and control, limitations include the difficulty of inducing large DNA circuits into the cells and risks associated with introducing foreign components, especially proteins, into cells.
Biofuels, pharmaceuticals and biomaterials
The most popular biofuel is ethanol produced from corn or sugar cane, but this method of producing biofuels is troublesome and constrained due to the high agricultural cost and inadequate fuel characteristics of ethanol. An substitute and potential source of renewable energy is microbes that have had their metabolic pathways altered to be more efficient at converting biomass into biofuels. Only if their production costs could be made to match or even exceed those of present fuel production can these techniques be expected to be successful. Related to this, there are several medicines whose pricey manufacturing procedures prevent them from having a larger therapeutic range. The creation of new materials and the microbiological manufacturing of biomaterials would both benefit substantially from novel artificial biology tools.[154]
CRISPR/Cas9
The clustered frequently interspaced short palindromic repetitions (CRISPR)/CRISPR associated (Cas) system is a powerful method of genome engineering in a range of organisms because of its simplicity, modularity, and scalability. In this technique, a guide RNA (gRNA) attracts the CRISPR nuclease Cas9 to a particular spot in the genome, causing a double strand break. Several DNA repair processes, including homology-directed recombination and non-homology end joining, can be used to accomplish the desired genome change (i.e., gene deletion or insertion). Additionally, dCas9 (dead Cas9 or nuclease-deficient Cas9), a Cas9 double mutant (H840A, D10A), has been utilised to control gene expression in bacteria or when linked to a stimulation of suppression site in yeast.[167]
Regulatory elements
To build and develop biological systems, regulating components including regulators, ribosome-binding sites (RBSs), and terminators are crucial. Despite years of study, there are many various varieties and numbers of promoters and terminators for Escherichia coli, but also for the well-researched model organism Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as well as for other organisms of interest, these tools are quite scarce. Numerous techniques have been invented for the finding and identification of promoters and terminators in order to overcome this constraint, including genome mining, random mutagenesis, hybrid engineering, biophysical modelling, combinatorial design, and rational design.[167]
Organoids
Synthetic biology has been used for organoids, which are lab-grown organs with application to medical research and transplantation.[168]
Bioprinted organs
There are many applications for 3D bioprinting in the medical field. An infant patient with a rare respiratory disease known as tracheobronchomalacia (TBM) was given a tracheal splint that was created with 3D printing.[169] 3D bioprinting can be used to reconstruct tissue from various regions of the body. Patients with end-stage bladder disease can be treated by using engineered bladder tissues to rebuild the damaged organ.[170] This technology can also potentially be applied to bone, skin, cartilage and muscle tissue.[171] Though one long-term goal of 3D bioprinting technology is to reconstruct an entire organ, there has been little success in printing fully functional organs.[172] Unlike implantable stents, organs have complex shapes and are significantly harder to bioprint. A bioprinted heart, for example, must not only meet structural requirements, but also vascularization, mechanical load, and electrical signal propagation requirements.[173] Israeli researchers constructed a rabbit-sized heart out of human cells in 2019.[174]
In 2022, first success of a clinical trial for a 3D bioprinted transplant that is made from the patient's own cells, an external ear to treat microtia,[175] was reported.[176]
Other transplants and induced regeneration
There is ongoing research and development into synthetic biology based methods for inducing regeneration in humans[relevant?] as well the creation of transplantable artificial organs.
Nanoparticles, artificial cells and micro-droplets
Synthetic biology can be used for creating nanoparticles which can be used for drug-delivery as well as for other purposes.[177] Complementing research and development seeks to and has created synthetic cells that mimics functions of biological cells. Applications include medicine such as designer-nanoparticles that make blood cells eat away – from the inside out – portions of atherosclerotic plaque that cause heart attacks.[178][179][180] Synthetic micro-droplets for algal cells or synergistic algal-bacterial multicellular spheroid microbial reactors, for example, could be used to produce hydrogen as hydrogen economy biotechnology.[181][182]
Ethics
This section needs to be updated. (January 2019) |
The creation of new life and the tampering of existing life has raised ethical concerns in the field of synthetic biology and are actively being discussed.[183][184]
Common ethical questions include:
- Is it morally right to tamper with nature?
