The use of natural biopolymers specifically polysaccharides in drug delivery has attracted particular interest due to their desirable biocompatible, biodegradable, hydrophilic and protective properties (Barichello JM, 1999).
https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.429.3225&rep=rep1&type=pdf
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349037873_Crustacean_Shell_Waste_As_A_Sustainable_Source_Of_Biodegradable_Biopolymers
https://www.stopsarcoidosis.org/wp-content/uploads/FSR-Physicians-Protocol1-1.pdf
https://www.nzma.org.nz/journal-articles/erysipelothrix-rhusiopathiae-bacteraemia-in-an-immunocompromised-host-the-unexpected-complication-of-a-crustacean-altercation
https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/5597521
https://repositorio.unesp.br/bitstream/handle/11449/162217/WOS000389098500018.pdf;jsessionid=6D03DC9909D2C94B8001F78F5872C89F?sequence=1
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/68f3/819979f39e1f9bed6ce529f591241077c6a3.pdf
https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/world-s-poultry-science-journal/article/abs/choline-betaine-and-methionine-interactions-in-chickens-pigs-and-fish-including-crustaceans/04AF0BFC8B2A5697D6E89EB980346CA3
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/223734/Green-Book-updated-170713.pdf
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some are found in freshwater. In addition, a few species of land crabs are eaten, for example Cardisoma guanhumi in the Caribbean. Shellfish are among the most common food allergens.[1]
Despite the name, shellfish are not fish. Most shellfish are low on the food chain and eat a diet composed primarily of phytoplankton and zooplankton.[2] Many varieties of shellfish, and crustaceans in particular, are actually closely related to insects and arachnids; crustaceans make up one of the main subphyla of the phylum Arthropoda. Molluscs include cephalopods (squids, octopuses, cuttlefish) and bivalves (clams, oysters), as well as gastropods(aquatic species such as whelks and winkles; land species such as snails and slugs).
Molluscs used as a food source by humans include many species of clams, mussels, oysters, winkles, and scallops. Some crustaceans that are commonly eaten are shrimp, lobsters, crayfish, and crabs.[3] Echinodermsare not as frequently harvested for food as molluscs and crustaceans; however, sea urchin roe is quite popular in many parts of the world, where the live delicacy is harder to transport.[4][5]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shellfish
https://oem.bmj.com/content/oemed/58/9/553.full.pdf
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09540105.2015.1039497
https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1076&context=foodscidiss
INSECTS AS INHALANT ALLERGENS
CONSIDERATION OF AEROBI~LOQY, BIOCHEMISTRY, PREPARATION OF MATERIAL, AND CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS
FRANK PERLMAN, M.D., PORTLAND, ORE.
“How many insects are there 1 And how many kinds of insects3 Maybe we shall never know. But wherever we go and whether we see them or not, we are surrounded by countless millions of insects. Every forest, every field, every back yard, every roadway is a gigantic insect zoo. A wide world of endless variety and interest is open to all who will do a little investigating on their own.”
--Curtis w. &Lbrosky.’
INTRODKCTIOS
SINCE common usage has caused the word i~~ct to include most, of the arthropods, this terminology will be used throughout the present discussion. This will also conform with the broad title of t,he Insect Allergen Subcommittee of the Research Council of The American Academy of Allergy, which has encouraged many of these studies. When the class of true insects is singled out, the term Hesapoda will often be used.
The role of insects in allergy h
https://www.jacionline.org/article/0021-8707(58)90037-6/pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyzicidae
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamiltosporidium
Ordospora colligata is an intracellular parasite belonging to the Microsporidia. It is an obligatory gut parasite with the crustacean Daphnia magna as its only host.[1] So far it has been reported from Europe and Asia.[1][2]
The lifecycle of O. colligata consists of two different stages, the merogonial stage with immature spores and the sporogonial stage with mature spores.[1]
| Ordospora colligata | |
|---|---|
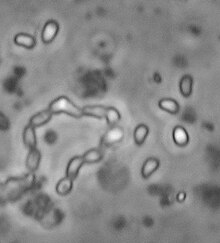 | |
| Ordospora colligata spores (2-3 µm long) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Family: | Ordosporidae |
| Genus: | Ordospora |
| Species: | O. colligata |
| Binomial name | |
| Ordospora colligata Larsson, 1997[1] | |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ordospora_colligata
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maxillopoda
Above. kesha die young
No comments:
Post a Comment