An antenna tuner is an electronic device inserted into the feedline between a radio transmitter and its antenna. Its purpose is to optimize power transfer by matching the impedance of the radio to the impedance of the end of the feedline connecting the antenna to the transmitter.
Various alternate names are used for this device: antenna matching unit, impedance matching unit, matchbox, matching network, transmatch, antenna match, antenna tuning unit (ATU), antenna coupler, feedline coupler. English language technical jargon makes no distinction between the terms.[citation needed][a]
Antenna tuners are particularly important for use with transmitters. Transmitters are typically designed to feed power into a reactance-free, resistive load of a specific value: Essentially all radio transmitters built after the 1950s are designed for 50 Ω (Ohm) output.[1][b] However the impedance of any antenna normally varies, depending on frequency and other factors, and consequently changes the impedance appearing at the other end of the feedline, connected to the transmitter. In addition to reducing the power radiated by the antenna, an impedance mismatch can distort the signal, and in high power transmitters may overheat the amplifier.[c]
To avoid possible damage resulting from applying power into a mismatched load, ATUs are a standard part of almost all radio transmitting systems.[d] The system ATU may be a circuit incorporated into the transmitter itself, or a separate piece of equipment connected into the feedline anywhere between the transmitter and the antenna, or a combination of several of these. In transmitting systems with an antenna distant from the transmitter and connected to it by a transmission line (feedline), in addition to an ATU where the feedline connects to the transmitter there may be a second matching network (or ATU) near the antenna, or incorporated into the design of the antenna, to match the transmission line's impedance to the antenna's.
Overview
Antenna tuners are particularly important for use with transmitters. Transmitters are designed to feed power into a resistive load of a specific value: 50 Ω (Ohms), by modern convention.[b][1] If the impedance seen by the transmitter departs from this design value due to improper tuning of the combined feedline and antenna, overheating of the transmitter final stage, distortion, or loss of output power may occur.[c]
Use with transmitters
Antenna tuners are used almost universally with solid-state transmitters. Without an ATU, in addition to reducing the power radiated by the antenna, the reflected (or "backlash") current can overheat transformer cores and cause signal distortion. In high-power transmitters it may overheat the transmitter's output amplifier.[c] When excessive reflected power is detected, self-protection circuits in modern transmitters automatically reduce power to safe levels, and hence reduce the power of the signal leaving the antenna even more than the loss from some of the power being reflected away from the antenna.
- Automatic power reduction by safety circuits typically causes most of the power loss (see below).
Because of this, ATUs are a standard part of almost all radio transmitting systems. They may be a circuit incorporated into the transmitter itself,[d] or a separate piece of equipment connected between the transmitter and the antenna. In transmitting systems with an antenna separated from the transmitter and connected to it by a transmission line (feedline), there may be another matching network (or ATU) at the antenna that matches the transmission line's impedance to the antenna.
Narrow-band transmitters like cell phones and walkie-talkies have an ATU circuit inside, permanently set to work with the installed antenna.[d] In multi-frequency communication stations like amateur radio stations, and for high power transmitters like radio broadcasting stations, the ATU is adjustable to accommodate changes in frequency, in the transmitting system, or to its environment.[e] Instruments such as SWR meters, antenna analyzers, or impedance bridges are used to measure the degree of match or mismatch. Testing to ensure the transmitter is correctly matched to the feedline from the antenna is needed after any change that might perturb the system.
High power transmitters like radio broadcasting stations have a matching unit that is adjustable, to accommodate changes in the transmit frequency, the transmitting unit, the antenna, or the antenna's environment.[e] Adjusting the ATU to match the transmitter to the antenna is an important procedure which is done after any work on the transmitter or antenna occurs, or any drastic change in the weather affecting the antenna, such as hoar frost or dust storms.
The effect of this adjustment is typically measured using an instrument called an SWR meter, which indicates the aggregate mismatch between a reference impedance (which should be the same as the transmitter: 50 + j 0 Ω[b]) and the complex impedance at the point on the feedline where the SWR meter is inserted. Other instruments such as antenna analyzers, or impedance bridges, provide more detailed information, such as the separate mismatches of the resistive and reactive parts of the impedance on the input and output sides of the ATU.
What an "antenna" tuner actually tunes
Despite its name, an "antenna" tuner does not actually tune the antenna: Actual 'tuning' of an antenna involves adjusting its length, or attaching extra segments to add capacitance or inductance to the path of currents through it, to eliminate reactance at the antenna feedpoint for the 'tuned' frequency.[f] Instead, an antenna "tuning" unit matches the complex resistive + reactive impedance presented at the end of the feedline (sometimes very far from the antenna feedpoint) to the reactance-free, purely resistive (real) impedance required at the transmitter output connection, and in the same step, raising or lowering the resistance to the level required (usually 50 Ω, by convention[b]).
If both the tuner and the feedline were ideal – lossless, or resistance-free – then tuning at the transmitter end would indeed produce a perfect match at every point in the transmitter-feedline-antenna system.[2] However, for realistic feed systems, lossy feed lines limit the ability of the antenna tuner to remotely change the antenna's resonant frequency.
The feedline power loss will be low if the line length between the transmitter and the antenna is short, or if it has very low DC resistance per meter of length, or if it is built to carry power primarily as high voltage and low current (high impedance, 300 Ω or higher). When feedline power loss is very low, a tuner at the transmitter end of the line can indeed produce a worthwhile degree of (imperfect) matching and tuning throughout the whole antenna and feedline network.[3][4] However that is not the case when lossy and low-impedance feedline is used – like common 50 or 75 Ω coaxial cable (low impedance: low voltage and high current). For low-impedance line, maximum power transfer occurs only if matching is done at the antenna, in conjunction with a matched transmitter and feedline, producing a match at both ends of the line and every point in between.
In any case, regardless of where it is placed, an ATU does not alter the gain, efficiency, or directivity of the antenna, nor does it change the internal complex impedances within the parts of the antenna itself, nor the impedance presented at the antenna's feedpoint.
Use in receivers
ATUs are not widely used in shortwave receivers, and almost never used in mediumwave or longwave receivers. They are, however, helpful for receivers operating in the upper shortwave (upper HF), and are needed for VHF and higher.
At the antenna, if the end of the transmission line connected to the antenna is not a conjugate match to the antenna's feedpoint impedance, a part of any intercepted signal will be trapped inside the antenna, eventually to be radiated back out. Similarly, at the receiver, if the complex impedance at the receiver end of the transmission line is not a match to the receiver's input connection, then some of the incoming signal will be reflected back to the antenna, and not enter the receiver. These losses of signal power are only important for frequencies at and above the middle HF band. In radio receivers working below roughly 10~20 MHz, atmospheric radio noise dominates the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the incoming radio signal, and the power of the atmospheric noise that arrives with the signal is far greater than the inherent thermal noise generated within the receiver's own circuitry. Therefore, the receiver can amplify the weak signal to compensate for any inefficiency caused by impedance mismatch without perceptibly increasing noise in the output.
However, at higher frequencies receivers encounter very little atmospheric noise, and the noise added by the receiver's own front end amplifier dominates the SNR. At frequencies above about 10~20 MHz the internal circuit noise is the factor limiting sensitivity of the receiver for weak signals. So as the receive frequency rises, it becomes increasingly important that the receiving antenna's complex impedance be conjugately matched to the input impedance at the antenna end of the transmission line, and the receiver end of the transmission line be matched to the receiver input connection; the combination of all this impedance matching effects the maximum transfer of power from a weak signal arriving at the antenna into the first amplifier, to provide the front end amplifier with a signal much louder than the amplifier's own internally-generated noise.
So impedance-matching circuits or impedance-matched antennas are incorporated in some receivers for the upper HF band, such as 'deluxe' CB radio receivers, and for most VHF and higher frequency receivers, such as FM broadcast receivers, and scanners for aircraft and public safety radio.
Broad band matching methods
Strictly speaking, transformers, autotransformers, and baluns are not complete impedance matching units: Even though they do transform the magnitude of impedances, they are not themselves able to bridge mismatched phases, and so are unable to produce a full conjugate match. None the less, transformers of these types are frequently incorporated into antenna feed systems to convert between balanced and unbalanced cabling, or seamlessly join different cabling impedances, providing an impedance match in the special case of reactance-free antenna feed systems. They are also sometimes used to augment the operation of the narrow band antenna tuner designs (discussed in following sections) since they can widen the range of impedances that an antenna tuner can match.
