Rosin (/ˈɹɒ.zən/), also called colophony or Greek pitch (Latin: pix graeca), is a solid form of resin obtained from pines and some other plants, mostly conifers, produced by heating fresh liquid resin to vaporize the volatile liquid terpene components. It is semi-transparent and varies in color from yellow to black. At room temperature rosin is brittle, but it melts at stove-top temperature. It chiefly consists of various resin acids, especially abietic acid.[1]The term "colophony" comes from colophonia resina, Latin for "resin from Colophon", an ancient Ionic city.[2]
Rosin is brittle and friable, with a faint piny odor. It is typically a glassy solid, though some rosins will form crystals, especially when brought into solution.[3] The practical melting point varies with different specimens, some being semi-fluid at the temperature of boiling water, others melting at 100 °C to 120 °C. It is very flammable, burning with a smoky flame, so care should be taken when melting it. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene and chloroform.
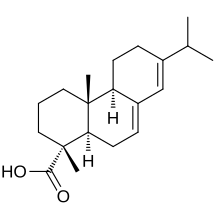
Rosin consists mainly of abietic acid, and combines with caustic alkalis to form salts (rosinates or pinates) that are known as rosin soaps. In addition to its extensive use in soap making, rosin is largely employed in making varnishes (including fine violin varnishes), sealing wax and various adhesives. It is also used for preparing shoemakers' wax, for pitching lager beer casks, and numerous other purposes such as providing backing surfaces to tin ware, copper ware, or even silver and gold vessels when embossing or engraving them. Its relatively low melting point, and firm solid form allows liquid rosin to be poured into the vessel, and when cooled allows embossing or engraving of the vessel without deforming the vessel - even if it has a skin which is quite thin. Afterwards, the object can be reheated in an oven, and the rosin poured out for reuse. Any remaining rosin film can easily be rinsed away with alcohol or other solvents.
Rosin is also sometimes used as internal reinforcement for very thin skinned metal objects - things like silver, copper or tin plate candlesticks, or sculptures, where it is simply melted, poured into a hollow thin-skinned object, and left to harden.
Prolonged exposure to rosin fumes released during soldering can cause occupational asthma (formerly called colophony disease[4]in this context) in sensitive individuals, although it is not known which component of the fumes causes the problem.[5]
The type of rosin used with bowed string instruments is determined by the diameter of the strings. Generally this means that the larger the instrument is, the softer the rosin should be. For instance, double bass rosin is generally soft enough to be pliable with slow movements. A cake of bass rosin left in a single position for several months will show evidence of flow, especially in warmer weather.
Prolonged exposure to rosin, by handling rosin-coated products, such as laser printer or photocopying paper, can give rise to a form of industrial contact dermatitis.[6]
Rosin is an ingredient in printing inks, photocopying and laser printing paper, varnishes, adhesives (glues), soap, paper sizing, soda, soldering fluxes, and sealing wax.
Rosin can be used as a glazing agent in medicines and chewing gum. It is denoted by E number E915. A related glycerol ester (E445) can be used as an emulsifier in soft drinks. In pharmaceuticals, rosin forms an ingredient in several plasters and ointments.
In industry, rosin is a flux used in soldering. The lead-tin solder commonly used in electronics has 1 to 2% rosin by weight as a flux core, helping the molten metal flow and making a better connection by reducing the refractory solid oxide layer formed at the surface back to metal. It is frequently seen as a burnt or clear residue around new soldering.
A mixture of pitch and rosin is used to make a surface against which glass is polishedwhen making optical components such as lenses.
Rosin is added in small quantities to traditional linseed oil/sand gap fillers ("mastic"), used in building work.
When mixed with waxes and oils, rosin is the main ingredient of mystic smoke, a gum which, when rubbed and suddenly stretched, appears to produce puffs of smoke from the fingertips.
Rosin is extensively used for its friction-increasing capacity in several fields:
- Players of bowed string instruments rub cakes or blocks of rosin on their bow hair so it can grip the strings and make them "speak", or vibrate clearly.[7] Extra substances such as beeswax, gold, silver, tin, or meteoric iron[8] are sometimes added to the rosin to modify its stiction/friction properties and the tone it produces.[9] Powdered rosin can be applied to new hair, for example with a felt pad or cloth, to reduce the time taken in getting sufficient rosin onto the hair. Rosin is often reapplied immediately before playing the instrument. Lighter rosin is generally preferred for violins and violas, and in high-humidity climates, while darker rosins are preferred for cellos, and for players in cool, dry areas.[10] There are also specific, distinguishing types for basses—for more see Bow (music).
- Violin rosin can be applied to the bridges in other musical instruments, such as the banjo and banjolele, in order to prevent the bridge from moving during vigorous playing.
- Ballet, flamenco, and Irish dancers are known to rub the tips and heels of their shoes in powdered rosin to reduce slippage on clean wooden dance floors or competition/performance stages. It was at one time used in the same way in fencing and is still used as such by boxers.
- Gymnasts and team handball players use it to improve grip. Rock climbers have used it in some locations.
- Olympic weightlifters rub the soles of their weightlifting boots in rosin to improve traction on the platform.
- It is applied onto the starting line of drag racing courses used to improve traction.
- Bull riders rub rosin on their rope and glove for additional grip.
- Baseball pitchers and ten-pin bowlers may use a small cloth bag of powdered rosin for better ball control. Baseball players sometimes combine rosin with sunscreen, creating a very sticky substance that allows far more grip on the ball than the rosin alone will; the use of such a substance is a violation of Major League Baseball rules.
- Rosin can be applied to the hands in aerial acrobatics such as aerial silks and pole dancing to increase grip.
Other uses that are not based on friction:
- Fine art uses rosin for tempera emulsions and as painting-medium component for oil paintings. It is soluble in oil of turpentine and turpentine substitute, and needs to be warmed.
- In a printmaking technique, aquatint rosin is used on the etching plate in order to create surfaces in gray tones.
- In archery, when a new bowstring is being made or waxed for maintenance purposes, rosin may be present in the wax mixture. This provides an amount of tackiness to the string to hold its constituent strands together and reduce wear and fraying.[citation needed]
- Dog groomers use powdered rosin to aid in removal of excess hair from deep in the ear canal.
- Some brands of fly paper use a solution of rosin and rubber as the adhesive.
- Rosin is sometimes used as an ingredient in dubbing wax used in fly tying.
- Rosin is used hot to de-encapsulate epoxy integrated circuits.[11]
- Rosin can be mixed with beeswax and a small amount of linseed oil to affix reeds to reed blocks in accordions.
- Rosin potatoes can be cooked by dropping potatoes into boiling rosin and cooking until they float to the surface.[12]
Rosin and its derivatives also exhibit wide-ranging pharmaceutical applications. Rosin derivatives show excellent film forming and coating properties.[13] They are also used for tablet film and enteric coating purpose. Rosins have also been used to formulate microcapsules and nanoparticles.[14][15]
Glycerol, sorbitol, and mannitol esters of rosin are used as chewing gum bases for medicinal applications. The degradation and biocompatibility of rosin and rosin-based biomaterials has been examined in vitro and ex vivo.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rosin

No comments:
Post a Comment