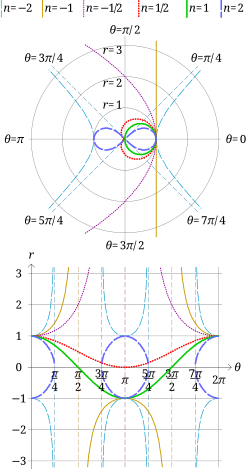
In geometry, the sinusoidal spirals are a family of curves defined by the equation in polar coordinates
where a is a nonzero constant and n is a rational number other than 0. With a rotation about the origin, this can also be written
The term "spiral" is a misnomer, because they are not actually spirals, and often have a flower-like shape. Many well known curves are sinusoidal spirals including:
- Rectangular hyperbola (n = −2)
- Line (n = −1)
- Parabola (n = −1/2)
- Tschirnhausen cubic (n = −1/3)
- Cayley's sextet (n = 1/3)
- Cardioid (n = 1/2)
- Circle (n = 1)
- Lemniscate of Bernoulli (n = 2)
The curves were first studied by Colin Maclaurin.
Properties[edit]
The inverse of a sinusoidal spiral with respect to a circle with center at the origin is another sinusoidal spiral whose value of n is the negative of the original curve's value of n. For example, the inverse of the lemniscate of Bernoulli is a rectangular hyperbola.
The isoptic, pedal and negative pedal of a sinusoidal spiral are different sinusoidal spirals.
One path of a particle moving according to a central force proportional to a power of r is a sinusoidal spiral.
When n is an integer, and n points are arranged regularly on a circle of radius a, then the set of points so that the geometric mean of the distances from the point to the n points is a sinusoidal spiral. In this case the sinusoidal spiral is a polynomial lemniscate.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sinusoidal_spiral
Pages in category "Plane curves"
The following 52 pages are in this category, out of 52 total. This list may not reflect recent changes (learn more).


No comments:
Post a Comment