Transformers and baluns are usually designed with coil windings that have the minimum inductance needed to function, to ensure that the reactance they inadvertently contribute has only a small effect on the resonant frequency of either the antenna or narrow band transmitter circuits. This results in a trade-off, since at lower frequencies the coupling between the two sides of a transformer may not be strong enough, and at higher frequencies the stray reactance may be too much to ignore. Although these high and low frequency problems constrain the useful bandwidth of the devices, they nevertheless are typically extremely broadbanded compared to any other method of impedance matching.
Ferrite transformers
Solid-state power amplifiers operating from 1–30 MHz typically use one or more wideband transformers wound on ferrite cores. MOSFETs and bipolar junction transistors typically used in modern radio frequency amplifiers are designed to operate into a low impedance, so the transformer primary typically has a single turn, while the 50 Ω secondary will have 2 to 4 turns. This design of feedline system has the advantage of reducing the retuning required when the operating frequency is changed.
A similar design can match an antenna to a transmission line: For example, many TV antennas have a 300 Ω impedance but feed the signal to the TV through a 75 Ω coaxial line. A small ferrite core transformer makes the broad band impedance transformation. This transformer does not need, nor is it capable of adjustment. For receive-only use in a TV the small SWR variation with frequency is not a significant problem.
Ferrites are ceramics that are very effective conductors of magnetic fields, made from iron oxides (rust) and varying small amounts of nickle, zinc, tin, manganese, and various other metals. Different mixtures are blended for particular frequency ranges, normally one to several megahertz wide. Each mix becomes less effective at frequencies higher or lower than its intended range, and this in turn imposes practical bandwidth limits on ferrite transformers.
Many ferrite transformers are configured to perform a balanced-to-unbalanced transformation in addition to the impedance change. When the balanced to unbalanced function is present these transformers are called a balun (otherwise an unun). The most common baluns have either a 1:1 or a 1:4 impedance transformation.[g]
Autotransformers
There are several designs for impedance matching using an autotransformer, which is a simple, single-coil transformer with different connection points or taps spaced along the coil windings. They are distinguished mainly by their impedance transform ratio,[g] and whether the input and output sides share a common ground, or are matched from a cable that is grounded on one side (unbalanced) to an ungrounded (usually balanced) cable. When autotransformers connect balanced and unbalanced lines they are called baluns, just as two-winding transformers are.[h]
The circuit pictured at the right has three identical windings wrapped in the same direction around either an "air" core (for very high frequencies) or ferrite core (for middle frequencies) or a powdered-iron core (for very low frequencies). The three equal windings shown are wired for a common ground shared by two unbalanced lines (so this design is an unun), and can be used as 1:1, 1:4, or 1:9 impedance match, depending on the tap chosen.[i]
For example, if the right-hand side is connected to a resistive load of 10 Ω, the user can attach a source at any of the three ungrounded terminals on the left side of the autotransformer to get a different impedance. Notice that on the left side, the line with more windings between the line's tap-point and the ground tap measures greater impedance for the same 10 Ω load on the right.
Narrow band vs. broad band matching methods
Antenna matching methods that use transformers, described above, tend to cover a wide range of frequencies. The "narrow band" tuned circuit methods described below all cover a very much smaller span of frequencies, by comparison.
For example, a single, exceptionally well-made, commercially available balun can cover frequencies from 3.5–29.7 MHz – a span over 26 MHz wide, or nearly the entire HF band. In contrast, matching a feedline to an antenna using a cut segment of transmission line (as described below) is perhaps the most efficient of all matching techniques, in terms of electrical power, but typically can only cover a range about 3.5~3.7 MHz wide in the HF band – a very small range indeed: The 26.2 MHz bandwidth of the example balun is a more than 7 times wider span of frequencies.
Antenna coupling or feedline matching networks are also narrow band for a single setting, but are built with variable components so they can be conveniently retuned – some modern transmatches can even automatically self-retune whenever the transmit frequency changes. A few amateur operators over-react to horror stories of wrongly adjusted transmatches, whose maladjustment causes high loss. However, despite any exaggerations, in terms of power-loss circuit-based matching networks are indeed the least efficient means of matching (aside from having no impedance matching at all!).
Transmission line antenna tuning methods
There are two different impedance matching techniques using sections of feedline: Either the original feedline can have a deliberately mismatched section of line spliced into it (called section matching), or a short stub of line can branch off from the original line, with the stub's end either shorted or left unconnected (called stub matching). In both cases, the location of the section of extra line on the original feedline and its length require careful placement and adjustment, which is nearly certain to work for only one desired frequency.
Section matching
A special section of transmission line spliced into the main feedline can be used to match the main line to the antenna, if the spliced section's characteristic impedance is different from that of the regular feedline. The technique is essentially to fix a mismatch by creating an opposite mismatch: A line segment with the proper impedance and proper length, inserted at the proper distance from the antenna, can perform complicated matching effects with very high efficiency. The drawback is that matching with line segments only works for a very limited frequency range for which the segment's length and position are appropriate.[5](p 22‑24)
A simple example of this method is the quarter-wave impedance transformer formed by a section of mismatched transmission line. If a quarter-wavelength of 75 Ω coaxial cable is linked to a 50 Ω load, the SWR in the 75 Ω quarter wavelength of line can be calculated as 75 Ω/ 50 Ω = 1.5 , when there is no reactance; the quarter-wavelength of line transforms the mismatched impedance to 112.5 Ω ( 75 Ω × 1.5 = 112.5 Ω ). Thus this inserted section matches a 112 Ω antenna to a 50 Ω main line.
The 1/ 6 wavelength coaxial transformer is a useful way to match 50 to 75 Ω using the same general method.[6][7]
Stub matching
A second common method is the use of a stub: Either a shorted or open section of line is connected in parallel with the main feedline, forming a dead-end branch off the main line.[j] A stub less than a quarter-wave long whose end is short-circuited subtracts susceptance from the line, functioning as an inductor; if its end is left open (unconnected) then the stub adds susceptance, functioning as a capacitor.[8][k] The stub can be any impedance: Unlike section matching, above, there is no need for it to be different from the main line.
The stub is placed at one of the points along the line where, at the desired frequency, the signal impedance's non-reactive part happens to match the characteristic impedance of the feedline. The length of the stub is chosen so that at that frequency, its susceptance is equal-and-opposite to the unwanted signal susceptance at the connection point. The combined effect of a proper location and correct length removes the susceptance from the signal (or correspondingly, removes reactance) and leaves the remaining signal conductance matched to the reciprocal of the feedline impedance beyond the connection point, eliminating any SWR from that point onward.[8]
The J-pole antenna and the related Zepp antenna are both examples of an antenna designed with a built-in stub match at the antenna feedpoint.
More elaborate stub matching methods involve using two stubs, either in series or in parallel, to create an L-C tuning circuit, some of which are electrically equivalent to ‘L’ networks, described in the following sub-sections.
Basic two-element L-network
The most basic form of lumped circuit matching is with the ‘L’-network: It is the simplest circuit that will achieve the desired transformation, and always consists of exactly two reactive components. The ‘L’ circuit is important not only in that many automatic antenna tuners use it, but also because more complicated circuits can be analyzed as chains of ‘L’-networks, as will be shown in later sections, in descriptions of larger tuning circuits.
For any one given load and frequency, one must use a circuit from one of the eight possible configurations shown below.
Commercially available automatic antenna tuners most often are ‘L’-networks, since they involve the fewest parts, and have a unique setting for the automatic self-adjustment circuitry to seek.
This circuit is called an "ell" network, not because it contains an inductor (customary symbol ) (in fact some ‘L’-networks consist of two capacitors), but instead because of the shape: In the schematic, the two components are at right angles to each other, in the shape of a Latin letter ‘L’ either rotated (┬─) or flipped and rotated (─┬). The basic circuit required when pairs of lumped capacitors and / or inductors are used is shown in the chart of schematics below.
