Category:Tertiary phosphines
Pages in category "Tertiary phosphines"
The following 25 pages are in this category, out of 25 total. This list may not reflect recent changes (learn more).
D
T
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Tertiary_phosphines
Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)2(2-C5H4N). It is the most widely used mono-pyridylphosphine ligand.[1]Other mono-pyridylphosphines ligands (3-, 4-) are not common in chemical literature; however, tris-pyridylphosphines have been thoroughly investigated as ligands in transition metal complexes used for catalysis. Pyridylphosphines, including diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine, may bind transition metals as monodentate or bidentate ligands4. Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine behaves as a P-bound monodentate ligand, or a P,N-bound bidentate ligand. Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine is a sought after ligand for its ability to relay protons to transition metals such as palladium(II) in homogeneous catalysis.[2]

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine
XPhos is a phosphine ligand derived from biphenyl. Its palladium complexes exhibit high activity for Buchwald-Hartwig amination reactions involving aryl chlorides and aryl tosylates. Both palladium and copper complexes of the compound exhibit high activity for the coupling of aryl halides and aryl tosylates with various amides.[1] It is also an efficient ligand for several commonly used C–C bond-forming cross-coupling reactions, including the Negishi, Suzuki, and the copper-free Sonogashira coupling reactions. It is especially efficient and general when employed as a (2-aminobiphenyl)-cyclometalated palladium mesylate precatalyst complex (Buchwald's third generation precatalyst system), XPhos-G3-Pd, which is commercially available and stable to bench storage.[2][3][4] The ligand itself also has convenient handling characteristics as a crystalline, air-stable solid.[5]
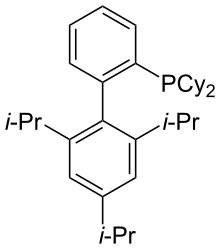
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XPhos
Xantphos is an organophosphorus compound derived from the heterocyclexanthene. It is used as a bidentate diphosphine ligand and is noteworthy for having a particularly wide bite angle (108°).[1] Such ligands are useful in the hydroformylationof alkenes.[2] Illustrative of its wide bite angle, it forms both cis and trans adducts of platinum(II) chloride. In the latter context, xantphos is classified as a trans-spanning ligand. A related bidentate ligand with a greater bite angle is spanphos.
The ligand is prepared by double directed lithiation of 9,9-dimethylxanthene with sec-butyllithium followed by treatment with chlorodiphenylphosphine.[3]

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xantphos
Triphos is the name for certain organophosphorus ligands. They are air-sensitive white solids that function as tridentate ligands in coordination and organometallic chemistry.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triphos
1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is an organophosphorus compound commonly used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such as 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1,1%27-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene
Tris(o-tolyl)phosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H4CH3)3. It is a white, water-insoluble solid that is soluble in organic solvents. In solution it slowly converts to the phosphine oxide. As a phosphine ligand, it has a wide cone angle of 194°. Consequently, it tends to cyclometalate when treated with metal halides and metal acetates. Complexes of this ligand are common in homogeneous catalysis.[1]
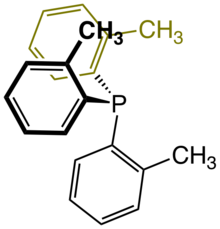
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tris(o-tolyl)phosphine
Tris(cyanoethyl)phosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(CH2CH2CN)3. It is white solid that is air stable, which is unusual for a trialkylphosphine. It is prepared by the hydrophosphination of acrylonitrile with phosphine.[1] The compound has been the subject of much research. For example, it is an effective reagent for the desulfurization of organic disulfides.[2]

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tris(cyanoethyl)phosphine

No comments:
Post a Comment