- Is one playing God when creating new life?
- What happens if a synthetic organism accidentally escapes?
- What if an individual misuses synthetic biology and creates a harmful entity (e.g., a biological weapon)?
- Who will have control of and access to the products of synthetic biology?
- Who will gain from these innovations? Investors? Medical patients? Industrial farmers?
- Does the patent system allow patents on living organisms? What about parts of organisms, like HIV resistance genes in humans?[185]
- What if a new creation is deserving of moral or legal status?
The ethical aspects of synthetic biology has three main features: biosafety, biosecurity, and the creation of new life forms.[186] Other ethical issues mentioned include the regulation of new creations, patent management of new creations, benefit distribution, and research integrity.[187][183]
Ethical issues have surfaced for recombinant DNA and genetically modified organism (GMO) technologies and extensive regulations of genetic engineering and pathogen research were in place in many jurisdictions. Amy Gutmann, former head of the Presidential Bioethics Commission, argued that we should avoid the temptation to over-regulate synthetic biology in general, and genetic engineering in particular. According to Gutmann, "Regulatory parsimony is especially important in emerging technologies...where the temptation to stifle innovation on the basis of uncertainty and fear of the unknown is particularly great. The blunt instruments of statutory and regulatory restraint may not only inhibit the distribution of new benefits, but can be counterproductive to security and safety by preventing researchers from developing effective safeguards.".[188]
The "creation" of life
One ethical question is whether or not it is acceptable to create new life forms, sometimes known as "playing God". Currently, the creation of new life forms not present in nature is at small-scale, the potential benefits and dangers remain unknown, and careful consideration and oversight are ensured for most studies.[183] Many advocates express the great potential value – to agriculture, medicine, and academic knowledge, among other fields – of creating artificial life forms. Creation of new entities could expand scientific knowledge well beyond what is currently known from studying natural phenomena. Yet there is concern that artificial life forms may reduce nature's "purity" (i.e., nature could be somehow corrupted by human intervention and manipulation) and potentially influence the adoption of more engineering-like principles instead of biodiversity- and nature-focused ideals. Some are also concerned that if an artificial life form were to be released into nature, it could hamper biodiversity by beating out natural species for resources (similar to how algal blooms kill marine species). Another concern involves the ethical treatment of newly created entities if they happen to sense pain, sentience, and self-perception. There is an ongoing debate as to whether such life forms should be granted moral or legal rights, though no consensus exists as to how these rights would be administered or enforced.
Ethical support for synthetic biology
Ethics and moral rationales that support certain applications of synthetic biology include their potential mititgation of substantial global problems of detrimental environmental impacts of conventional agriculture (including meat production), animal welfare, food security and human health,[189][190][191][192] as well as potential reduction of human labor needs and, via therapies of diseases, reduction of human suffering and prolonged life.
Biosafety and biocontainment
What is most ethically appropriate when considering biosafety measures? How can accidental introduction of synthetic life in the natural environment be avoided? Much ethical consideration and critical thought has been given to these questions. Biosafety not only refers to biological containment; it also refers to strides taken to protect the public from potentially hazardous biological agents. Even though such concerns are important and remain unanswered, not all products of synthetic biology present concern for biological safety or negative consequences for the environment. It is argued that most synthetic technologies are benign and are incapable of flourishing in the outside world due to their "unnatural" characteristics as there is yet to be an example of a transgenic microbe conferred with a fitness advantage in the wild.