The‘π’ ("pie" / "pee") network and the ‘T’ ("tee") network also have their parts laid out in a shape similar to the Latin and Greek letters they are named after: The ‘π’ network is equivalent to two nose-to-nose ‘L’ networks, e.g. ┬─ ─┬ ≅ ┬─┬ ≅ ‘π’ ; the ‘T’ network is electrically equivalent to two back-to-back ‘L’ networks, since ─┬ ┬─ ≅ ─┬┬─ ≅ ─┬─ ≅ ‘T’ . (See the individual ‘π’ and ‘T’ network descriptions below for more detail.)
L-network math
This basic network is able to act as an impedance transformer. If the output has an impedance consisting of resistive part Rload and reactive part Xload, which add to make a single complex number The input is to be attached to a source which has an impedance of Rsource resistance and Xsource reactance, then
and
- .
In this example circuit, XL and XC could be swapped. All the ATU circuits below create this network, which exists between systems with different impedances.
For instance, if the source has a resistive impedance of 50 Ω and the load has a resistive impedance of 1000 Ω :
If the frequency is 28 MHz,
As,
then,
So,
While as,
then,
‘L’-network theory and practice
A parallel network, consisting of a resistive element (1000 Ω) and a reactive element (−j 229.415 Ω), will have the same impedance and power factor as a series network consisting of resistive (50 Ω) and reactive elements (−j 217.94 Ω).
By adding another element in series (which has a reactive impedance of +j 217.94 Ω), the impedance is 50 Ω (resistive).
Types of ‘L’ networks and their uses
There are eight different configurations of components for an ‘L’ network, which are shown in the two left columns of the diagrams at the right, marked with numbers 1–8 with corresponding colors. The right column is three versions of the same Smith chart, showing antenna resistance (R) increasing toward the right on the horizontal axis, with the conventional 50 Ohms at the center point. Antenna reactance varies along vertical direction, with increasing inductive reactance (L) going upward from the big circle's center-line, and capacitive (C) reactance increasing going downward. The horizontal line cutting through the middle of the large circle is reactance-free.[l]
Network selection
If a load impedance is plotted on a Smith chart, it will fall into one of the four regions shown: Upper half-labrys (rounded axe head) , lower half-labrys , left inner-circle ∘ ⃝ and ∘ ⃝, and right inner-circle ◯⃘ and ◯⃘.[9] For a complex impedance falling anywhere in the chart, either two, or four different ‘L’ networks may be used, so the user may choose other criteria to decide which of the two or four networks to use. Impedances falling into either of the two inner circles, ∘ ⃝ (and ∘ ⃝) or ◯⃘ (and ◯⃘), can be matched by two different ‘L’ networks (high pass and low pass), and each of the half-labryses, and , allows four.
Each region is color coded as well as marked with corresponding numbers to indicate which networks can be used to match an impedance in that region. For example, an impedance that falls within the right inner circle (either green, ◯⃘, or yellow, ◯⃘, labeled "R > 50") can be matched using networks 1 or 3.[m][l]
The networks in the left column, all shaped ─┬, are called "step down" networks: Viewed from the radio connection, the antenna's resistive impedance is lowered; the networks in the right column, ┬─, are called "step up", since the resistive part of the antenna impedance is increased. In both cases, the vertical or "shunt" element is on the side with the higher resistive impedance.
Measuring instrument limitations
Commonly used SWR meters do not indicate complex impedance, so they are not very helpful for determining which of the ‘L’ networks to use. Antenna analyzers, however, can separately show the resistive and reactive parts of the antenna impedance, and are suitable for selecting the orientation of an ‘L’ network. The most convenient of these analyzers are able to display the complex impedance on a Smith chart screen, and are able to switch back and forth between series and parallel representation.
If an instrument indicates the complex series impedance, but not the shunt (parallel) equivalent, the formulas[10] or a calculator [11] shown below can be used to make the conversion to the parallel values.[n] The formulas for calculating the series or parallel (shunt) impedance in the mandatory case that neither of the resistances is zero, the usual case when neither of the reactances is zero are as follows:
In the special case when the series reactance then In that case, the resistance formulas are still good, and show that the series and parallel resistances become the same, but the formulas for the series and parallel reactances fail (become singular). The series reactance is replaced by a wire (short-circuited) and the parallel reactance becomes nominally infinite (disconnected, or open circuit).
The unrealistic case where either resistance is zero is not even of academic interest: Any antenna with zero total resistance is non-functional (see radiation resistance).
Additional selection criteria
Networks 1–4, shown in the top two rows, use one inductor and one capacitor; the pair with a series inductor (1 and 2) are low-pass; the next two, with the capacitor in series (3 and 4) are high pass. Normally, low-pass would be preferred with a transmitter, in order to attenuate possible harmonics. The high-pass configuration shown in the second row, (3 and 4) may be chosen if the required component values are more convenient, or if the radio already contains an internal low-pass filter, or if attenuation of low frequencies is desirable.[p]
In some cases it may be desirable that the network either pass through DC currents used for power feed to devices on the antennas, such as relay switches, or to block DC used for those devices from reaching the transmitter. Thus, the series (horizontal) component should be either an inductor (L) to pass DC, or a capacitor (C) to block DC. In addition, it may be useful for the phase shift across the network to be either advanced or delayed (see below).
Automatic and manual ‘L’ networks often use either network 1 or 2.[q] Many commercial tuners include a simple SPDT switch that connects the vertical (shunt, C) component to either the left or right side of the horizontal (series, L) component, making both networks 1 and 2 available with the same transmatch (see schematics, right). As shown by the green and red sections of the top Smith chart, these two networks can together handle all possible loads.[o] Likewise the yellow and blue parts of the middle Smith chart show that one of either network 3 or 4 can match any load.[o]
- Small loop example
- Loads such as a small transmitting loop may be highly inductive. The impedance will fall well into the region of the Smith chart dominated by inductive reactance (orange shaded upper half-labrys, , labelled "L dominant"). In addition to networks 1 and 4, they can use the low-loss all-capacitor networks 5 or 6.[r]
- Short whip example
- Short vertical antennas such as used for HF mobile, are dominated by capacitive reactance (purple shaded lower half-labrys, , labelled "C dominant"), in addition to networks 2 and 3, they can be easily matched with inductor-only networks 7 or 8, which is somewhat similar to connecting two taps onto a single grounded coil at the base of the whip.
Q and phase shift
Unlike the more complicated networks, described below, the ‘L’ network does not allow independent choice of operating Q, nor phase shift. High Q implies less loss, but also narrow operating bandwidth. ‘L’ network Q is fixed at the geometric mean of the input and output impedances, hence it is greater when the impedances to be matched are greatly different.
Phase shift can be made to either lead or lag by choosing an alternate network, but like the Q, for ‘L’ networks its value is fixed by the impedance ratio, and odds are that none of the two or four possible networks will provide both a desired phase shift and the right impedance match with the same setting. However, phase shift is only important if two or more loads are to be fed, such as used for directional arrays for AM broadcasting at high powers;[12](p 1211) luckily for many radio amateurs and small-scale broadcasters, transmitting from a single antenna doesn't require shifting phase.
Three-component unbalanced tuners
In contrast to two-element ‘L’-networks, the circuits described below all have three or more components, and hence have many more choices for inductance and capacitance that will produce an impedance match, unfortunately including some bad choices.[13] The two main goals of a good match are:
- to minimize losses in the matching circuit, and
- to maximize bandwidth – e.g. the widest span of frequencies that are matched tolerably well.
To obtain good matches and avoid bad ones, with every antenna and matching circuit combination, the radio operator must experiment, test, and use judgement to choose among the many adjustments that match the same impedances (see the maximum capacitance rule below).
All of the three element designs also allow a somewhat independent choice of how much the phase is shifted by the matching unit.[14] Since phase matching is an advanced topic, mainly of use for multi-tower broadcast arrays, it is omitted here for brevity. A good summary of phase change by matching networks is given in the Antenna Engineering Handbook[15] and the NAB Engineering Handbook.[12]
High-pass ‘T’-network
This configuration is currently popular because at shortwave frequencies it is capable of matching a large impedance range with capacitors in commonly available sizes. However, it is a high-pass filter and will not attenuate spurious radiation above the cutoff frequency nearly as well[13] as other designs (see the low pass ‘T’-network and ‘π’-network sections, below). Due to its low losses and simplicity, many home-built and commercial manually tuned ATUs use this circuit.[13] The tuning coil is normally also adjustable (not shown).
