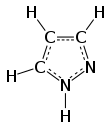
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H3N2H. It is a heterocyclecharacterized by a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms. Pyrazole is a weak base, with pKb 11.5 (pKa of the conjugated acid 2.49 at 25 °C).[2] Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms.[3] Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib(Celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol.
History[edit]
The term pyrazole was given to this class of compounds by German Chemist Ludwig Knorr in 1883.[7] In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene and diazomethane.[8]
Conversion to scorpionates[edit]
Pyrazoles react with potassium borohydride to form a class of ligands known as scorpionate. Pyrazole itself reacts with potassium borohydride at high temperatures (~200 °C) to form a tridentate ligand known as Tp ligand:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyrazole

No comments:
Post a Comment