In general, existing hazard controls, risk assessment methodologies, and regulations developed for traditional genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are considered to be sufficient for synthetic organisms. "Extrinsic" biocontainment methods in a laboratory context include physical containment through biosafety cabinets and gloveboxes, as well as personal protective equipment. In an agricultural context they include isolation distances and pollen barriers, similar to methods for biocontainment of GMOs. Synthetic organisms may offer increased hazard control because they can be engineered with "intrinsic" biocontainment methods that limit their growth in an uncontained environment, or prevent horizontal gene transfer to natural organisms. Examples of intrinsic biocontainment include auxotrophy, biological kill switches, inability of the organism to replicate or to pass modified or synthetic genes to offspring, and the use of xenobiological organisms using alternative biochemistry, for example using artificial xeno nucleic acids (XNA) instead of DNA.[193][194] Regarding auxotrophy, bacteria and yeast can be engineered to be unable to produce histidine, an important amino acid for all life. Such organisms can thus only be grown on histidine-rich media in laboratory conditions, nullifying fears that they could spread into undesirable areas.
Biosecurity and bioterrorism
Some ethical issues relate to biosecurity, where biosynthetic technologies could be deliberately used to cause harm to society and/or the environment. Since synthetic biology raises ethical issues and biosecurity issues, humanity must consider and plan on how to deal with potentially harmful creations, and what kinds of ethical measures could possibly be employed to deter nefarious biosynthetic technologies. With the exception of regulating synthetic biology and biotechnology companies,[195][196] however, the issues are not seen as new because they were raised during the earlier recombinant DNA and genetically modified organism (GMO) debates and extensive regulations of genetic engineering and pathogen research are already in place in many jurisdictions.[197]
Additionally, the development of synthetic biology tools has made it easier for individuals with less education, training, and access to equipment to modify and use pathogenic organisms as bioweapons. This increases the threat of bioterrorism, especially as terrorist groups become aware of the significant social, economic, and political disruption caused by pandemics like COVID-19. As new techniques are developed in the field of synthetic biology, the risk of bioterrorism is likely to continue to grow.[198] As Juan Zarate, who served as Deputy National Security Advisor for Combating Terrorism from 2005 to 2009, noted that ""the severity and extreme disruption of a novel coronavirus will likely spur the imagination of the most creative and dangerous groups and individuals to reconsider bioterrorist attacks."[199]
European Union
The European Union-funded project SYNBIOSAFE[200] has issued reports on how to manage synthetic biology. A 2007 paper identified key issues in safety, security, ethics and the science-society interface, which the project defined as public education and ongoing dialogue among scientists, businesses, government and ethicists.[201][202] The key security issues that SYNBIOSAFE identified involved engaging companies that sell synthetic DNA and the biohacking community of amateur biologists. Key ethical issues concerned the creation of new life forms.
A subsequent report focused on biosecurity, especially the so-called dual-use challenge. For example, while synthetic biology may lead to more efficient production of medical treatments, it may also lead to synthesis or modification of harmful pathogens (e.g., smallpox).[203] The biohacking community remains a source of special concern, as the distributed and diffuse nature of open-source biotechnology makes it difficult to track, regulate or mitigate potential concerns over biosafety and biosecurity.[204]
COSY, another European initiative, focuses on public perception and communication.[205][206][207] To better communicate synthetic biology and its societal ramifications to a broader public, COSY and SYNBIOSAFE published SYNBIOSAFE, a 38-minute documentary film, in October 2009.[200]
The International Association Synthetic Biology has proposed self-regulation.[208] This proposes specific measures that the synthetic biology industry, especially DNA synthesis companies, should implement. In 2007, a group led by scientists from leading DNA-synthesis companies published a "practical plan for developing an effective oversight framework for the DNA-synthesis industry".[195]
United States
In January 2009, the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation funded the Woodrow Wilson Center, the Hastings Center, and the J. Craig Venter Institute to examine the public perception, ethics and policy implications of synthetic biology.[209]
On July 9–10, 2009, the National Academies' Committee of Science, Technology & Law convened a symposium on "Opportunities and Challenges in the Emerging Field of Synthetic Biology".[210]