The ‘T’ network shown here may be analyzed as a high-pass step-down ‘L’ network on the input side feeding into a high-pass step-up ‘L’ network on the output side (─┬ ┬─). The two side-by-side vertical (shunt) inductors in the conjoined circuit are combined into an equivalent single inductor.
Low-pass ‘T’-network
This configuration is popular for mediumwave transmitting systems, since it requires a shunt capacitor in commonly available sizes, whereas the high-pass form, if used at the same frequencies, would require exceptionally large capacitors in its series sections. Because it is a low-pass filter this network will effectively eliminate spurious harmonic radiation above its tuned frequency essentially equally as well as any other design, and AM broadcasters are liable to stricter surveillance and larger financial penalties for interference with other commercial stations' signals, than are amateurs operating in the shortwaves are.
Further, at medium frequencies (MF) the use of inductors as series elements is convenient in several ways: The left and right inductors, which may need to be roughly 10× larger than those used in HF circuits, are easily made by hand from commonly available copper tubing, and in the lower MF range, the nuisance resistive losses in the coil at HF are reduced by roughly 5~10 dB. Using inductors for the series elements is also preferable for MF, since feasible antennas tend to be short, and hence show bothersome capacitive reactance; the needed contrary reactance can be straightforwardly provided just by making the antenna-side inductor extra large.
Like the high-pass ‘T’ network in the prior section, this low-pass network may also be analyzed as a step-down ‘L’ network on the input side feeding into a step-up ‘L’ network on the output side (─┬ ┬─). The two side-by-side capacitors from the two ‘L’ networks are merged in the conjoined network into a single capacitor with the same total capacitance. The only real distinction between the high-pass network above, and this low-pass design, is that in this network both constituent ‘L’ networks are low-pass, whereas the network in the previous section uses back-to-back high-pass ‘L’ networks.
Theory and practice
An example schematic for matching with the low pass ‘T’ network is shown at the right.
The load measures Zload = 200 Ω − j 75 Ω with 200 Ω (without j ) representing the real, resistive part, and −j 75 Ω the capacitively reactive part of the combined impedance Zload. Conceptually, the −j 75 Ω can be cancelled by adding a series inductor with +j 75 Ω reactance. Doing so leaves a purely resistive (real) 200 Ω to be matched to 50 Ω.
The resistance-matching is done with a circuit that mimics a 100 Ω Quarter wave impedance transformer, consisting of two inductors with +j 100 Ω reactance and a shunt capacitor with −j 100 Ω . The quarter wave-style transformer circuit uses equal and opposite reactances, each of which is the geometric mean of the two resistances to be matched:
The output inductor of the quarter wave network can be merged with the inductor used to cancel the reactance of the load, by replacing the pair with one inductor with the sum of the two inductances. The final network will have +j 100 Ω for the input inductor, −j 100 Ω for the capacitor and +j 175 Ω for the output inductor.
This quarter-wave-style solution will cause a phase shift of 90 degrees. If the output phase matters, then one of the many other possible solutions for the capacitance and two inductances can be used instead.[14] This solution uses a low pass configuration. Swapping the inductors and capacitors, and appropriately adjusting their reactances, would give a high pass configuration.
Low-pass ‘π’ network
A ‘π’ (pi) network can also be used; it is the electrical conjugate[s] of the low pass ‘T’ network shown in the prior section. This ATU has exceptionally good attenuation of harmonics, and was incorporated into the output stage of tube-based ‘vintage’ transmitters and many modern tube-based RF amplifiers. However, the standard ‘π’ circuit is not popular for stand-alone multiband antenna tuners, since the variable capacitors needed for the 160 m and 80 / 75 m amateur bands are prohibitively large and expensive.
The ‘π’ network shown here may be described mathematically as a low-pass step-up ‘L’ network on the input side feeding into a low-pass step-down ‘L’ network on the output side (┬─ ─┬). The two noze-to-noze inductors in the joined circuit are replaced with a single inductor with the same total inductance.
Drake's modified ‘π’ network
A modified version of the ‘π’ network is more practical as it uses a fixed input capacitor (left-most), which can be several thousand picofarads, allowing the variable capacitors (the two on the right) to be smaller. A band switch (not shown) sets the inductor and the left-side input capacitor (shown as fixed components in the schematic).[16] This circuit was used in tuners covering 1.8–30 MHz made before the popularity of the simpler ‘T’‑network, above.[17]
In all antenna tuner circuits each of the available adjustments affects both the reactive and resistive parts of the impedance match. Drake’s modified ‘π’ network circuit is somewhat unusual in that regard: For a given setting of the band switch, the upper right, series capacitor mostly adjusts the reactive part of the impedance match, and the lower right, shunt capacitor mostly affects the resistive part of the impedance match. This makes it easier to estimate how to adjust the two variable capacitor settings, when the operator knows the type and location of the antenna's resonant frequency nearest to the radio's operating frequency.
It can also be viewed as two ‘L’ networks coupled front to back: A capacitor-inductor low pass step-up network on the left, feeding into a capacitor-capacitor step-up network on the right (┬─ ┬─).
SPC tuner
The series parallel capacitor or SPC tuner uses a band-pass circuit that can act both as an antenna coupler and as a preselector. Because it is a band-pass circuit, the SPC tuner has much better harmonic suppression than the high-pass ‘T’ match above, but uses similar-cost tuning capacitors; its performance is better than the "Ultimate" circuit below. The SPC’s harmonic suppression is only surpassed by the low-pass ‘T’ and ‘π’ network tuners, described above, and then only when the SPC is adjusted in favor of low loss rather than narrow bandwidth.[18][19]
The SPC circuit is equivalent to a back-to-back pair of ‘L’ networks: A high-pass capacitor-inductor step down network on the input side feeding into a capacitor-capacitor step up network on the output side (─┬ ┬─). The combination of the vertical (shunt) inductor and shunt capacitor parallel to it is a tank circuit that grounds out-of-tune signals. When tuned to exploit that action, the tank circuit makes the SPC a band-pass filter that eliminates harmonics as effectively as the low-pass ‘T’ and ‘π’ networks, although the SPC requires careful adjustment for best narrow band results, whereas the low-pass networks are effective at blocking harmonics at any matched setting.
With the SPC tuner the losses will be somewhat higher than with the ‘T’ network, since the grounded capacitor will shunt some reactive current to ground, which must be cancelled by additional current in the inductor.[20][19] The trade-off is that the effective inductance of the coil is increased, thus allowing operation at lower frequencies than would otherwise be possible.[18]
Ultimate Transmatch
Originally, the Ultimate transmatch was promoted as a way to make the components more manageable at the lowest frequencies of interest, and to also get some harmonic attenuation. A version of McCoy's Ultimate transmatch network is shown in the illustration to the right.[21][19] The circuit is now considered obsolete; the design goals were better realized by the Series-Parallel Capacitor (SPC) network, shown above,[19] using identical parts.[18]
The 'Ultimate' circuit has the same general front-to-back topology (┬─ ┬─) as the Drake modified ‘π’, above, but with a high-pass ‘L’ component (instead of a low-pass component) which is placed on the output side instead of input. Unfortunately, with the capacitor-capacitor ‘L’ component placed on the input side, it can neither help match impedance, nor appreciably reduce harmonic output.[19]
Balanced versions of unbalanced tuner circuits
The previous sections only discuss networks designed for unbalanced lines; this section and all the following sections discuss tuners generally, or tuners for balanced lines.
Balanced (open line) transmission lines require a tuner that has two "hot" output terminals, rather than one "hot" terminal and one "cold" (grounded). Since all modern transmitters have unbalanced (co-axial) output – almost always 50 Ω – the most efficient system has the tuner provide a balun (balanced to unbalanced) transformation as well as providing an impedance match.[17]
There is a simple standard method for converting any of the unbalanced tuner circuits described in the preceding main section into a balanced version of the same circuit (see balanced circuit). The diagram at the right shows low-pass unbalanced networks in the top row (an ‘L’ network in the left column, a ‘T’ network in the right column), above their equivalent balanced versions of in the bottom row.
