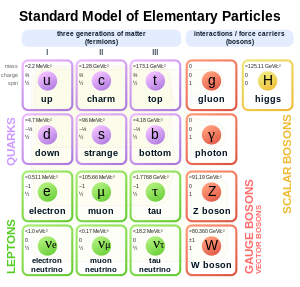
In particle physics, a gauge boson is a bosonic elementary particle that mediates interactions among elementary fermions, and thus acts as a force carrier. Gauge bosons can carry any of the four fundamental interactions of nature.[1][2] Elementary particles, whose interactions are described by a gauge theory, interact with each other by the exchange of gauge bosons; usually as virtual particles.
Photons, W and Z bosons, gluons, and the hypothetical gravitons are gauge bosons. All known gauge bosons have a spin of 1; for comparison, the Higgs boson has spin zero. Therefore, all known gauge bosons are vector bosons.
Gauge bosons are different from the other kinds of bosons: first, fundamental scalar bosons (the Higgs boson); second, mesons, which are composite bosons, made of quarks; third, larger composite, non-force-carrying bosons, such as certain atoms.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauge_boson

No comments:
Post a Comment