Mange /ˈmeɪndʒ/ is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites.[1] Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infection, is sometimes reserved for pathological mite-infestation of nonhuman mammals. Thus, mange includes mite-associated skin disease in domestic mammals (cats and dogs), in livestock (such as sheep scab), and in wild mammals (for example, coyotes, cougars, and bears).[2][3] Since mites belong to the arachnid subclass Acari (also called Acarina), another term for mite infestation is acariasis.
Parasitic mites that cause mange in mammals embed themselves in either skin or hair follicles in the animal, depending upon their genus. Sarcoptes spp. burrow into skin, while Demodex spp. live in follicles.
In humans, these two types of mite infections, which would otherwise be known as "mange" in furry mammals, are instead known respectively as scabies and demodicosis.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mange
Sarcoptes is a genus of mites.
In some contexts, the types are all considered subordinate to Sarcoptes scabiei.
- Sarcoptes scabiei var. bovis
- S. s. var. canis
- S. s. var. caprae
- S. s. var. equi
- S. s. var. hominis
- S. s. var. ovis
- S. s. var. suis
In other cases, (as with S. equi and S. anthracis), these are sometimes considered distinct species.
The term Sarcoptes canis appears in older references,[1] but is now usually described as Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis[2] or Sarcoptes scabiei canis.
| Sarcoptes | |
|---|---|
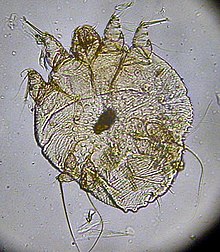 | |
| Sarcoptes scabei | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Sarcoptes |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sarcoptes
No comments:
Post a Comment