Commercially available "inherantly balanced" tuners are made as balanced versions of ‘L’, ‘T’, and ‘π’ circuits.[17] Their drawback is that the components used for each of the two output channels must be carefully matched and attached pairs, so that adjusting them causes an identical tuning change to both "hot" sides of the circuit. Hence, most "inherently balanced" tuners are much more difficult to make, and more than twice as expensive as unbalanced tuners.
Balanced voltage taps on the coil of an unbalanced circuit
Even with a single-winding transformer, some unbalanced transmatch designs can be adapted to create balanced output without the need for two, independent windings:[17] Most matching networks include a coil, and that coil can accept or produce balanced output if the antenna feed's tap-points are placed symmetrically above and below an electrically neutral point on the coil.
The effect is to force balanced voltages, instead of the desired balanced currents.[t]
This technique was experimented with in early years of the 20th century, but appears to no longer be in use.[citation needed] This article does not include any such circuit designs, as yet.
Balanced-line matching with tuned-transformers
The following balanced networks (see diagram)[u] all have been used for line matching. They are all based on tuned transformer circuits; none of the designs discussed in this section are balanced versions of the unbalanced circuits, mentioned above.
Fixed link with taps
The Fixed link with taps (top left on the diagram) is the most basic circuit. The factor will be nearly constant and is set by the number of relative turns on the input link. The match is found by tuning the capacitor and selecting taps on the main coil, which may be done with a switch accessing various taps or by physically moving clips from turn to turn. If the turns on the main coil are changed to move to a higher or lower frequency, the link turns should also change.
Hairpin tuner
The Hairpin tuner (top right) is effectively the same electrical circuit as the fixed link with taps, above, but uses "hairpin" inductors (a tapped transmission line, short-circuited at the far end) instead of coiled inductors.[5](p 24‑12) Moving the tap points along the hairpin allows continuous adjustment of the impedance transformation, which is difficult on a solenoid coil.
It is useful for very short wavelengths from about 10 meters to 70 cm (frequencies about 30 MHz to 430 MHz) where a coiled inductor would have too few turns to allow fine adjustment. These tuners typically operate over at most a 2:1 frequency range.
Series cap with taps & for low-Z lines
The middle row of the illustration shows two alternate configurations of nearly the same circuit: Series cap with taps (left middle) attaches the antenna in parallel with the transformer coil and capacitor C2, via taps, and For low-Z lines (right middle) attaches the antenna in series with the coil and capacitor C2.
- Series cap with taps (middle, left) adds a series capacitor to the input side of the Fixed link with taps. The input capacitor allows fine adjustment with fewer taps on the main coil.
- For low-Z lines (middle, right) shows an alternate connection for the series capacitor circuit that dispenses with taps on the coil, but is only useful for feedlines showing low impedance at their ends.
Swinging link with taps
Swinging link with taps (bottom left). A swinging link inserted into the Fixed link with taps also allows fine adjustment with fewer coil taps. The swinging link is a form of variable transformer, that changes the coils' mutual inductance by swinging the input coil in and out of the gap between halves of the main coil. The variable inductance makes these tuners more flexible than the basic circuit, but at some cost in complexity, both in terms of construction and in terms of dealing with more possible adjustments.
Fixed link with differential capacitors
The Fixed link with differential capacitors circuit (bottom right) was the design used for the well-regarded Johnson Matchbox (JMB) tuners.
The four output capacitor-sections (C2) are a "ganged" double-differential capacitor: The axes of the four sections are mechanically connected and their plates aligned, so that as the top and bottom capacitor sections increase in value the two middle sections decrease in value, and vice versa (notice the arrow heads on C2 in the diagram are shown with both matching and contrary directions). This provides a smooth change of loading that is electrically equivalent to moving taps on the main coil. The Johnson Matchbox used a band switch (not shown) to change the number of turns on the main inductor for each of the five frequency bands available to hams in the 1940s.[22]
The JMB design has been criticized since the two middle-section capacitors in C2 are not strictly necessary to obtain a match; however, the middle sections conveniently limit the disturbance of the adjustment for C1 caused by changes to C2.
Double-tuned link with differential capacitors
Later designs enhancing the limited range of the otherwise respected Johnson Matchbox (JMB), to accommodate the many more modern shortwave amateur bands, either add switched taps to the link (input) inductor, or may include a capacitor in series with the input coil winding. Both of these extra adjustments are shown in the schematic, right.[22][23][24] As in the case of the input capacitor and swinging link, described above, these are both ways to allow fine-tuning without requiring changes to the JMB bandswitch (not shown) and its intricately soldered connections to the output-side coil which changes the number of turns used on the output coil.
Adjusting the number of taps on the input coil changes the Q of the network, widening or narrowing its matched frequency span, and gives purpose to the generally unused extra output-coil windings intended for separate 600 Ω receivers still in use during the 1940s. Using C1 to tune or de-tune the left side of the transformer to the setting for C2 on the right side, has approximately the same effect as moving the two sides of the transformer closer or further apart, hence simulating a swinging link.
Including the band switch (not shown), this circuit has five separate available controls, which makes it complicated to adjust.
Z match
The approach taken with the Z-match design is to incorporate a conventional two-winding transformer into the transmatch in order to deliver (optionally) balanced output from a matching circuit. The separate input and output windings isolate the ground on the input side from the output side (grounded or ungrounded), which permits the connection of either balanced or unbalanced loads on the output side, regardless of the input side connection, ensures that the output currents are balanced, and allows the output voltages to float with respect to ground.
The Z-match is an ATU widely used for low-power amateur radio which is commonly used both as an unbalanced and as a balanced tuner.[25][26] The Z match is a doubled version of a resonant transformer circuit, with three tuning capacitors.[w]
Two of the capacitors with separate connections to the primary transformer coil are ganged, and effectively constitute two separate resonant transformer circuits, which simultaneously tune two distinct resonant frequencies. The double-resonance enables the single circuit across the coil to cover a wider frequency range without needing to switch the inductance: Every setting offers two different frequencies, in separate frequency bands, that are both impedance matched at once. Because the output side is a transformer secondary (optionally grounded) it can be used to feed either balanced or unbalanced transmission lines, without any modification to the circuit.
The Z-match design is limited in its power output by the core used for the output transformer. A powdered iron or ferrite core about 1.6 inches in diameter should handle 100 W. A tuner built for low-power use ("QRP" – typically 5 W or less) can use a smaller core.[26]
Balanced match from an unbalanced tuner and a balun
Another approach to feeding balanced lines is to use an unbalanced tuner with a balun on either the input (transmitter) or output (antenna) side of the tuner. Most often using the popular high pass T circuit described above, with either a 1:1 current balun on the input side of the unbalanced tuner or a balun (typically 4:1) on the output side. It can be managed, but doing so both efficiently and safely is not easy.
Balun between the antenna and the ATU
Any balun placed on the output (antenna) side of a tuner must be built to withstand high voltage and current stresses, because of the wide range of impedances it must handle.[27]
For a wide range of frequencies and impedances it may not be possible to build a robust balun that is adequately efficient. For a narrow range of frequencies, using transmission line stubs or sections for impedance transforms (as described above) may well be more feasible and will certainly be more efficient.
Balun between the transmitter and the ATU
The demands put on the balun are more modest if the balun is put on the input end of the tuner – between the tuner and the transmitter. Placed on that end it always operates into a constant 50 Ω impedance from the transmitter on one side, and has the matching network to protect it from wild swings in the feedline impedance on the other side: All to the good. Unfortunately, making the input from the transmitter balanced creates "hot ground" problems that must be remedied.
If an unbalanced tuner is fed with a balanced line from a balun instead of directly from the transmitter, then its normal antenna connection – the center wire of its output coaxial cable – provides the signal as usual to one side of the antenna. However the ground side of that same output connection now becomes the feed of an equal and opposite current to the other side of the antenna; the only unsatisfactory consequence is that the entire grounded portion of the tuner becomes "hot" with RF power, including the tuner's metal chassis, metal control knobs, and insulated knobs' metal set-screws, all touched by the operator.
The "hot ground" inside the ATU
The "true" external ground voltage at the antenna and transmitter must lie halfway between the two "hot" feeds, one of which is the internal ground: Inside the ATU, the matching circuit's "false" ground level is equally different from the "true" ground level at either the antenna or the transmitter as the original "hot" wire is, but with opposite polarity. Either the usual "hot" output wire or the matching circuit "hot ground" will give you exactly the same shock if you touch it.
