Pipradrol (Meratran) is a mild central nervous system stimulant (norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor) that is no longer widely used in most countries due to concerns about its abuse potential. Pipradrol is still used in some European countries, and even in the United States, albeit rarely.

Pipradrol was developed in the 1940s,[1] and found use initially for treating obesity.[2]It was subsequently used for the treatment of a variety of other conditions such as narcolepsy, ADHD, and most particularly for counteracting the symptoms of senile dementia, this being the only application for which it is still used medically.[medical citation needed]
Common side effects include insomnia, anorexia, tachycardia, and anxiety. Rarer side effects include dry mouth, tremor, hypertension, euphoria, depression, etc..
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pipradrol
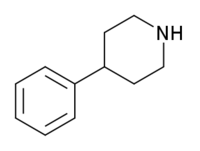
4-Phenylpiperidine is a chemical compound. It features a benzene ring bound to a piperidine ring.
4-Phenylpiperidine is the base structure for a variety of opioids, such as pethidine(meperidine), ketobemidone, alvimopan, loperamide, and diphenoxylate.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4-Phenylpiperidine
- Stimulants
- Carboxamides
- 4-Phenylpiperidines
- Chloroarenes
- Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors
- Nervous system drug stubs
Stimulants
showvte
Monoamine reuptake inhibitors
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Monoamine_neurotoxins
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JZ-IV-10
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Monoamine_metabolism_modulators
No comments:
Post a Comment