After the publication of the first synthetic genome and the accompanying media coverage about "life" being created, President Barack Obama established the Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues to study synthetic biology.[211] The commission convened a series of meetings, and issued a report in December 2010 titled "New Directions: The Ethics of Synthetic Biology and Emerging Technologies." The commission stated that "while Venter's achievement marked a significant technical advance in demonstrating that a relatively large genome could be accurately synthesized and substituted for another, it did not amount to the "creation of life".[212] It noted that synthetic biology is an emerging field, which creates potential risks and rewards. The commission did not recommend policy or oversight changes and called for continued funding of the research and new funding for monitoring, study of emerging ethical issues and public education.[197]
Synthetic biology, as a major tool for biological advances, results in the "potential for developing biological weapons, possible unforeseen negative impacts on human health ... and any potential environmental impact".[213] The proliferation of such technology could also make the production of biological and chemical weapons available to a wider array of state and non-state actors.[214] These security issues may be avoided by regulating industry uses of biotechnology through policy legislation. Federal guidelines on genetic manipulation are being proposed by "the President's Bioethics Commission ... in response to the announced creation of a self-replicating cell from a chemically synthesized genome, put forward 18 recommendations not only for regulating the science ... for educating the public".[213]
Opposition
On March 13, 2012, over 100 environmental and civil society groups, including Friends of the Earth, the International Center for Technology Assessment and the ETC Group issued the manifesto The Principles for the Oversight of Synthetic Biology. This manifesto calls for a worldwide moratorium on the release and commercial use of synthetic organisms until more robust regulations and rigorous biosafety measures are established. The groups specifically call for an outright ban on the use of synthetic biology on the human genome or human microbiome.[215][216] Richard Lewontin wrote that some of the safety tenets for oversight discussed in The Principles for the Oversight of Synthetic Biology are reasonable, but that the main problem with the recommendations in the manifesto is that "the public at large lacks the ability to enforce any meaningful realization of those recommendations".[217]
Health and safety
The hazards of synthetic biology include biosafety hazards to workers and the public, biosecurity hazards stemming from deliberate engineering of organisms to cause harm, and environmental hazards. The biosafety hazards are similar to those for existing fields of biotechnology, mainly exposure to pathogens and toxic chemicals, although novel synthetic organisms may have novel risks.[193] For biosecurity, there is concern that synthetic or redesigned organisms could theoretically be used for bioterrorism. Potential risks include recreating known pathogens from scratch, engineering existing pathogens to be more dangerous, and engineering microbes to produce harmful biochemicals.[218] Lastly, environmental hazards include adverse effects on biodiversity and ecosystem services, including potential changes to land use resulting from agricultural use of synthetic organisms.[219][220] Synthetic biology is an example of a dual-use technology with the potential to be used in ways that could intentionally or unintentionally harm humans and/or damage the environment. Often "scientists, their host institutions and funding bodies" consider whether the planned research could be misused and sometimes implement measures to reduce the likelihood of misuse.[221]
Existing risk analysis systems for GMOs are generally considered sufficient for synthetic organisms, although there may be difficulties for an organism built "bottom-up" from individual genetic sequences.[194][222] Synthetic biology generally falls under existing regulations for GMOs and biotechnology in general, and any regulations that exist for downstream commercial products, although there are generally no regulations in any jurisdiction that are specific to synthetic biology.[223][224]
See also
- ACS Synthetic Biology (journal)
- Bioengineering
- Biomimicry
- Carlson Curve
- Chiral life concept
- Computational biology
- Computational biomodeling
- DNA digital data storage
- Engineering biology
- International Genetically Engineered Machine
- Non-cellular life
- Open synthetic biology
- Regenerative medicine
- Synthetic intelligence
- Synthetic morphology
- Synthetic virology
- Systems and Synthetic Biology (journal)
- Tissue engineering
- Xenobiology
- Protocell#Artificial models
- Jeewanu
- Hypothetical types of biochemistry
References
- Trump BD (November 2017). "Synthetic biology regulation and governance: Lessons from TAPIC for the United States, European Union, and Singapore". Health Policy. 121 (11): 1139–1146. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2017.07.010. PMID 28807332.
Bibliography
- Church G, Regis E (2012). How Synthetic Biology will Reinvent Nature and Ourselves. New York, NY: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0465021758.
- Synthetic biology and biodiversity ; Science for Environment Policy (PDF). Future Brief 15. Produced for the European Commission DG Environment by the Science Communication Unit, UWE, Bristol (Report). European Commission. 2016.