The tuner circuit must "float" above or below the exterior ground level in order for the ATU circuit ground (or common side) that formerly was attached to the output cable's ground wire to feed the second hot wire: The circuit's floating ground must provide a voltage difference adequate to drive current through an output terminal to make the second output "hot".[5](p 24‑13)
High voltages are normal in any efficient ("high Q") impedance matching circuit bridging a wide mismatch. Unless the incompatible grounds are carefully kept separate, the high voltages present between this interior floating ground (the "false" ground) and the exterior transmitter and antenna "true" grounds can lead to arcing, corona discharge, capacitively coupled ground currents, and electric shock.
Carefully keeping the incompatible grounds separate
To reduce power loss and protect the operator and the equipment, the tuner chassis must be double-layered: An outer chassis and an inner chassis. The outer chassis must enclose and separate the tuning circuit and its floating ground from the outside, while itself remaining at the level of the exterior "true" ground(s). With the protective outer chassis, the inner chassis can maintain its own incompatible floating ground level, safely isolated.
The inner chassis can be reduced to nothing more than a mounting platform inside the outer chassis, elevated on insulators to keep a safe distance between the "floating ground" and the outer chassis wired to the "true" electrical ground line(s). The inner tuning circuit's metal mounting chassis, and in particular the metal rods connected to adjustment knobs on the outer chassis must all be kept separate from the surface touched by the operator and from direct electrical contact with the transmitter's ground on its connection cable ("true" ground).
Isolating the controls is usually done by replacing at least part of the metal connecting rods between knobs on the outside surface and adjustable parts on the inside platform with an insulated rod, either made of a sturdy ceramic or a plastic that tolerates high temperatures. Further, the metal inner and outer parts must be spaced adequately far apart to prevent current leaking out via capacitive coupling when the interior voltages are high. Finally, all these arrangements must be secured with greater than usual care, to ensure that jostling, pressure, or heat expansion cannot create a contact between the inner and outer grounds.
Summary
Using an inherently unbalanced circuit for a balanced tuner puts difficult constraints on the tuner's construction and high demands on the builder's craftsmanship. The advantage of such a design is that its inner, inherently unbalanced matching circuit always requires only a single component where a balanced version of the same circuit often requires two. Hence it does not require identical pairs of components for the two "hot" ends of the circuit(s) in order to ensure balance to ground within the ATU, and its output current is inherently balanced, even though its interior circuit is unbalanced with respect to the interior "false" ground.
Antenna system losses
Efficiency and SWR
If there is still a high standing wave ratio (SWR) beyond the ATU, in a significantly long segment of feedline, any loss in that part of the feedline is typically increased by the transmitted waves reflecting back and forth between the impedance change at the tuner output and the impedance change at the antenna feedpoint, compounding the normal resistive losses in the transmission line by making multiple passes through it. Even with a matching unit at both ends of the feedline – the near ATU matching the transmitter to the feedline and the remote ATU matching the feedline to the antenna – loss in the circuitry of the two ATUs will still slightly reduce power delivered to the antenna.
- The most efficient use of a transmitter's power is to use a resonant antenna, cabled via a feedline whose impedance is the same as the antenna's feedpoint, fed by a transmitter which has that same feed impedance. There are still small losses in every realistic feedline, even when all impedances match, but matching minimizes loss.
- It is almost equally efficient to feed a remote antenna tuner attached directly to the antenna, via a feedline matched to both the transmitter and the ATU feed. The only extra losses are in the tuner circuitry, which can be kept small if the tuner is adjusted for a "good" match (see below) and the degree of mismatch carefully tested at or near the antenna (not at the transmitter).
- It is usually inefficient to operate an antenna far from one of its resonant frequencies and attempt to compensate with an ATU next to the transmitter, far from the antenna; the entire feedline from the ATU to the antenna is still mismatched, which will aggravate normal loss in the feedline, particularly if it is low-impedance line, like standard 50 Ω coax.
- The least efficient way to transmit is to feed a non-resonant antenna through a mis-matched, lossy feedline, with no impedance matching anywhere.
ATU placement
An ATU can be inserted anywhere along the line connecting the radio transmitter or receiver to the antenna.[28] The antenna feedpoint is usually high in the air or far away,[x] and a transmission line (feedline) must carry the signal between the transmitter and the antenna. The ATU can be placed anywhere along the feedline – at the transmitter output, at the antenna input, or anywhere in between – and if desired, two or more ATUs can be placed at different locations between the antenna and the transmitter (usually at the two ends of the feedline) and adjusted so that they co‑operatively create an impedance match throughout the antenna system.
Antenna matching is best done as close to the antenna feedpoint connection as possible, to increase bandwidth, and to minimize loss in the transmission line by reducing its voltage and current peaks. Ideally, a tuning circuit made from nearly quarter-wave stubs might be incorporated into the body of the antenna itself, producing at least an approximate match at the antenna feed. Also, when the information being transmitted has frequency components whose wavelength is a significant fraction of the electrical length of the feed line, distortion of the transmitted information will occur if there are standing waves on the line. Analog TV and FM stereo broadcasts are affected in this way; for those modes, matching at or very near the antenna is mandatory.
When possible, an automatic or remotely-controlled tuner in a weather-proof case at or near the antenna is convenient and makes for an efficient system. With such a tuner, it is possible to match a wide variety of antennas over a broad range of frequencies[29] (including concealed antennas).[30][31]
High-impedance feedline
(A) Outer plastic jacket, (B) Woven copper shield, (C) Inner dielectric insulator, (D) Copper core
When the ATU must be located near the radio for convenient adjustment, any significant SWR will increase the loss in the feedline, unless the antenna feedpoint itself is positioned at the radio and directly connects to the back of the tuner. For that reason, when using a remote antenna with an ATU sitting at the transmitter, low-loss, high-impedance feedline is a great advantage (open-wire line, for example).
Through to the 1950s balanced transmission lines of at least 300 Ω were more-or-less standard for all shortwave transmitters and antennas, including amateurs' equipment. Most shortwave broadcasters continue to use high-impedance feedlines,[12](Ch. 7.2 )[b] even after automatic impedance matching has become commonly available.
High impedance lines – such as most parallel-wire lines – carry power mostly as high voltage rather than high current, and current alone determines the power lost to line resistance. So for the same number of Watts delivered to the antenna, typically very little power is lost in high-impedance line even at severe SWR levels, when compared to losses for the same SWR in low-impedance line, like typical coaxial cable. For that reason, radio operators using high-impedance feedline can be more casual about where along the line they bother to match up the impedances.
A short length of coaxial line with low loss is acceptable, but with longer coaxial lines the greater losses, aggravated by SWR, become very high.[32](p 7‑4) It is important to remember that when an ATU is placed near the transmitter and far from the antenna, even though the ATU matches the transmitter to the line there is no change in the line beyond the ATU. The backlash currents reflected from the antenna are retro-reflected by the ATU and so are invisible on the transmitter-side of the ATU. Individual wave fronts are usually reflected between the antenna and the ATU several times; the result of the multiple reflections is compounded loss, higher voltage and / or higher currents on the line and in the ATU, and narrowed bandwidth. None of these bad effects can be remediated by an ATU sitting beside the transmitter.
Loss in antenna tuners
Every means of impedance match will introduce some power loss. This will vary from a few percent for a transformer with a ferrite core, to 50% or more for a complicated ATU that has been naïvely adjusted to a "bad" match, or is working near the limits of its tuning range.[13][32](p 4‑3)
Among the narrow-band tuner circuits, the ‘L’ network typically has low loss, or the lowest loss,[citation needed] partly because it has the fewest components, but mainly because it can match at just one setting, and that setting is necessarily the lowest Q possible for a given impedance transformation.[y] In effect, any ‘L’ network gives its operator no option to choose a "bad" match: The only ‘L’ network settings that produce a match are as good as it gets with the selected network.
