Paragonimus westermani is the major species of lung fluke that infects humans, causing paragonimiasis.[2] The species sometimes is called the Japanese lung fluke or oriental lung fluke. Human infections are most common in eastern Asia and in South America. Paragonimus westermani was discovered when two Bengal tigers died of paragonimiasis in zoos in Europe in 1878. Several years later, infections in humans were recognised in Formosa(present-day Taiwan).
| Paragonimus westermani | |
|---|---|
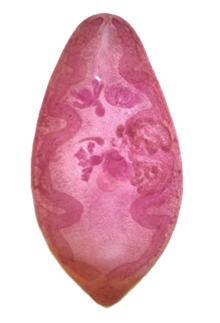 | |
| An adult specimen stained with carmine | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Rhabditophora |
| Order: | Plagiorchiida |
| Family: | Paragonimidae |
| Genus: | Paragonimus |
| Species: | P. westermani |
| Binomial name | |
| Paragonimus westermani | |
| Subspecies | |
P. westermani filipinus | |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paragonimus_westermani
No comments:
Post a Comment