- Venter C (2013). Life at the Speed of Light: The Double Helix and the Dawn of Digital Life. New York, NY: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0670025404.
External links
- Engineered Pathogens and Unnatural Biological Weapons: The Future Threat of Synthetic Biology . Threats and considerations
- Synthetic biology books popular science book and textbooks
- Introductory Summary of Synthetic Biology. Concise overview of synthetic biology concepts, developments and applications
- Collaborative overview article on Synthetic Biology
- Controversial DNA startup wants to let customers create creatures (2015-01-03), San Francisco Chronicle
- It's Alive, But Is It Life: Synthetic Biology and the Future of Creation (28 September 2016), World Science Festival
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synthetic_biology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Emerging_technologies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Emerging_technologies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Augmented_reality
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Fiber_to_the_premises
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Life_extension
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Silicon_photonics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Space_elevator
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_optical_data_storage
5D optical data storage (also branded as Superman memory crystal,[1] a reference to the Kryptonian memory crystals from the Superman franchise) is an experimental nanostructured glass for permanently recording digital data using a femtosecond laser writing process.[2] Discs using this technology could be capable of storing up to 360 terabytes worth of data[3][4] for billions of years.[5][6][7][8] The concept was experimentally demonstrated in 2013.[9][10][11] Hitachi and Microsoft have researched glass-based optical storage techniques, the latter under the name Project Silica.[12][13]
The "5-dimensional" descriptor is for marketing purposes, since the device has 3 physical dimensions and no exotic higher dimensional properties. The fractal/holographic nature of its data storage is also purely 3-dimensional. The size, orientation and three-dimensional position of the nanostructures make up the claimed five dimensions.[3]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/5D_optical_data_storage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/5G_network_slicing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/100K_Pathogen_Genome_Project
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_cell
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellular_V2X
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemical_computer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloak_of_invisibility
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coilgun
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combustion_light-gas_gun
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_effect_train
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Head_transplant
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Helicon_double-layer_thruster
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human-in-the-loop
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De-extinction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_Fusion_Drive
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2000
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Directed-energy_weapon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ion_thruster
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_resurrected_species