The ‘L’ network using only capacitors will have the lowest loss, but this network only works where the load impedance is very inductive, making it a good choice for a small loop antenna. Inductive impedance also occurs with straight-wire antennas used at frequencies above their first resonance and below the second, where the antenna is too long – for example, a monopole longer than a quarter wave and shorter than half wave long at the operating frequency. One can deliberately configure the size of an antenna so that it will be inductive on all its design frequencies (similar to a small loop) with the intention of using only capacitors to tune it, so as to have minimal tuning losses without concern for settings. Doing so requires making a straight-wire antenna a bit too long for its lowest operating frequency, but unfortunately the typical problem encountered in the lower HF bands is that antennas are too short for the frequency in use; their matching circuits require inductance.
With the high-pass ‘T’ network, the loss in the tuner can vary from a few percent – if tuned for lowest loss – to over 50% if the tuner is adjusted to a "bad match" instead of a good one.[13][33]
Maximum capacitance rule
As a rule of thumb, using the maximum possible capacitance (and minimum possible inductance) for every tuner setting will involve the least loss, as compared to simply tuning for any match, without regard for the settings.[13][33] In general, this is because increasing the capacitance produces less reactance. In the common ‘T’ and ‘π’ designs, setting either the left or right capacitor to its maximum causes it to have almost no reactance, and it almost vanishes from the circuit, leaving the remaining two components to approximate an ‘L’ network, which will make an approximately optimal match.
The usual consequence of high capacitance (low reactance) is that less counter-balancing reactance is needed from the inductor[13] which means running current through fewer turns of wire on the inductor coil, and the loss in almost every ATU is mainly from resistance in the inductor wire (loss from dirty capacitor contacts comes in a distant second).[33]
Recognizing "bad" matches
Every matching network with three reactive components, given fixed settings for the first two components, almost always has two distinct settings (or no settings at all!) for the third component that each achieve a match.[z] One setting typically results in higher loss than the other, and sometimes the difference is enough to be important; usually, but not necessarily, the setting that needs the highest inductance is the "bad" match (highest loss), and that is what the "maximum capacitance rule", above, seeks to avoid. However, it is sometimes possible for a lower-inductance setting to wind up circulating more current through the coil, perhaps enough more to cause higher loss at the lower inductance. In that case, the above rule of thumb does not give good guidance.
The infallible guide is to "try it and see, measure it, and record it". Once a table of optimal settings has been found for a transmatch + antenna combination, the settings for a new frequency (with very rare exceptions where the settings "jump") will lie between the settings for the two optimal matches previously found at an adjacent higher and adjacent lower frequency in the same band. A table of previous optimal settings can be used as close starting points for a search at a new bracketed frequency. Where the entries are spaced close enough in frequency, the table will give a start that's near enough that the new optimum setting can be reached using only an SWR meter, even though it will be unable to verify the "goodness" of the match. For the "measure it" part that creates or extends a table of optimum settings in the first place, an SWR meter won't work, since it can't measure the losses in the transmatch; with a few hookup changes, the matching network's losses can be found with an antenna analyzer or impedance bridge. A low-tech approach to measure ATU loss is to power-off the transmitter, soon after transmitting, and place one's hand directly on the coil (after first discharging the coil to the matchbox chassis). If it feels too hot to touch or too warm to comfortably hold, then the coil losses are high and the setting is "bad"; if the coil feels cool or just mildly warm then there is no significant loss, either because of a "good" match or because of low power transmission.[aa]
One of the reasons for technical horror stories[13][32] about high loss in tuning circuits arises when the settings produce a path for an internal resonance among the components that lie inside the matching network itself, without circulating through the antenna: Multiple internal passes through the tuning coil will compound its normal losses, just like multiple passes through a mismatched feedline can. When the configured path does not route most of the current through the antenna, then that fraction of the current only flowing in the coil and not the antenna will only deliver power as heat, not radio waves. Situations like this are possible when a near-resonant capacitor-inductor combination is used to raise voltage for a much higher impedance output.
At some point near the extreme possible settings for any one of the installed components, the possible match settings for the system will be curtailed, and the best match may be the first to drop out (require an impossibly high or low setting[o]). If the configuration of component settings with the least loss isn't feasible with the installed components, and the loss for the achievable setting is appreciably worse, then despite still being able to find a match for the impedance, the only match the ATU is able to provide is "bad". A simple clue that the matching network has reached or is near that point is when an available configuration has one of the setting knobs "pegged out", or nearly so, and adjusting away from the pegged setting worsens the match and it cannot be improved by slight adjustment of the other components' settings.
Sacrificing efficiency in exchange for harmonic suppression
If additional filtering is desired, the inductor in any of the three-element designs can be deliberately set to slightly larger values than the minimum necessary, raising the circuit Q and so provide a partial band pass effect. Ordinary harmonics are always above the operating frequency, so low-pass networks always block harmonics. Optimally adjusted high-pass networks will not block harmonics, however either the high-pass ‘T’ or low-pass ‘π’ can be adjusted to have a slight band-pass effect if their inductance is set above its minimum: The additional attenuation at harmonic frequencies can be increased significantly with only a small percentage of additional loss at the tuned frequency.[34][13]
The low-pass ‘π’, low-pass ‘T’, and low-pass ‘L’ networks always have exceptional harmonic attenuation at any setting, including the lowest-loss. The only benefit of adjusting the low-pass ‘π’ or ‘T’ networks for higher Q would be to partially block interference below the operating frequency.
The SPC tuner is a band-pass circuit, so it always blocks out-of-band signals, both above and below, but it can be made to have an especially narrow pass-band when adjusted for similarly higher-than-necessary Q. At any match setting, the SPC tuner will always have much better harmonic rejection than the high-pass ‘T’, although the ‘T’ match's obtainable factor of 99% (20 dB)[34] may be enough harmonic rejection, if the small additional loss is acceptable.
Standing wave ratio
It is a common misconception that a high standing wave ratio (SWR) per se causes loss, or that an antenna must be resonant in order to transmit well; neither is true.[3][4][35]
A well-adjusted ATU feeding an antenna through a low-loss line may have only a small percentage of additional loss compared with an intrinsically matched antenna, even with a high SWR (4:1, for example).[35] An ATU sitting beside the transmitter just re-reflects energy reflected from the antenna ("backlash current") back yet again along the low-loss feedline to the antenna ("retro-reflection"), so the part of the reflected waves that survive the losses do eventually radiate out.[3]
High losses arise from RF resistance in the feedline, the close-by soil below the antenna, and the metal of the antenna. Multiple reflections due to high SWR cause all these losses to be compounded. However, the total of the losses for multiple passes greatly depends on the original, single-pass loss. Using a good ground system and low-loss, high-impedance feedline results in very little loss, even with multiple reflections, because even low radiation resistance in the antenna can out-compete line and ground resistances, if those are very low. However, if the combined feedline and ground-system is "lossy", like coaxial line,[b] or a mere ground rod, then an identical high SWR may waste a considerable fraction of the transmitter's power output heating up the coax and warming the soil. In comparison, parallel-wire, high impedance line typically has extremely low loss, even when SWR is high. For that reason, radio operators using high-impedance line with an extensive ground system can be more relaxed about use of matching units and their placement on the feedline.
Without an ATU, the SWR from a mismatched antenna and feedline can present an improper load to the transmitter, causing distortion and loss of power or efficiency with heating and / or burning components in the output stage. Modern solid state transmitters are designed to automatically protect themselves by reducing power when confronted with backlash current. Consequently, all modern solid-state power stages are designed to only produce weak signals when the SWR rises above some cutoff level, often set at 1.5 : 1 .[c] This output stage power cutback is the main reason for poor transmitter performance at high SWR, not the lesser losses from heat generated in the feedline, antenna, and surrounding soil.
Were it not for the problem created by the design conflict between circuit safety and delivered transmit power, even the marginal losses from an SWR of 2:1 might otherwise be tolerated, since only 11 percent of transmitted power would be reflected and 89 percent sent through to the antenna (a loss of only 1/ 2 dB). So the main loss of power at high SWR is due to the output amplifier "backing off" its power when challenged by a high SWR.
Tube transmitters and amplifiers usually have an adjustable output network (a ‘π’ network) that can feed mismatched loads up to perhaps 3:1 SWR without trouble. Essentially, the ‘π’ network in the output stage is a built-in transmatch. Further, tubes are electrically robust (despite being mechanically fragile) and as long as the line voltage stays moderate they can shrug off very high backlash current with impunity; so tube-based output stage amplifiers benefit from "backing off" their output power only in response to high backlash voltage, and their self-protection circuitry (if any) can be configured to function in a more restrained manner.
