Leukemia, also known as leukaemia, is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells.[9] These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells.[2] Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections.[2] These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells.[2] Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy.[2]
| Leukemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Leukaemia |
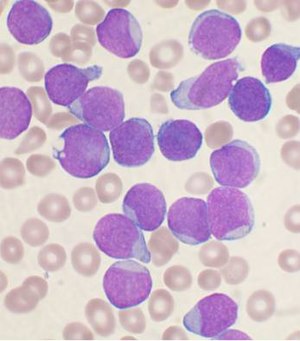 | |
| A Wright's stained bone marrow aspirate smear from a person with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Hematology and oncology |
| Symptoms | Bleeding, bruising, fatigue, fever, increased risk of infections[2] |
| Usual onset | All ages,[3] most common in 60s and 70s.[4] It is the most common malignant cancer in children, but the cure rates are also higher for them. |
| Causes | Inherited and environmental factors[5] |
| Risk factors | Smoking, family history, ionizing radiation, some chemicals, prior chemotherapy, Down syndrome.[3][5] |
| Diagnostic method | Blood tests, bone marrow biopsy[2] |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, bone marrow transplant, supportive care[3][6] |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate 57% (USA)[4] |
| Frequency | 2.3 million (2015)[7] |
| Deaths | 353,500 (2015)[8] |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leukemia
No comments:
Post a Comment