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feedback-controlled_electromigration
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_nanothread
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_nanotube_field-effect_transistor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain-reading
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_implant
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biological_immortality
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilayer_graphene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beam-powered_propulsion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_womb
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_brain
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aerographite
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasma_magnet
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gyroradius























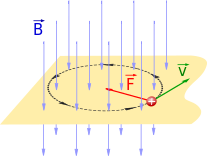









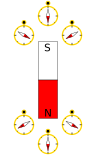








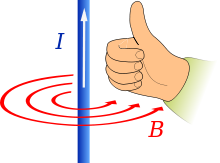


























































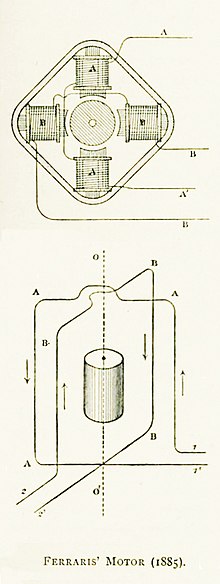




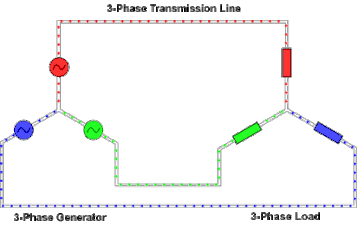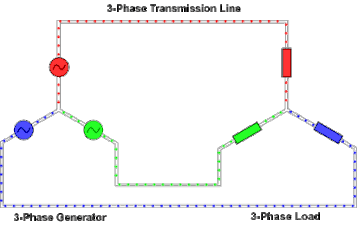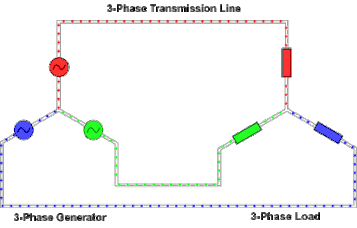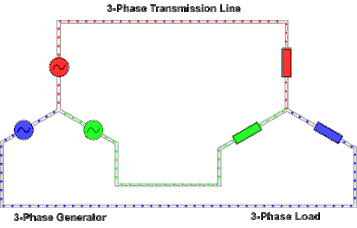





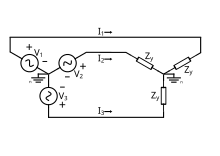
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}I_{1}&={\frac {V_{1}}{\left|Z_{\text{total}}\right|}}\angle (-\theta ),\\[2pt]I_{2}&={\frac {V_{2}}{\left|Z_{\text{total}}\right|}}\angle \left(-120^{\circ }-\theta \right),\\[2pt]I_{3}&={\frac {V_{3}}{\left|Z_{\text{total}}\right|}}\angle \left(120^{\circ }-\theta \right),\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cc5b2b2960f118272ac3e34043ab8220f7e3b41c)


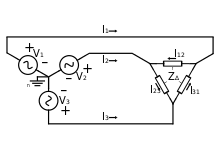
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}V_{12}&=V_{1}-V_{2}=\left(V_{\text{LN}}\angle 0^{\circ }\right)-\left(V_{\text{LN}}\angle {-120}^{\circ }\right)\\&={\sqrt {3}}V_{\text{LN}}\angle 30^{\circ }={\sqrt {3}}V_{1}\angle \left(\phi _{V_{1}}+30^{\circ }\right),\\[3pt]V_{23}&=V_{2}-V_{3}=\left(V_{\text{LN}}\angle {-120}^{\circ }\right)-\left(V_{\text{LN}}\angle 120^{\circ }\right)\\&={\sqrt {3}}V_{\text{LN}}\angle {-90}^{\circ }={\sqrt {3}}V_{2}\angle \left(\phi _{V_{2}}+30^{\circ }\right),\\[3pt]V_{31}&=V_{3}-V_{1}=\left(V_{\text{LN}}\angle 120^{\circ }\right)-\left(V_{\text{LN}}\angle 0^{\circ }\right)\\&={\sqrt {3}}V_{\text{LN}}\angle 150^{\circ }={\sqrt {3}}V_{3}\angle \left(\phi _{V_{3}}+30^{\circ }\right).\\\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/97c0c02e448dc7d255968fb031da1cb7491fd3ba)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}I_{12}&={\frac {V_{12}}{\left|Z_{\Delta }\right|}}\angle \left(30^{\circ }-\theta \right),\\[2pt]I_{23}&={\frac {V_{23}}{\left|Z_{\Delta }\right|}}\angle \left(-90^{\circ }-\theta \right),\\[2pt]I_{31}&={\frac {V_{31}}{\left|Z_{\Delta }\right|}}\angle \left(150^{\circ }-\theta \right),\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/40341769568f3f58a0c4288d44dc4f7e42353304)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}I_{2}&={\sqrt {3}}I_{23}\angle \left(\phi _{I_{23}}-30^{\circ }\right)={\sqrt {3}}I_{23}\angle \left(-120^{\circ }-\theta \right),\\[2pt]I_{3}&={\sqrt {3}}I_{31}\angle \left(\phi _{I_{31}}-30^{\circ }\right)={\sqrt {3}}I_{31}\angle \left(120^{\circ }-\theta \right),\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e41bd9b0412324f0224b1ae99bec6d5849a9f751)









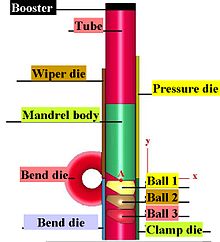
















No comments:
Post a Comment