The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capable of movement (non-motile). If the male gamete (sperm) is capable of movement, the type of sexual reproduction is also classified as oogamous. A nonmotile female gamete formed in the oogonium of some algae, fungi, oomycetes, or bryophytes is an oosphere.[1] When fertilized the oosphere becomes the oospore.[clarification needed]
When egg and sperm fuse during fertilisation, a diploid cell (the zygote) is formed, which rapidly grows into a new organism.
| Egg cell | |
|---|---|
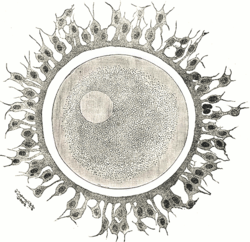 A human egg cell with surrounding corona radiata |
In all mammals the ovum is fertilized inside the female body.
The human ova grow from primitive germ cells that are embedded in the substance of the ovaries. Each of them divides repeatedly to give secretions of the uterine glands, ultimately forming a blastocyst.[9]
The ovum is one of the largest cells in the human body, typically visible to the naked eye without the aid of a microscope or other magnification device.[10] The human ovum measures approximately 120 μm (0.0047 in) in diameter.[11]
The egg cell's cytoplasm and mitochondria are the sole means the egg can reproduce by mitosis and eventually form a blastocyst after fertilization.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Egg_cell

No comments:
Post a Comment