Broadcast applications
AM broadcast transmitters
One of the oldest applications for antenna tuners is in mediumwave and shortwave AM broadcast transmitters. Typical AM band transmitters use vertical tower antennas, usually between 1 /5 and 5 /8 wavelengths tall. An ATU housed in the "coupling hut" at the base of the tower[36] is used to match the antenna to the transmission line from the transmitter. The most commonly used circuit is a low-pass ‘T’ network.[15]
When multiple towers are used, the matching network may also need to provide for a phase adjustment, to advance or delay the current to each tower, relative to the others; done properly, phasing can aim the combined signal in a desired direction.[ab]
High-power shortwave transmitters
High-power (50 kW and above) international shortwave broadcast stations change frequencies seasonally – even daily – to adapt to ionospheric propagation conditions, so their signals can best reach their intended audience.[37] Frequent transmitting frequency changes require frequent adjustment of antenna matching, but modern broadcast transmitters typically include built-in automatic impedance-matching circuitry that can accommodate modest impedance changes, with similar circuitry increasingly common in amateur transmitters as well.
Modern internal ATU circuits typically can self-adjust to a new frequency or new output impedance within 15 seconds, for SWR up to 2:1 (at least).[12](Ch. 7.2 ) The matching networks in transmitters sometimes incorporate a balun or an external one can be installed at the transmitter in order to feed a balanced line.
The most commonly used shortwave antennas for international broadcasting are the HRS antenna (curtain array), which covers a 2:1 frequency range, and the log-periodic antenna, which can cover up to an 8:1 frequency range.[38] Within the design range, the antenna SWR will vary, but these designs usually keep the SWR below 1.7 : 1 , which is easily within the range of SWR that can be tuned by built-in automatic antenna matching in many modern transmitters. So when feeding well-chosen antennas, a modern transmitter will be able to adjust itself as needed to match to the antenna at any frequency.
Automatic tuners
Automatic antenna tuning is used in flagship mobile phones; in transceivers for amateur radio; and in land mobile, marine, and tactical HF radio transceivers.
Several control schemes can be used, in a radio transceiver or radio transmitter, to automatically adjust an antenna tuner (AT). Each AT shown in the figure has a port, referred to as ″antenna port″, which is directly or indirectly coupled to an antenna, and another port, referred to as ″radio port″ (or as ″user port″), for transmitting and/or receiving radio signals through the AT and the antenna. Each AT shown in the figure is a single-antenna-port (SAP) AT, but a multiple-antenna-port (MAP) AT may be needed for MIMO radio transmission.
Several control schemes, which can be used to automatically adjust a SAP AT of a wireless transmitter, are based on one of the two configurations shown in the figure. In both configurations, the transmitter comprises: an antenna; the AT; a sensing unit (SU); a control unit (CU); and a transmission and signal processing unit (TSPU) which consists of all parts of the transmitter not shown elsewhere in the figure. The TX port of the TSPU delivers an excitation. The SU delivers, to the TSPU, one or more sensing unit output signals determined by one or more electrical variables (such as voltage, current, incident or forward voltage, etc) caused by the excitation, sensed at the radio port in the case of configuration (a) or at the antenna port in the case of configuration (b).
It is possible to define five types of antenna tuner control schemes.[39] Type 0 designates the open-loop AT control schemes that do not use any SU, the adjustment being typically only based on the knowledge of an operating frequency. Type 1 and type 2 control schemes use configuration (a), type 2 using extremum-seeking control whereas type 1 doesn't. Type 3 and type 4 control schemes use configuration (b), type 4 using extremum-seeking control whereas type 3 doesn't. The control schemes may be compared as regards: their use of closed-loop control and/or open-loop control; the measurements used; their ability to mitigate the effects of the electromagnetic characteristics of the surroundings; their aim; their accuracy and speed; and their dependence on a model of the AT and CU.
See also
Footnotes
Since the early 1960‑s, perhaps earlier, almost all available coaxial cable is either 48~52 Ω or 70~75 Ω impedance.[citation needed] (Television cabling adopted 75 Ω cable, which is sometimes used by radio amateurs.) The only benefit of designing radios for 50 Ω cabling is standardization; it is merely convenient – not ideal – and like many standards, is only used for historical reasons.
After WW II, surplus 50 Ω military cable became available at low cost, and amateur radio operators started using it. Coaxial cable is much less "fussy" about where it is placed than unshielded cable, and if driven with balanced current will be unaffected by nearby metal fences, metal roofs or siding, or car chassis, and can be run through metal pipes or buried in soil. The previously common unshielded parallel wire cable types are vulnerable to their impedance being distorted if run near any such large piece of metal.
Because the originally used coaxial cabling happened to be made for 50 Ω – a good compromise for the military radar equipment it was made for – that impedance became a de facto standard for amateur radio equipment. There is usually no benefit to use of 50 Ω impedance for amateur radio, and several drawbacks, discussed under the heading § "High impedance feedline".
- AM stations are often required by the terms of their operating licenses to prevent signals in directions that would interfere with other stations' broadcasts. The transmitting station also benefits from more of the station's signal power (its electrical bill being an operating cost) going into its assigned target area, on which its advertising revenue is based. Adjustment of the ATUs in a multitower array is a complicated, time-consuming process, requiring considerable expertise and advanced measuring equipment.
References
Cavell, Garrison C.; et al., eds. (2018). National Association of Broadcasters Engineering Handbook (11th ed.). Focal Press / National Association of Broadcasters. ISBN 978-1-138-93051-3.
Griffith, Andrew S., W4ULD (January 1995). "Getting the most out of your T‑network antenna tuner". QST Magazine. Newington, CT: American Radio Relay League. pp. 44–47. ISSN 0033-4812. OCLC 1623841.
Belrose, John, VE2CV (January 1984). "Balanced antenna matching". Technical correspondence. QST Magazine. Newington, CT: American Radio Relay League. p. 48. ISSN 0033-4812. OCLC 1623841.
de Maw, Doug, W1FB (1984). "Transmatch for balanced or unbalanced lines". In Hutchinson, Charles L.; et al. (eds.). The ARRL Handbook for the Radio Amateur (62nd ed.). Newington, CT: American Radio Relay League. Chapter 22 – Station setup and accessory projects: A transmatch for balanced or unbalanced lines, Figure 22.100. ISSN 0890-3565.
Maxwell, Walter M., W2DU (August 1981). "The Ultimate vs. the SPC transmatch". QST. Newington, CT: American Radio Relay League. pp. 42–43.
The TCI model 530 log-periodic antenna is designed specifically to support sky-wave communications at short (0–500 km) ranges.
- Broydé, F.; Clavelier, E. (June 2020). "A typology of antenna tuner control schemes, for one or more antennas". Excem Research Papers in Electronics and Electromagnetics (1). doi:10.5281/zenodo.3902749.
Further reading
- The Radio Communication Handbook (5th ed.). Bedford, UK: Radio Society of Great Britain. 1976. ISBN 0-900612-58-4.
- Rohde, Ulrich L. (1974). "Die Anpassung von kurzen Stabantennen für KW-Sender" [Matching of short rod-antennas for shortwave transmitters]. Funkschau (in German). No. 7.
- Rohde, Ulrich L. (13 September 1975). "Match any antenna over the 1.5 to 30 MHz range with only two adjustable elements". Electronic Design. Vol. 19.
- Wright, H.C. (1987). An Introduction to Antenna Theory. London, UK: Bernard Babani. BP198.
External links
- "American Radio Relay League website" (main page).
- How Antenna Tuners Work. lcfgroup – via YouTube.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antenna_tuner#SPC_tuner





































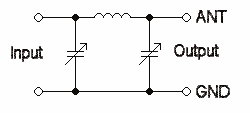











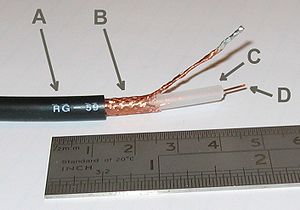




No comments:
Post a Comment