Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), also known as subacute spongiform encephalopathy or neurocognitive disorder due to prion disease, is a fatal degenerative brain disorder.[4][1] Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, and visual disturbances.[4]Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, weakness, and coma.[4] About 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis.[4]The name Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease was introduced by Walther Spielmeyerin 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob.[5]
CJD is caused by a type of abnormal protein known as a prion.[6] Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded.[4] About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant manner.[4][7] Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread.[4] There is no evidence that sporadic CJD can spread between people via normal contact or blood transfusions,[4] although this is possible in variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease.[8][9] Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes.[4] An electroencephalogram, spinal tap, or magnetic resonance imaging may support the diagnosis.[4]
There is no specific treatment for CJD.[4] Opioids may be used to help with pain, while clonazepam or sodium valproate may help with involuntary movements.[4] CJD affects about one per million people per year.[4] Onset is typically around 60 years of age.[4] The condition was first described in 1920.[4] It is classified as a type of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy.[10] Inherited CJD accounts for about 10% of prion disease cases.[7] Sporadic CJD is different from bovine spongiform encephalopathy(mad cow disease) and variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD).[11]
| Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Classic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease[1] |
 | |
| Magnetic resonance image of sporadic CJD[2] | |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Creutzfeldt–Jakob_disease
Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD), commonly referred to as "mad cow disease", is a type of brain disease within the transmissible spongiform encephalopathy family.[6] Initial symptoms include psychiatric problems, behavioral changes, and painful sensations.[1] In the later stages of the illness, patients may exhibit poor coordination, dementia and involuntary movements.[2] The length of time between exposure and the development of symptoms is unclear, but is believed to be years to decades.[3] Average life expectancy following the onset of symptoms is 13 months.[1]
It is caused by prions, which are misfolded proteins.[7] Spread is believed to be primarily due to eating bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)-infected beef.[6][7] Infection is also believed to require a specific genetic susceptibility.[4][6] Spread may potentially also occur via blood products or contaminated surgical equipment.[8] Diagnosis is by brain biopsy but can be suspected based on certain other criteria.[3] It is different from classic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, though both are due to prions.[7]
Treatment for vCJD involves supportive care.[5] As of 2012, about 170 cases of vCJD have been recorded in the United Kingdom, due to a 1990s outbreak, and 50 cases in the rest of the world.[6] The disease has become less common since 2000.[6] The typical age of onset is less than 30 years old.[3] It was first identified in 1996 by the National CJD Surveillance Unit in Edinburgh, Scotland.[6]
| Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names | New variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (nvCJD) |
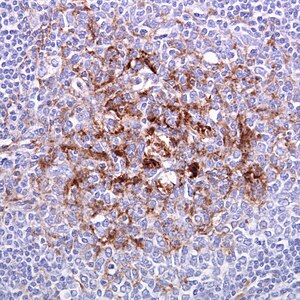 | |
| Biopsy of the tonsil in variant CJD. Prion protein immunostaining. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease, Neurology |
| Symptoms | Initial: Psychiatric problems, behavioral changes, painful sensations[1] Later: Poor coordination, Dementia, Involuntary movements[2] |
| Usual onset | Years after initial exposure[3] |
| Duration | ~13-month life expectancy[1] |
| Causes | Prion |
| Risk factors | Eating beef from cows with bovine spongiform encephalopathy[3][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Suspected based on symptoms, confirmed by Brain biopsy[3] |
| Differential diagnosis | Multiple sclerosis, standard Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease |
| Prevention | Not eating contaminated beef |
| Treatment | Supportive care[5] |
| Prognosis | Invariably fatal |
| Frequency | Fewer than 250 reported cases as of 2012[6] |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Variant_Creutzfeldt–Jakob_disease
No comments:
Post a Comment