Cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to diffuse into the cell. Water can enter the cell by diffusion through the cell membrane or through selective membrane channels called aquaporins, which greatly facilitate the flow of water.[1] It occurs in a hypotonic environment, where water moves into the cell by osmosis and causes its volume to increase to the point where the volume exceeds the membrane's capacity and the cell bursts. The presence of a cell wall prevents the membrane from bursting, so cytolysis only occurs in animaland protozoa cells which do not have cell walls. The reverse process is plasmolysis.
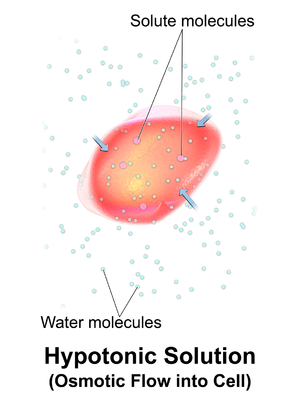
Blood cells in solutions with different osmotic pressure. Cytolysis would result in the image on the far right.
See also[edit]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytolysis
No comments:
Post a Comment